The global business process outsourcing market is projected to reach $347.95 billion in 2025, with fractional leadership roles doubling from 60,000 to 120,000 professionals between 2022 and 2024 [1]. As marketing budgets decline to 7.7% of company revenue and CMO representation at Fortune 500 companies drops from 71% to 66%, organizations increasingly turn to outsourced marketing leadership models [2]. Research from McKinsey reveals that companies with a single customer-oriented executive role achieve up to 2.3 times more growth than those with fragmented leadership structures [3]. This comprehensive analysis examines two dominant models—CMO-as-a-Service and Fractional CMO—providing data-driven insights to guide strategic decision-making in an evolving marketing landscape.
Market Context and Industry Evolution
The marketing leadership landscape has undergone fundamental transformation in recent years, driven by economic pressures, technological advancement, and evolving customer expectations. Understanding this context is essential for organizations evaluating outsourced marketing leadership models in 2025 and beyond.
Budget Constraints and Resource Optimization
Marketing departments face unprecedented budget pressures, with Gartner’s 2024 CMO Survey revealing that marketing budgets have declined to 7.7% of overall company revenue, down from 9.1% in 2023 [2]. This represents a continuation of a concerning trend that began in 2020, when marketing budgets averaged 11.2% of revenue. The consistent downward trajectory reflects broader economic uncertainties and increased scrutiny on marketing return on investment.
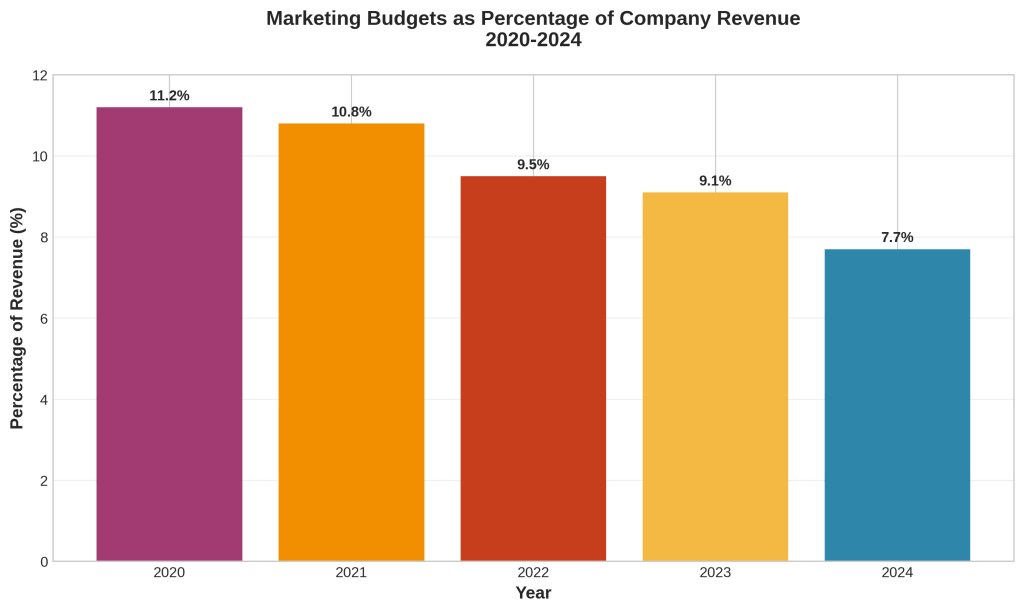
This budget compression occurs simultaneously with increasing complexity in customer acquisition and retention. Organizations must accomplish more with fewer resources, creating demand for flexible, expertise-driven solutions that can deliver measurable results without the overhead of full-time executive compensation packages.
Leadership Fragmentation and Alignment Challenges
McKinsey’s research identifies a critical organizational challenge: CEO-CMO misalignment has increased by 20% between 2023 and 2025 [3]. This disconnect stems from fragmented responsibilities across marketing, sales, digital, and customer experience functions. The average Fortune 100 executive team size increased by 50% between 2020 and 2022, according to executive search firm Heidrick & Struggles International, yet this expansion has not improved customer-centricity or growth outcomes.
“When everyone is responsible for acquiring customers and driving growth, no one is. Companies with a single customer- or growth-oriented role in an executive committee see up to 2.3 times more growth than those with multiple roles.”— McKinsey & Company, “The CMO’s comeback: Aligning the C-suite to drive customer-centric growth” (2025)
The fragmentation problem is compounded by declining CMO representation at the highest levels of corporate leadership. Spencer Stuart reports that CMO representation at Fortune 500 companies declined from 71% in 2023 to 66% in 2024, while Forrester Research indicates that only 63% of Fortune 500 companies currently have CMOs [4].
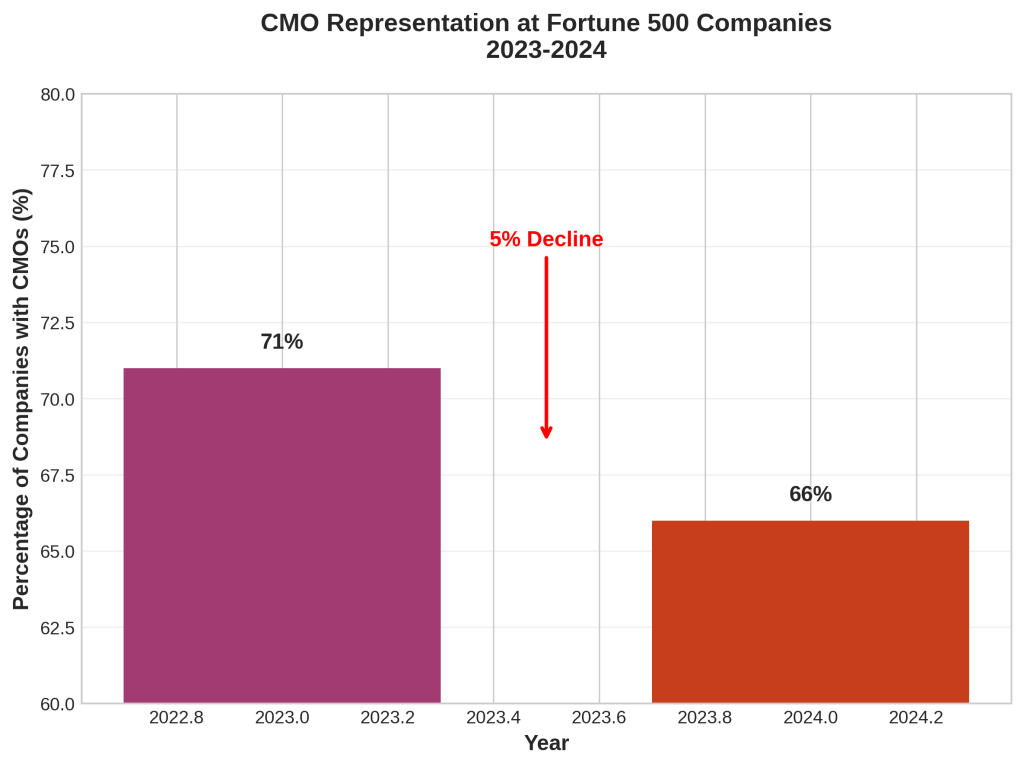
Customer Journey Complexity
The modern B2B customer journey has evolved from a linear, five-touchpoint process in 2016 to a complex, interconnected web involving ten or more interaction points in 2025 [3]. This evolution reflects the digital transformation of business processes and the proliferation of communication channels, requiring sophisticated marketing orchestration capabilities.
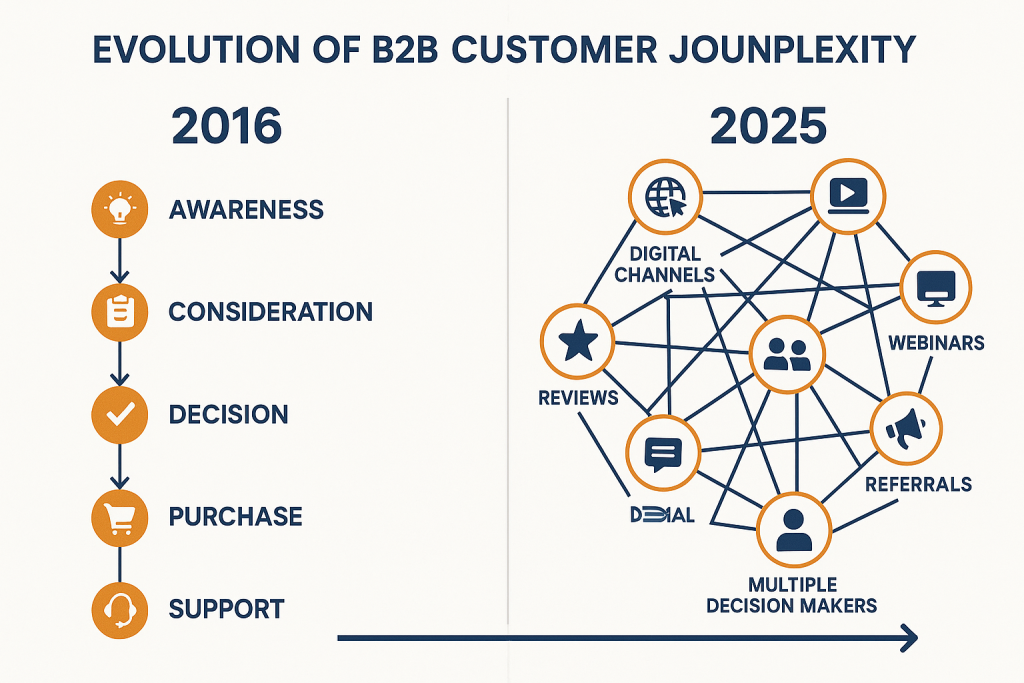
More than 80% of consumers now use multiple channels for product research or purchase, creating demand for omnichannel marketing expertise that many organizations lack internally [3]. This complexity necessitates strategic leadership capable of designing cohesive customer experiences across diverse touchpoints while maintaining message consistency and brand integrity.
The Rise of Outsourced Leadership Models
Against this backdrop of budget constraints, leadership fragmentation, and operational complexity, outsourced marketing leadership models have gained significant traction. The fractional leadership market has experienced remarkable growth, with the number of fractional leaders doubling from 60,000 in 2022 to 120,000 in 2024 [5]. This 100% growth rate over two years indicates strong market demand for flexible, expertise-driven leadership solutions.
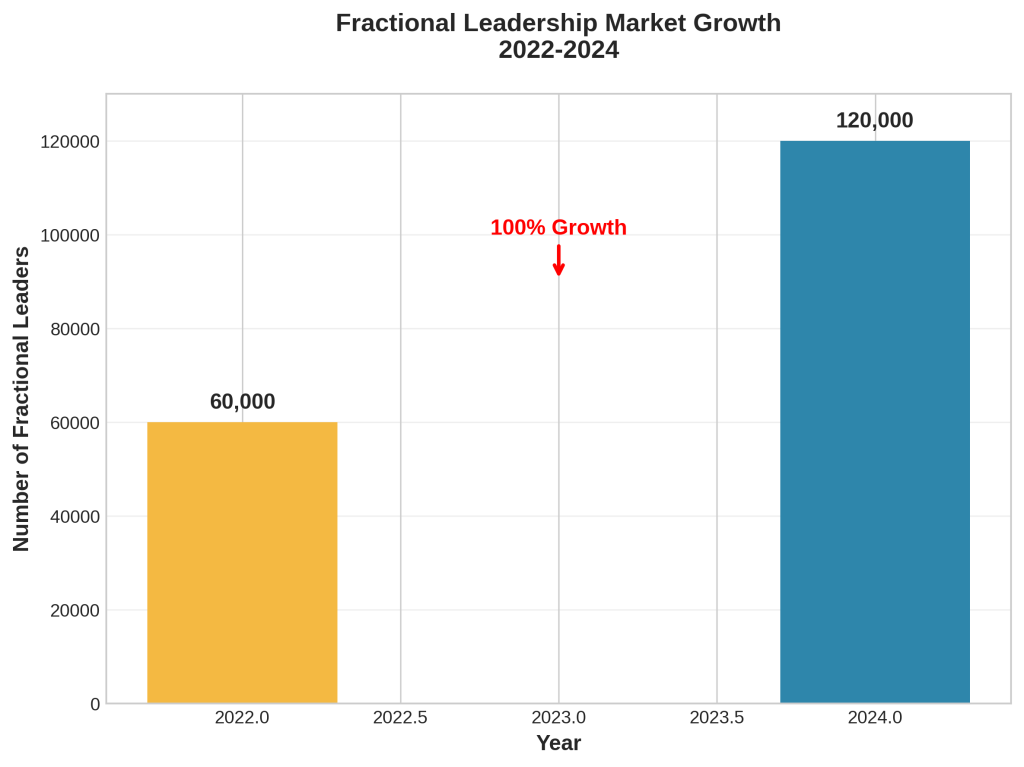
Chief Outsiders research demonstrates that attitudes toward fractional CMOs are becoming increasingly positive, with 73% of surveyed organizations expressing favorable views of the model [6]. The adoption of fractional CMOs has increased by over 60% in the past five years, reflecting growing recognition of the model’s value proposition in addressing specific organizational challenges.
Understanding CMO-as-a-Service
CMO-as-a-Service (CMOaaS) represents a comprehensive outsourcing model that provides organizations with complete marketing leadership infrastructure through a dedicated team of specialists. Unlike traditional consulting arrangements, CMOaaS functions as an integrated extension of the client organization, delivering strategic oversight, tactical execution, and performance optimization across all marketing disciplines.
Core Service Architecture
The CMOaaS model is built on a multi-disciplinary team structure that combines strategic leadership with specialized execution capabilities. This architecture typically includes strategists who develop overarching marketing plans, analysts who interpret performance data and market intelligence, content specialists who create campaign materials, and digital experts who manage technology platforms and automation systems.
| Service Component | Function | Typical Team Size | Key Deliverables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic Leadership | Overall marketing strategy and planning | 1-2 senior executives | Marketing strategy, budget allocation, KPI framework |
| Data Analytics | Performance measurement and optimization | 2-3 analysts | Performance reports, attribution analysis, ROI measurement |
| Content Creation | Campaign development and execution | 3-5 specialists | Campaign materials, content calendar, brand assets |
| Digital Operations | Technology management and automation | 2-4 technologists | Platform management, automation workflows, integration |
| Project Management | Coordination and delivery oversight | 1-2 managers | Project timelines, resource allocation, quality assurance |
This team-based approach enables CMOaaS providers to deliver comprehensive marketing capabilities that would typically require multiple full-time hires. The integrated structure ensures consistency across all marketing activities while providing the flexibility to scale resources based on campaign requirements and business cycles.
Market Positioning and Value Proposition
CMOaaS positions itself as a complete marketing department replacement or augmentation, targeting organizations that require comprehensive marketing capabilities but lack the resources or expertise to build these functions internally. The model is particularly attractive to companies experiencing rapid growth, entering new markets, or undergoing digital transformation initiatives that demand sophisticated marketing orchestration.
The value proposition centers on three core benefits: immediate access to senior-level expertise without recruitment delays, comprehensive capabilities that eliminate the need for multiple vendor relationships, and scalable resources that can adapt to changing business requirements. This positioning differentiates CMOaaS from traditional marketing agencies, which typically focus on specific services or campaigns rather than ongoing strategic leadership.
Integration and Operational Model
Successful CMOaaS implementations require deep integration with client organizations, extending beyond typical vendor relationships to function as an embedded marketing department. This integration involves establishing direct reporting relationships with executive leadership, participating in strategic planning processes, and maintaining ongoing communication with sales, product, and customer success teams.
“CMOaaS provides executive level, strategic marketing leadership specifically focused on growing businesses of all size and shape. CMOaaS combines a dynamic, focused team in contrast to a traditional role that would rely on a single individual.”— Industry Analysis, Marketing Leadership Models (2025)
The operational model typically begins with a comprehensive business audit that identifies marketing gaps, opportunities, and resource requirements. This assessment informs the development of a customized marketing strategy that aligns with broader business objectives and establishes measurable performance targets. The CMOaaS team then assumes responsibility for strategy execution, performance monitoring, and continuous optimization based on market feedback and business results.
Technology and Infrastructure Requirements
CMOaaS providers must maintain sophisticated technology infrastructure to support multiple client engagements simultaneously while ensuring data security and performance optimization. This infrastructure typically includes marketing automation platforms, customer relationship management systems, analytics tools, content management systems, and project management software.
The technology requirements extend beyond software platforms to include data integration capabilities that enable seamless information flow between client systems and CMOaaS tools. This integration is essential for maintaining real-time visibility into campaign performance, customer behavior, and business impact metrics that inform strategic decision-making.
Scalability and Resource Allocation
One of the primary advantages of the CMOaaS model is its inherent scalability, which allows organizations to access additional resources during peak periods or special projects without the long-term commitments associated with full-time hiring. This flexibility is particularly valuable for companies with seasonal business cycles, product launch requirements, or expansion initiatives that demand temporary increases in marketing capacity.
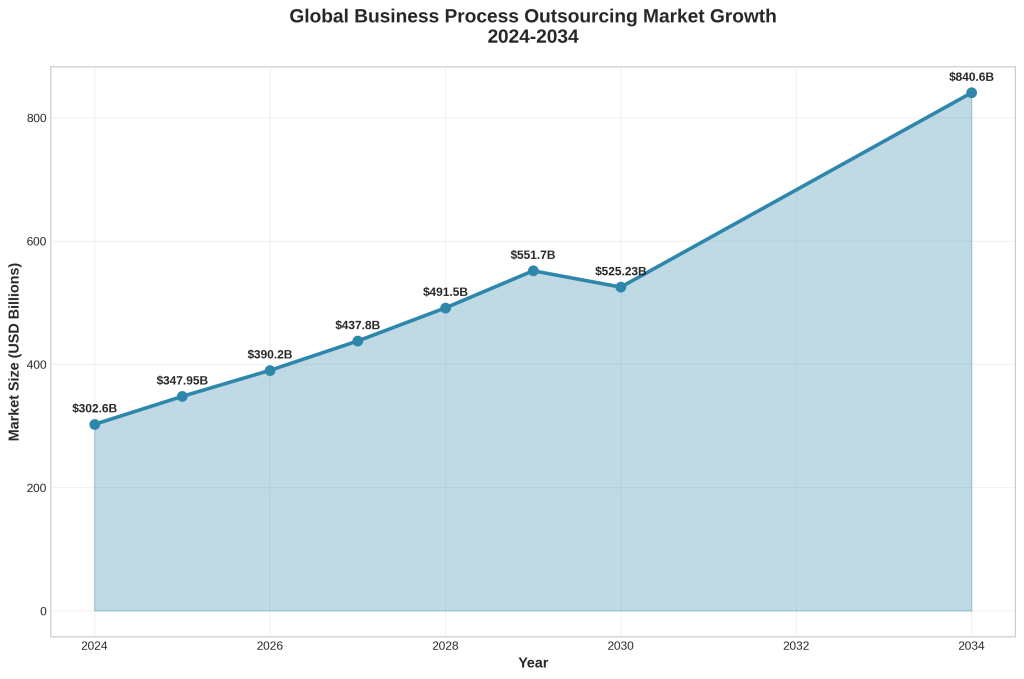
The broader business process outsourcing market, which encompasses CMOaaS services, is projected to grow from $302.6 billion in 2024 to $840.6 billion by 2034, representing a compound annual growth rate of approximately 10.7% [1]. This growth trajectory reflects increasing organizational recognition of outsourcing benefits and the maturation of service delivery models that can effectively support complex business functions.
Resource allocation within CMOaaS engagements typically follows a tiered structure that provides core strategic leadership on a consistent basis while enabling tactical resources to scale based on campaign requirements and business priorities. This approach ensures continuity in strategic direction while optimizing cost efficiency through flexible resource deployment.
Fractional CMO Model Deep Dive
The Fractional CMO model provides organizations with access to senior-level marketing leadership on a part-time basis, typically engaging experienced executives who work with multiple clients simultaneously. This approach focuses on strategic guidance, team development, and high-level marketing oversight rather than comprehensive service delivery, making it particularly suitable for organizations with existing marketing capabilities that require executive-level direction.
Executive Leadership Focus
Fractional CMOs operate at the strategic level, providing the same executive functions as full-time CMOs but on a reduced time commitment basis. These professionals typically possess extensive experience in senior marketing roles, often having served as full-time CMOs at multiple organizations before transitioning to fractional work. Their value proposition centers on bringing proven strategic frameworks, industry expertise, and executive-level decision-making capabilities to organizations that cannot justify or afford full-time executive compensation.
The strategic focus of fractional CMOs aligns with research from Salary.com indicating significant compensation differences between strategic and tactical marketing roles. In 2022, the median salary for a Vice President of Marketing (strategic role) was $268,663, compared to $98,200 for a Marketing Supervisor (tactical role) [7]. This 2.5x compensation differential reflects the market’s recognition of strategic leadership value and explains why organizations seek fractional access to executive-level expertise.
| Role Level | Primary Focus | 2022 Median Salary | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| VP Marketing (Strategic) | Strategy and Leadership | $268,663 | Strategic planning, team leadership, executive reporting |
| Marketing Supervisor (Tactical) | Execution and Management | $98,200 | Campaign execution, team coordination, performance tracking |
| Compensation Ratio | Strategic Premium | 2.5x Higher | Reflects strategic value and decision-making authority |
Engagement Models and Time Allocation
Fractional CMO engagements typically range from 10-30 hours per week, depending on organizational needs and complexity requirements. The most common engagement model involves 15-20 hours weekly, providing sufficient time for strategic planning, team meetings, performance review, and executive reporting while maintaining cost efficiency compared to full-time executive compensation.
Time allocation within fractional engagements follows a structured approach that prioritizes high-impact activities. Strategic planning and goal setting typically consume 30-40% of available time, team development and coaching account for 25-35%, performance analysis and optimization require 20-25%, and executive communication and reporting utilize the remaining 10-15%. This distribution ensures focus on activities that generate the greatest organizational impact while maintaining accountability to executive leadership.
ROI Analysis and Performance Metrics
Forbes Business Council research provides compelling evidence of fractional CMO effectiveness through detailed ROI analysis. In a comparative study of a $20 million revenue company, an experienced fractional CMO generated 5% revenue growth ($1 million additional revenue) with total fees and expenses of $145,000, resulting in a net revenue increase of $855,000 and an ROI of 589% [7].
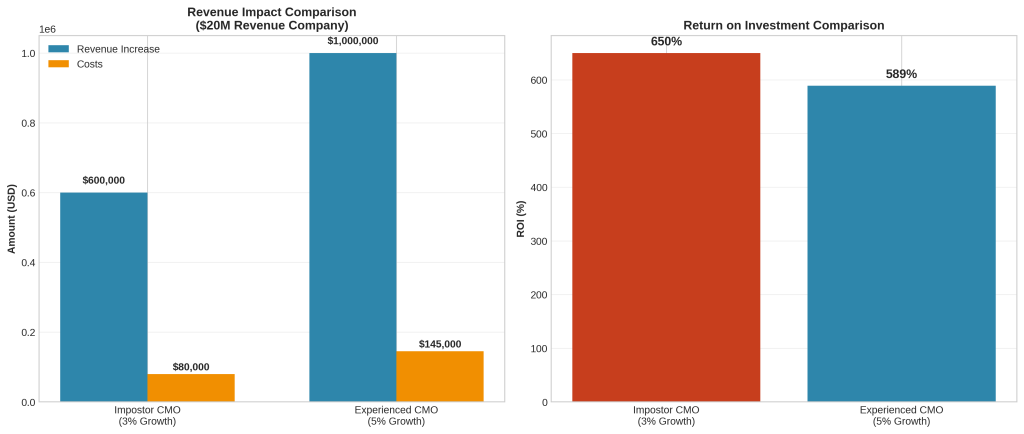
This performance contrasts sharply with “impostor” fractional CMOs who lack genuine executive experience. The same study found that impostor CMOs generated only 3% growth ($600,000 additional revenue) with fees of $80,000, resulting in a net increase of $520,000. While the impostor’s fees were 67% lower, the experienced CMO generated 64% more net revenue, totaling $335,000 in additional value [7].
“A fractional CMO generates the greatest ROI by attaining optimal revenue growth. To do so, the CMO must develop coordinated marketing strategies that drive the end-to-end execution of marketing programs. The CMO is the architect that designs the blueprint and the project manager that oversees the construction.”— Ferris Ayar, Forbes Business Council (2023)
Market Growth and Adoption Trends
The fractional CMO market has experienced significant expansion, driven by both supply-side factors (experienced executives seeking flexible work arrangements) and demand-side pressures (organizations requiring strategic expertise without full-time commitments). Zippia research indicates that 36% of the U.S. workforce engages in freelance work as of 2022, with freelancing expected to grow by 14% over the next six years [7].
However, this growth has created quality control challenges, as many marketing professionals have adopted the “fractional CMO” title to justify higher rates without possessing genuine executive experience. This market saturation with unqualified providers has created a “buyer beware” environment where organizations must carefully evaluate credentials and track records to identify truly qualified fractional executives.
Specialization Areas and Industry Expertise
Successful fractional CMOs typically develop specialization in specific industries, business models, or marketing disciplines that enable them to provide targeted expertise and accelerated value delivery. Common specialization areas include B2B technology, healthcare, financial services, e-commerce, and professional services, each requiring distinct marketing approaches and regulatory considerations.
Industry specialization enables fractional CMOs to leverage previous experience, established vendor relationships, and proven frameworks that can be rapidly deployed in new client environments. This specialization also supports premium pricing models, as organizations value expertise that directly addresses their specific challenges and market dynamics.
Key Performance Indicators and Success Metrics
Fractional CMO performance evaluation typically focuses on two primary metrics: Revenue Growth Rate (RGR) and Return on Investment (ROI). These financial indicators provide clear measurement of marketing contribution to business objectives while enabling comparison across different engagement models and service providers.
| KPI Category | Specific Metrics | Measurement Frequency | Success Benchmarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue Impact | Revenue Growth Rate, Customer Acquisition Cost | Monthly | 5%+ annual growth, decreasing CAC |
| Financial Returns | ROI, Marketing Efficiency Ratio | Quarterly | 400%+ ROI, improving efficiency |
| Operational Excellence | Lead Quality, Conversion Rates | Weekly | Improving lead scores, higher conversions |
| Strategic Development | Team Capability, Process Maturity | Quarterly | Enhanced skills, documented processes |
Additional metrics include Cost Per Lead (CPL), Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), and marketing attribution accuracy, which provide operational insights that support strategic decision-making and resource optimization. The Forbes research recommends evaluating fractional CMO performance over extended periods—at least six months following implementation, with one year being ideal for comprehensive assessment [7].
Comparative Analysis Framework
A systematic comparison of CMO-as-a-Service and Fractional CMO models reveals fundamental differences in service delivery, resource allocation, cost structures, and organizational impact. Understanding these distinctions is essential for organizations evaluating which approach best aligns with their strategic objectives, operational requirements, and resource constraints.
Service Delivery Models
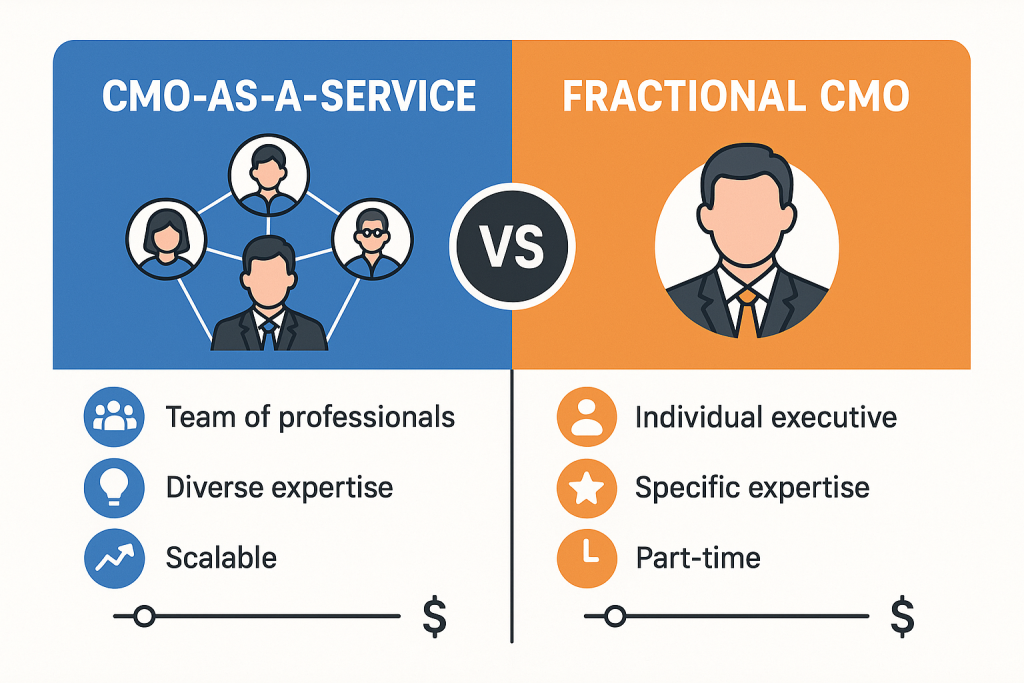
The most significant difference between these models lies in their fundamental service delivery approach. CMO-as-a-Service operates on a team-based model that provides comprehensive marketing capabilities through multiple specialists working in coordination. This approach enables simultaneous execution across multiple marketing disciplines while maintaining strategic coherence through centralized leadership.
Fractional CMO services, conversely, center on individual executive expertise delivered through part-time engagement. This model prioritizes strategic guidance and leadership development over comprehensive execution, making it most effective for organizations with existing marketing capabilities that require senior-level direction and optimization.
| Comparison Factor | CMO-as-a-Service | Fractional CMO | Optimal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Service Structure | Multi-disciplinary team | Individual executive | CMOaaS for comprehensive needs |
| Execution Capability | Full implementation | Strategic guidance | CMOaaS for execution gaps |
| Time Commitment | Full-time equivalent | Part-time (10-30 hours/week) | Fractional for strategic oversight |
| Scalability | Highly scalable team | Limited by individual capacity | CMOaaS for growth phases |
| Integration Depth | Embedded department | Executive advisor | CMOaaS for operational integration |
| Expertise Breadth | Multiple specializations | Deep individual expertise | Fractional for specialized needs |
Cost Structure Analysis
Cost considerations represent a critical decision factor, with each model offering distinct advantages depending on organizational requirements and engagement duration. CMO-as-a-Service typically involves higher absolute costs due to team-based delivery, but provides comprehensive capabilities that may eliminate the need for additional vendor relationships or internal hiring.
Fractional CMO engagements generally offer lower absolute costs, making them attractive for organizations with budget constraints or limited marketing requirements. However, the total cost of ownership may increase if additional resources are required for execution, technology management, or specialized capabilities not provided by the fractional executive.
Deloitte research indicates that outsourcing CMO services can result in cost savings of up to 30% compared to full-time executive hiring, while simultaneously boosting performance through access to specialized expertise and proven methodologies [8]. These savings reflect reduced overhead costs, elimination of recruitment expenses, and optimized resource utilization through flexible engagement models.
Performance Measurement and Accountability
Both models require robust performance measurement frameworks, but the specific metrics and accountability structures differ based on service delivery approaches. CMO-as-a-Service providers typically accept broader accountability for marketing outcomes, including lead generation, conversion optimization, and revenue attribution, reflecting their comprehensive service delivery model.
Fractional CMO accountability focuses primarily on strategic outcomes such as marketing strategy development, team capability enhancement, and process optimization. While revenue impact remains important, the part-time nature of engagement and reliance on client execution capabilities create more complex attribution challenges.
“Less than half of organizations report productivity gains from outsourcing, and only 25% are seeing reduction in cost of vendor services. However, approximately 55% of organizations with a global business services leader role have achieved over 20% average savings.”— Deloitte Global Outsourcing Survey (2024)
Implementation Complexity and Timeline
Implementation requirements vary significantly between models, with CMO-as-a-Service typically requiring more extensive onboarding and integration processes due to team-based delivery and comprehensive service scope. Initial implementation may take 4-8 weeks to establish team structure, technology integration, and operational procedures.
Fractional CMO implementations generally proceed more rapidly, often beginning productive work within 1-2 weeks of engagement initiation. The individual-based model reduces coordination complexity and enables faster strategic assessment and planning activities. However, execution of strategic recommendations may require additional time for internal resource allocation or vendor selection.
Risk Factors and Mitigation Strategies
Each model presents distinct risk profiles that organizations must evaluate and mitigate through appropriate selection criteria and engagement management practices. CMO-as-a-Service risks include vendor dependency, integration complexity, and potential cultural misalignment between provider teams and client organizations.
Fractional CMO risks center on individual dependency, limited execution capability, and potential quality variations among providers. The Forbes research highlighting “impostor” fractional CMOs demonstrates the importance of thorough vetting processes and credential verification [7].
| Risk Category | CMO-as-a-Service Risks | Fractional CMO Risks | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quality Control | Team coordination challenges | Individual capability limitations | Detailed vetting, performance SLAs |
| Dependency | Vendor lock-in potential | Key person dependency | Contract flexibility, backup plans |
| Integration | Cultural misalignment | Limited organizational integration | Cultural assessment, integration planning |
| Execution | Over-reliance on external team | Execution gaps without internal capability | Capability development, hybrid models |
Decision Framework Application
Organizations can apply a structured decision framework to evaluate which model best addresses their specific requirements and constraints. This framework considers budget availability, team size requirements, scalability needs, and timeline constraints to guide model selection.
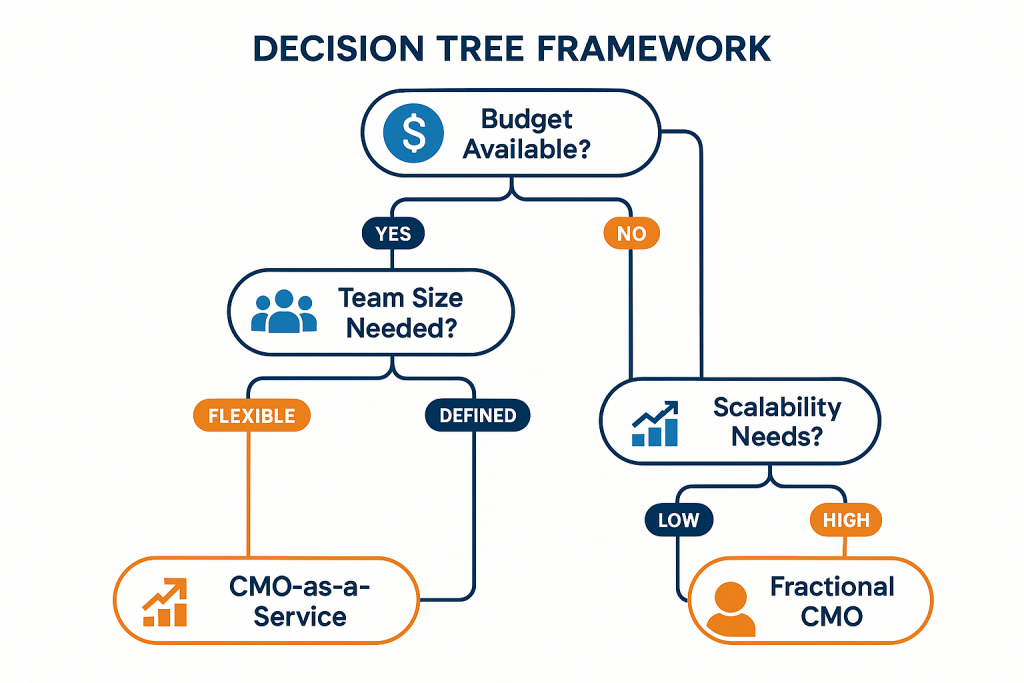
The decision framework begins with budget assessment, as this factor often determines feasibility for each model. Organizations with limited budgets may find fractional CMO services more accessible, while those with adequate resources can consider the comprehensive capabilities offered by CMO-as-a-Service providers.
Team size requirements represent the second decision point, with organizations needing flexible, multi-disciplinary capabilities favoring CMO-as-a-Service, while those requiring focused strategic guidance may prefer fractional CMO expertise. Scalability needs complete the framework, with high-growth organizations typically benefiting from the expandable team structure of CMO-as-a-Service models.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Comprehensive cost-benefit analysis requires examination of both direct financial impacts and indirect organizational benefits that may not appear in traditional ROI calculations. Organizations must consider total cost of ownership, opportunity costs, and strategic value creation when evaluating outsourced marketing leadership models.
Direct Cost Comparisons
Direct costs for CMO-as-a-Service typically range from $15,000 to $50,000 monthly, depending on team size, service scope, and engagement complexity. This investment provides access to 5-10 marketing professionals with diverse specializations, equivalent to $180,000-$600,000 annually. When compared to hiring equivalent internal capabilities, organizations often achieve 20-40% cost savings while gaining immediate access to senior-level expertise.
Fractional CMO engagements generally cost $5,000 to $20,000 monthly for 10-30 hours of executive time weekly. Annual costs range from $60,000 to $240,000, representing significant savings compared to full-time CMO compensation, which averages $268,663 according to Salary.com data [7]. However, organizations must factor additional costs for execution resources, technology platforms, and specialized services not provided by the fractional executive.
Opportunity Cost Analysis
Opportunity costs represent a critical but often overlooked component of cost-benefit analysis. Organizations attempting to build internal marketing capabilities face recruitment delays, onboarding periods, and learning curves that can extend 6-12 months before achieving full productivity. During this period, competitive opportunities may be lost, market positioning may deteriorate, and revenue growth may stagnate.
McKinsey research demonstrates that companies with aligned marketing leadership achieve 2.3 times more growth than those with fragmented structures [3]. This growth differential suggests that delayed implementation of effective marketing leadership can result in substantial opportunity costs that exceed the direct costs of outsourced solutions.
Strategic Value Creation
Beyond direct cost considerations, outsourced marketing leadership models provide strategic value through access to proven methodologies, industry best practices, and established vendor relationships. CMO-as-a-Service providers bring systematic approaches developed across multiple client engagements, enabling faster implementation and reduced trial-and-error costs.
Fractional CMOs contribute strategic value through executive-level perspective, industry expertise, and leadership development capabilities that enhance internal team performance. The Forbes case study demonstrating 589% ROI illustrates the potential for strategic value creation that significantly exceeds direct engagement costs [7].
Implementation Strategies
Successful implementation of outsourced marketing leadership requires systematic planning, clear expectation setting, and structured integration processes. Organizations must establish governance frameworks, communication protocols, and performance measurement systems that enable effective collaboration and accountability.
Assessment and Selection Framework
Implementation begins with comprehensive assessment of organizational needs, existing capabilities, and strategic objectives. This assessment should evaluate current marketing performance, identify capability gaps, and establish success criteria that will guide provider selection and engagement management.
| Assessment Area | Key Questions | Success Criteria | Documentation Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current Capabilities | What marketing functions exist internally? | Clear capability inventory | Skills matrix, performance data |
| Performance Gaps | Where are current shortfalls? | Prioritized gap analysis | Performance benchmarks, competitor analysis |
| Strategic Objectives | What outcomes are required? | Measurable goals | Business plan, growth targets |
| Resource Constraints | What budget and timeline limitations exist? | Realistic parameters | Budget allocation, timeline requirements |
Provider Evaluation Criteria
Provider selection requires systematic evaluation of credentials, experience, methodology, and cultural fit. Organizations should prioritize providers with demonstrated success in similar industries, proven methodologies, and strong references from comparable engagements. The Forbes research emphasizing the importance of distinguishing between experienced professionals and “impostors” highlights the critical nature of thorough vetting processes [7].
Evaluation criteria should include track record verification, methodology assessment, team composition review, and cultural alignment evaluation. Organizations should request detailed case studies, speak with previous clients, and assess the provider’s understanding of industry-specific challenges and opportunities.
Integration and Governance
Successful integration requires establishing clear governance structures, communication protocols, and decision-making authorities. Organizations should designate internal champions who will work closely with outsourced providers, establish regular review cycles, and create feedback mechanisms that enable continuous optimization.
Governance frameworks should address reporting relationships, approval processes, budget management, and performance review procedures. Clear documentation of roles, responsibilities, and expectations prevents misunderstandings and enables effective collaboration throughout the engagement.
Performance Monitoring and Optimization
Implementation success depends on robust performance monitoring systems that track both leading and lagging indicators of marketing effectiveness. Organizations should establish baseline measurements, implement regular review cycles, and create optimization processes that enable continuous improvement based on performance data and market feedback.
| Implementation Phase | Duration | Key Activities | Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment & Selection | 4-6 weeks | Needs analysis, provider evaluation, contract negotiation | Completed assessment, selected provider |
| Onboarding & Integration | 2-4 weeks | Team introduction, system access, process alignment | Operational readiness, team integration |
| Strategy Development | 4-6 weeks | Strategic planning, goal setting, roadmap creation | Approved strategy, implementation plan |
| Execution & Optimization | Ongoing | Campaign implementation, performance monitoring, optimization | Performance targets, continuous improvement |
Future Market Outlook
The outsourced marketing leadership market is positioned for continued expansion, driven by persistent budget pressures, increasing marketing complexity, and growing recognition of flexible engagement models’ strategic value. Multiple converging trends suggest sustained growth in both CMO-as-a-Service and Fractional CMO segments through 2030 and beyond.
Market Growth Projections
The broader business process outsourcing market, which encompasses marketing leadership services, is projected to grow from $347.95 billion in 2025 to $840.60 billion by 2034, representing a compound annual growth rate of approximately 10.7% [1]. This growth trajectory reflects increasing organizational comfort with outsourcing strategic functions and the maturation of service delivery models that can effectively support complex business requirements.
Fractional leadership specifically has demonstrated even more aggressive growth, with the number of fractional professionals doubling from 60,000 to 120,000 between 2022 and 2024 [5]. If this growth rate continues, the fractional leadership market could exceed 300,000 professionals by 2028, creating substantial capacity for organizations seeking part-time executive expertise.
Technology Integration and Automation
Artificial intelligence and marketing automation technologies are reshaping service delivery models, enabling more sophisticated campaign management, performance optimization, and customer experience personalization. These technological advances benefit both CMO-as-a-Service and Fractional CMO models by enhancing productivity, improving attribution accuracy, and enabling more strategic focus on high-value activities.
However, technology integration also creates new challenges around data privacy, platform complexity, and skill requirements that may favor providers with dedicated technology expertise. Organizations should evaluate providers’ technology capabilities and integration experience as part of their selection criteria.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Increasing data privacy regulations, advertising standards, and industry-specific compliance requirements create additional complexity for marketing leadership. Organizations in regulated industries such as healthcare, financial services, and telecommunications may require providers with specialized compliance expertise and proven track records in navigating regulatory environments.
These regulatory pressures may favor larger CMO-as-a-Service providers with dedicated compliance resources over individual fractional CMOs who may lack specialized regulatory expertise. Organizations should assess regulatory requirements as part of their model selection process.
Competitive Landscape Evolution
The success of outsourced marketing leadership models is attracting new entrants, including traditional consulting firms, marketing agencies, and technology companies seeking to expand their service offerings. This increased competition may drive innovation in service delivery models while potentially creating quality control challenges as the market becomes more crowded.
Organizations should expect continued evolution in pricing models, service offerings, and engagement structures as providers differentiate themselves in an increasingly competitive market. The Forbes research highlighting “impostor” providers suggests that quality differentiation will become increasingly important as the market matures [7].
Key Takeaways
- Market Growth and Opportunity: The business process outsourcing market is projected to reach $840.60 billion by 2034, with fractional leadership roles doubling from 60,000 to 120,000 professionals between 2022-2024, indicating strong demand for flexible marketing leadership solutions.
- ROI Potential: Experienced fractional CMOs can deliver 589% ROI through strategic leadership, while CMO-as-a-Service models provide cost savings of up to 30% compared to full-time hiring, with companies achieving single customer-oriented leadership seeing 2.3x more growth.
- Model Selection Criteria: Organizations should choose CMO-as-a-Service for comprehensive execution needs and team scalability, while Fractional CMO models suit strategic guidance requirements with existing internal capabilities, based on budget, team size, and scalability needs.
- Quality Control Imperative: With 36% of the workforce engaging in freelance work and market saturation with unqualified providers, organizations must implement rigorous vetting processes to distinguish between experienced professionals and “impostor” providers lacking genuine executive experience.
- Implementation Success Factors: Successful outsourced marketing leadership requires systematic assessment, clear governance frameworks, robust performance monitoring, and cultural alignment, with implementation timelines typically spanning 10-16 weeks from selection to full operational effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the typical cost difference between CMO-as-a-Service and Fractional CMO models?
CMO-as-a-Service typically costs $15,000-$50,000 monthly ($180,000-$600,000 annually) for comprehensive team-based services, while Fractional CMO engagements range from $5,000-$20,000 monthly ($60,000-$240,000 annually) for part-time executive guidance. However, total cost of ownership may vary based on additional execution resources required.
How long does implementation typically take for each model?
CMO-as-a-Service implementation generally requires 4-8 weeks due to team onboarding and system integration complexity. Fractional CMO engagements can begin productive work within 1-2 weeks, though execution of strategic recommendations may require additional time for internal resource allocation.
What ROI can organizations expect from outsourced marketing leadership?
Forbes research demonstrates that experienced fractional CMOs can achieve 589% ROI through strategic leadership and revenue growth optimization. Deloitte studies indicate cost savings of up to 30% compared to full-time hiring, while McKinsey research shows companies with aligned marketing leadership achieve 2.3x more growth.
How can organizations avoid “impostor” providers lacking genuine experience?
Organizations should verify executive track records, request detailed case studies, speak with previous clients, and assess industry-specific expertise. Look for providers with proven C-level experience, measurable results, and specialized knowledge relevant to your industry and business model.
Which model is better for rapidly growing companies?
CMO-as-a-Service typically better serves rapidly growing companies due to its scalable team structure, comprehensive execution capabilities, and ability to handle increasing marketing complexity. Fractional CMO models may be limited by individual capacity constraints during high-growth periods.
What performance metrics should organizations use to evaluate success?
Key metrics include Revenue Growth Rate (RGR), Return on Investment (ROI), Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), and marketing attribution accuracy. Evaluation should occur over extended periods—at least six months, with one year being ideal for comprehensive assessment.
References
- Precedence Research. “Business Process Outsourcing Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034.” Market Research Report, 2025. https://www.precedenceresearch.com/business-process-outsourcing-market
- Gartner, Inc. “Gartner CMO Survey Reveals Marketing Budgets Have Dropped to 7.7% of Overall Company Revenue in 2024.” Press Release, May 13, 2024. https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2024-05-13-gartner-cmo-survey-reveals-marketing-budgets-have-dropped-to-seven-point-seven-percent-of-overall-company-revenue-in-2024
- Bettati, Aurélia, Jeff Jacobs, Kelsey Robinson, and Robert Tas. “The CMO’s comeback: Aligning the C-suite to drive customer-centric growth.” McKinsey & Company, June 16, 2025. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/growth-marketing-and-sales/our-insights/the-cmos-comeback-aligning-the-c-suite-to-drive-customer-centric-growth
- Spencer Stuart. “Fortune 500 CMO Representation Study.” Executive Search Research, 2024.
- Breakthrough3X. “Boosting ROI with Top Tips for Fractional CMOs.” Industry Research Report, May 26, 2025. https://breakthrough3x.com/resources/boosting-roi-with-top-tips-for-fractional-cmos/
- Chief Outsiders. “Fractional CMO Adoption and Attitude Survey.” Market Research Study, 2024.
- Ayar, Ferris. “The ROI Of A Fractional CMO.” Forbes Business Council, March 21, 2023. https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbesbusinesscouncil/2023/03/21/the-roi-of-a-fractional-cmo/
- Deloitte. “Global Outsourcing Survey 2024.” Consulting Research Report, 2024. https://www.deloitte.com/us/en/services/consulting/articles/global-outsourcing-survey.html

