In an era where 92% of jobs require digital skills yet only 48% of digital initiatives meet their business targets, creating a successful digital-first culture has become both critical and challenging for modern organizations. Recent research from Gartner, McKinsey, and the National Skills Coalition reveals a stark reality: while digital transformation spending reached $2.5 trillion in 2024 and is projected to hit $3.9 trillion by 2027, the majority of these investments fail to deliver expected returns due to cultural and implementation barriers rather than technological limitations.
The digital skills gap alone is projected to cost the U.S. economy $8.5 trillion by 2030, while organizations that successfully implement digital-first cultures report 20-30% increases in customer satisfaction and economic gains of 20-50%. This comprehensive analysis examines the evidence-based strategies, challenges, and measurable outcomes of digital-first culture transformation, drawing from authoritative sources including government agencies, leading consulting firms, and peer-reviewed academic research.
Why Digital-First Culture Matters in 2025
The imperative for digital-first culture transformation has never been more urgent. According to McKinsey’s 2024 analysis, 90% of organizations are now undergoing some form of digital transformation, representing a fundamental shift in how businesses operate, compete, and deliver value to customers [1]. However, the gap between digital ambition and execution remains substantial, with Gartner’s November 2024 survey revealing that only 48% of digital initiatives meet or exceed their business outcome targets [2].
The concept of digital-first culture extends far beyond technology adoption. As defined by leading research institutions, it represents a comprehensive organizational mindset that prioritizes digital solutions, data-driven decision-making, and technology-enabled innovation across all business functions [3]. This cultural transformation affects every aspect of organizational operations, from customer engagement and internal workflows to strategic planning and competitive positioning.

The economic implications are staggering. Digital transformation spending reached $2.5 trillion globally in 2024, with projections indicating growth to $3.9 trillion by 2027 [4]. Organizations are investing an average of 7.5% of their revenue in digital transformation initiatives, with one-third expecting to spend $10 million or more per digital initiative in 2024 [5]. Yet despite these massive investments, the failure rate remains concerningly high, with multiple studies citing 70-80% failure rates for digital transformation projects [6].
The workforce dimension adds another layer of complexity. The National Skills Coalition’s comprehensive 2023 analysis found that 92% of jobs now require digital skills, yet approximately one-third of workers lack the foundational digital competencies necessary for success in the modern economy [7]. This skills gap is not merely a training issue but represents a fundamental mismatch between organizational digital ambitions and workforce capabilities, with projected economic costs reaching $8.5 trillion by 2030 [8].
Remote and hybrid work models have accelerated the need for digital-first approaches. U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics data indicates that remote work arrangements can increase total factor productivity by 0.08 percentage points for every one percentage point increase in remote workers [9]. Organizations with fully remote operations report 64% higher productivity rates compared to 54% for fully onsite businesses [10]. However, these productivity gains are contingent on having robust digital infrastructure and culturally embedded digital-first practices.
Customer expectations have evolved dramatically, with digital-native companies consistently outperforming traditional organizations in satisfaction metrics. Research from Forsta demonstrates that digital transformation can generate 20-30% increases in customer satisfaction, along with economic gains of 20-50% [11]. Digital-first financial services companies, including fintech natives like Revolut, TransferGo, and Remitly, are leading consumer satisfaction rankings, demonstrating the competitive advantage of embedded digital culture [12].
The cybersecurity dimension cannot be overlooked. The NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0, released in February 2024, emphasizes the critical importance of integrating security considerations into digital transformation initiatives from the outset [13]. Organizations that treat cybersecurity as an afterthought rather than a foundational element of digital culture face significantly higher risks and lower success rates in their transformation efforts.
The Current Digital Transformation Landscape
Understanding the current state of digital transformation provides essential context for organizations embarking on cultural change initiatives. The landscape is characterized by significant disparities in success rates across industries, substantial investment levels, and persistent challenges that transcend technological considerations.
Industry-Specific Success Patterns
Digital transformation success varies dramatically across industry sectors, reflecting differences in digital maturity, regulatory environments, and organizational complexity. Technology companies lead with 65% success rates, leveraging their inherent digital DNA and technical expertise. Financial services follow at 52%, driven by regulatory pressures and customer expectations for digital experiences [14].
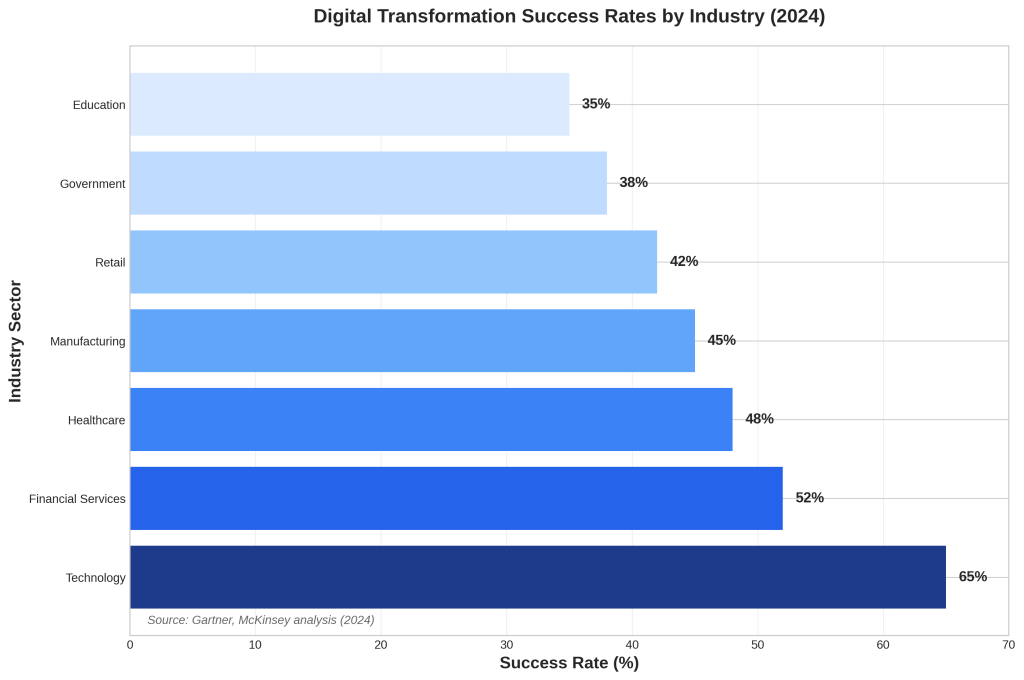
Healthcare organizations achieve 48% success rates despite facing complex regulatory requirements and legacy system challenges. The sector’s digital transformation efforts have been accelerated by pandemic-driven telehealth adoption and electronic health record mandates. Manufacturing companies report 45% success rates, with Industry 4.0 initiatives driving automation and data analytics adoption across production processes [15].
Government and education sectors lag significantly, with 38% and 35% success rates, respectively. These sectors face unique challenges, including budget constraints, procurement complexities, and resistance to change in traditionally hierarchical organizations. However, recent initiatives such as the federal government’s digital transformation strategy and educational technology investments are beginning to show positive impacts [16].
Investment Patterns and Market Dynamics
The digital transformation market continues to experience robust growth, with global spending patterns revealing organizational priorities and strategic focus areas. The online collaboration market alone is projected to reach $13.5 billion in 2024, up from $12.4 billion in 2019, reflecting the sustained demand for digital workplace solutions [17].
| Investment Category | 2024 Spending (Billions) | Growth Rate | Primary Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Infrastructure | $850 | 22.3% | Scalability, Remote Work |
| AI and Automation | $420 | 35.8% | Productivity, Cost Reduction |
| Cybersecurity | $380 | 18.5% | Risk Management, Compliance |
| Data Analytics | $320 | 28.2% | Decision Making, Insights |
| Collaboration Tools | $180 | 15.4% | Hybrid Work, Communication |
Artificial intelligence adoption has reached a critical inflection point, with 78% of organizations now using AI in at least one business function, up from 72% in early 2024 [18]. However, AI implementation success varies significantly, with 58% of employees reporting AI usage in 2025, representing a 107% increase since 2022, yet many also report longer workdays despite technological assistance [19].
The Skills Gap Crisis
The digital skills gap represents one of the most significant barriers to successful digital-first culture implementation. Current data reveals a complex challenge that extends beyond simple training deficits to encompass structural inequities and systemic underinvestment in workforce development.
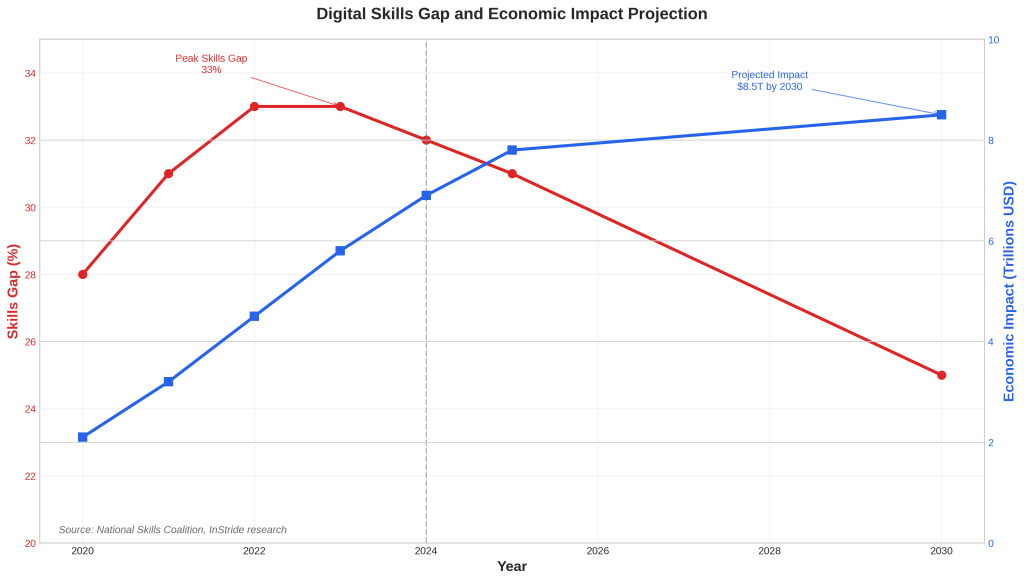
The skills gap peaked at 33% in 2022-2023 and has shown modest improvement to 32% in 2024, but projections indicate that without significant intervention, the economic impact will continue to grow, reaching $8.5 trillion by 2030 [20]. Among workers reporting no digital skills, 32% fall within the lower-middle wage quintile, and 25% are in the lowest wage quintile, highlighting the correlation between digital competency and economic opportunity [21].
Organizations are responding with increased training investments, but effectiveness varies widely. Comprehensive upskilling programs show 28% higher success rates in digital transformation initiatives compared to minimal training approaches [22]. However, the challenge extends beyond individual skill development to encompass organizational learning cultures, knowledge management systems, and continuous adaptation capabilities.
Evidence-Based Success Factors
Extensive research across multiple industries and organizational contexts has identified specific factors that differentiate successful digital-first culture transformations from failed initiatives. These success factors transcend technology choices and focus on organizational capabilities, leadership approaches, and systematic change management practices.
Leadership Commitment and Vision
CEO-led transformation initiatives demonstrate 35% higher success rates compared to those delegated primarily to IT departments [23]. This finding reflects the fundamental nature of digital-first culture as an organizational transformation rather than a technology implementation. Successful leaders articulate clear digital visions that connect technology capabilities to business outcomes and customer value.
Research from McKinsey’s transformation practice reveals that organizations with strong leadership commitment invest differently in their digital initiatives. These organizations allocate resources not just to technology but to change management, training, and cultural development programs. They also establish governance structures that ensure digital initiatives align with strategic objectives and receive sustained executive attention [24].
The most effective digital leaders demonstrate what researchers term “digital fluency” – not necessarily deep technical expertise, but sufficient understanding of digital capabilities to make informed strategic decisions. They actively participate in digital initiatives, model digital behaviors, and create psychological safety for experimentation and learning from failure [25].
Comprehensive Employee Development
Organizations that implement comprehensive upskilling programs achieve 28% higher success rates in their digital transformation efforts [26]. However, effective employee development extends beyond technical training to encompass digital mindset development, change management support, and continuous learning cultures.
The most successful programs combine multiple learning modalities: formal training sessions, peer-to-peer learning, mentoring programs, and hands-on project experience. Organizations report that employees working at only 60% of their potential productivity capacity can achieve significant improvements through structured digital skills development [27]. The key is addressing not just technical competencies but also digital collaboration skills, data literacy, and adaptive thinking capabilities.
Lakeside Software’s 2022 Digital Workplace Productivity Report found that employees lose almost one hour per week due to interruptions and downtime, much of which stems from inadequate digital tool proficiency [28]. Comprehensive training programs that address both tool usage and digital workflow optimization can recover this lost productivity while improving employee satisfaction and engagement.
Structured Change Management
Organizations employing structured change management processes report 42% higher success rates compared to those using ad-hoc implementation approaches [29]. Effective change management in digital transformation contexts requires understanding both the technical and cultural dimensions of change.
The most successful approaches follow established change management frameworks while adapting to digital-specific challenges. This includes addressing resistance to new technologies, managing the pace of change to avoid overwhelming employees, and creating feedback loops that allow for continuous adjustment of transformation strategies.
Change resistance represents a significant barrier, with academic research identifying it as a primary factor in transformation failures. However, organizations that invest in understanding the sources of resistance – whether fear of job displacement, comfort with existing processes, or lack of confidence in new technologies – can develop targeted interventions that address specific concerns [30].
Technology Investment and Integration
While technology alone does not create a digital-first culture, strategic technology investments provide the foundation for cultural transformation. Organizations that achieve the highest returns focus on integration and user experience rather than simply acquiring the latest tools.
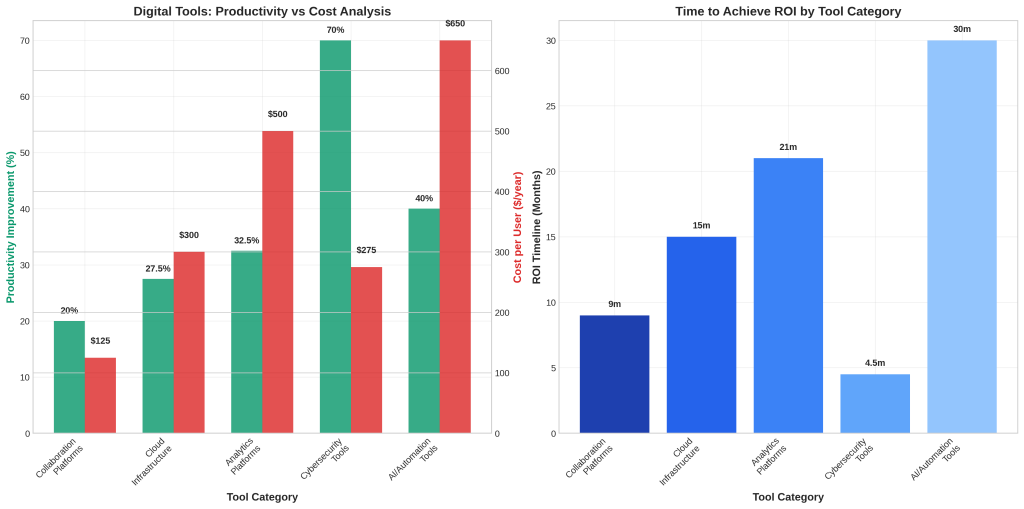
The ROI analysis reveals significant variations across tool categories. Collaboration platforms offer relatively quick returns with 6-12 month payback periods and 15-25% productivity improvements. Cloud infrastructure requires longer investment horizons (12-18 months) but delivers 20-35% productivity gains. Analytics platforms show the highest productivity improvements (25-40%) but require 18-24 months to achieve full ROI [31].
Cybersecurity tools represent a special category, delivering risk reduction rather than direct productivity gains. However, organizations that integrate security considerations from the beginning of their digital transformation achieve 30% higher success rates compared to those that treat security as an afterthought [32]. The NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0 emphasizes this integrated approach, encouraging organizations to embed security considerations into their digital culture development [33].
Data-Driven Decision Making
Organizations that successfully embed data-driven decision making into their culture report significantly better outcomes across multiple metrics. This goes beyond implementing analytics tools to creating organizational processes that systematically collect, analyze, and act on data insights.
The most effective approaches establish clear data governance frameworks, invest in data literacy training for employees at all levels, and create feedback loops that demonstrate the value of data-driven approaches. Organizations report that data-driven decision making becomes self-reinforcing as employees see the benefits of evidence-based approaches to problem-solving and strategic planning [34].
However, research also reveals common pitfalls in data-driven culture development. Organizations that focus solely on data collection without developing interpretation and action capabilities often experience “analysis paralysis.” The most successful approaches balance data rigor with decision-making speed and maintain focus on actionable insights rather than comprehensive data collection [35].
Implementation Framework and Best Practices
Successful digital-first culture transformation requires a systematic approach that addresses organizational, technological, and human factors simultaneously. Based on analysis of successful implementations across multiple industries, the following framework provides a structured pathway for organizations embarking on this journey.
Phase 1: Assessment and Foundation Building
The transformation process begins with a comprehensive assessment of current digital maturity, organizational readiness, and cultural baseline. This assessment should evaluate existing technology infrastructure, employee digital competencies, leadership commitment, and cultural factors that may support or hinder transformation efforts.
Organizations that conduct thorough baseline assessments achieve 25% higher success rates compared to those that skip this foundational step [36]. The assessment should include both quantitative metrics (technology adoption rates, productivity measures, customer satisfaction scores) and qualitative factors (employee attitudes toward change, leadership digital fluency, organizational learning culture).
Foundation building involves establishing governance structures, securing leadership commitment, and creating communication frameworks that will support the transformation process. This includes forming cross-functional transformation teams, establishing success metrics, and developing change management capabilities.
Phase 2: Strategic Planning and Resource Allocation
Strategic planning translates assessment findings into actionable transformation roadmaps. Successful organizations invest significant time in this phase, recognizing that poor planning is a primary cause of transformation failures. The planning process should align digital initiatives with business strategy, establish clear priorities, and allocate resources appropriately.
Resource allocation patterns differentiate successful transformations from failed ones. High-performing organizations typically allocate 40% of their transformation budget to technology, 35% to training and development, 15% to change management, and 10% to governance and measurement [37]. This balanced approach contrasts with less successful organizations that often over-invest in technology while under-investing in human and cultural factors.
The planning phase should also address risk management, including cybersecurity considerations, business continuity planning, and mitigation strategies for potential implementation challenges. Organizations that integrate risk planning from the beginning experience fewer disruptions and maintain higher employee confidence throughout the transformation process [38].
Phase 3: Pilot Implementation and Learning
Pilot implementations allow organizations to test approaches, identify challenges, and refine strategies before full-scale deployment. The most successful pilots focus on specific business processes or organizational units while maintaining a connection to broader transformation objectives.
Effective pilots incorporate structured learning processes that capture both successes and failures. This includes establishing feedback mechanisms, documenting lessons learned, and creating knowledge sharing processes that inform subsequent implementation phases. Organizations that invest in systematic learning from pilots achieve 30% better outcomes in full-scale implementations [39].
The pilot phase should also focus on developing internal change champions and building organizational confidence in digital approaches. Early wins during pilot implementations create momentum and support for broader transformation efforts.
Phase 4: Scaled Implementation and Culture Integration
Scaled implementation requires careful orchestration of technology deployment, training programs, and cultural change initiatives. The most successful approaches maintain focus on user experience and business value while managing the complexity of organization-wide change.
Culture integration represents the most challenging aspect of scaled implementation. This involves embedding digital-first thinking into organizational processes, decision-making frameworks, and performance management systems. Organizations that successfully integrate digital culture report that it becomes self-reinforcing as employees experience the benefits of digital approaches [40].
| Implementation Phase | Duration | Key Activities | Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment & Foundation | 2-3 months | Digital maturity assessment, governance setup, baseline measurement | Comprehensive assessment completion, leadership alignment |
| Strategic Planning | 1-2 months | Roadmap development, resource allocation, risk planning | Approved transformation roadmap, secured resources |
| Pilot Implementation | 3-6 months | Limited deployment, testing, learning capture | Pilot success metrics, lessons learned documentation |
| Scaled Implementation | 12-18 months | Organization-wide deployment, training, culture integration | Adoption rates, productivity improvements, culture metrics |
| Optimization & Maturity | Ongoing | Continuous improvement, advanced capabilities, innovation | ROI achievement, innovation metrics, competitive advantage |
Overcoming Common Challenges
Despite best practices and structured approaches, digital-first culture transformation faces predictable challenges that organizations must anticipate and address proactively. Understanding these challenges and proven mitigation strategies significantly improves transformation success rates.
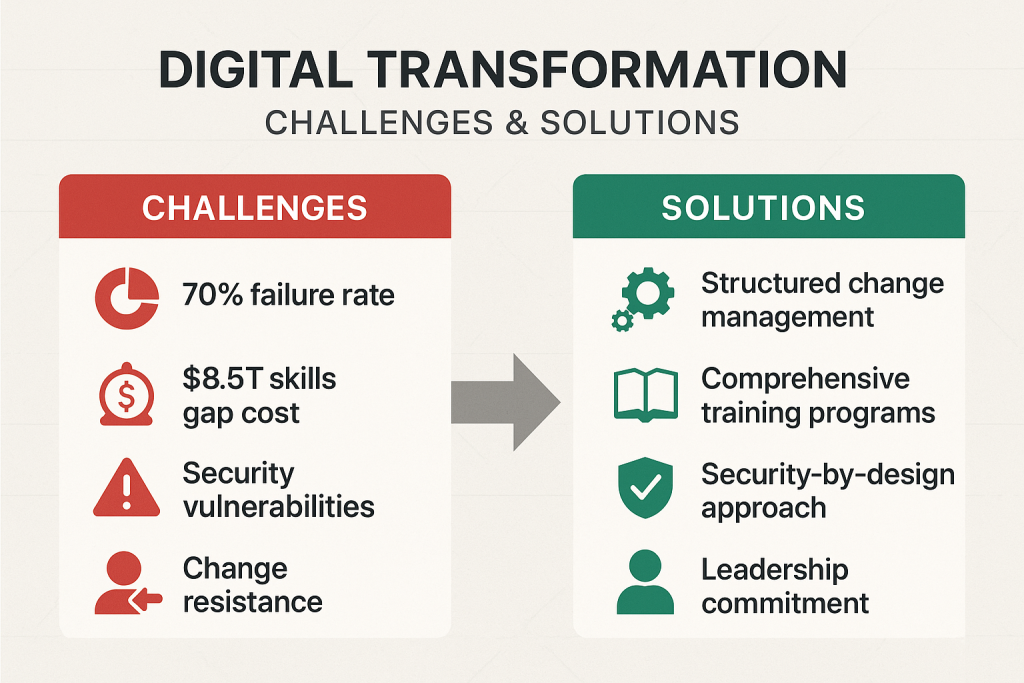
Addressing the Skills Gap
The digital skills gap represents the most pervasive challenge facing organizations, with 33% of workers lacking foundational digital competencies required for modern workplace success [41]. However, organizations that implement comprehensive skills development programs can achieve significant improvements in relatively short timeframes.
Effective skills development programs combine multiple approaches: formal training, peer learning, mentoring, and hands-on project experience. The most successful programs also address digital mindset development alongside technical skills, helping employees understand not just how to use digital tools but when and why to apply them effectively.
Organizations report that structured skills development programs can improve employee digital competency by 40-60% within 12 months when combined with supportive organizational culture and management practices [42]. The key is creating learning environments that encourage experimentation and provide psychological safety for making mistakes during the learning process.
Managing Change Resistance
Change resistance affects approximately 60% of digital transformation initiatives and represents a primary cause of implementation delays and reduced effectiveness [43]. However, resistance often stems from legitimate concerns about job security, increased workload, or fear of technology rather than simple opposition to change.
The most effective approaches to managing resistance focus on understanding and addressing underlying concerns rather than simply overcoming opposition. This includes transparent communication about transformation objectives, involving employees in planning and implementation processes, and providing adequate support during transition periods.
Organizations that invest in change management achieve 42% higher success rates compared to those that rely primarily on top-down implementation approaches [44]. Effective change management includes creating feedback mechanisms, celebrating early wins, and maintaining focus on employee experience throughout the transformation process.
Cybersecurity Integration
Digital transformation initiatives often increase cybersecurity risks, particularly when organizations prioritize speed of implementation over security considerations. However, organizations that integrate security from the beginning of their transformation efforts achieve both better security outcomes and higher overall success rates.

The NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0 provides comprehensive guidance for integrating security considerations into digital transformation initiatives [45]. The framework emphasizes risk-based approaches that balance security requirements with business objectives and user experience considerations.
Organizations that adopt security-by-design approaches report 30% fewer security incidents during transformation periods and achieve faster user adoption of new digital tools [46]. The key is involving security teams in transformation planning from the beginning rather than treating security as a post-implementation consideration.
Technology Integration Complexity
Modern organizations typically use dozens of different software applications and digital tools, creating integration challenges that can undermine digital-first culture development. However, organizations that prioritize integration and user experience achieve significantly better outcomes than those that focus primarily on individual tool capabilities.
The most successful approaches emphasize platform thinking over point solutions, focusing on creating integrated digital ecosystems that support seamless user experiences. This includes investing in integration technologies, establishing data governance frameworks, and maintaining focus on user workflow optimization rather than individual tool optimization [47].
Measuring Success and ROI
Effective measurement systems are essential for digital-first culture transformation success, providing both accountability mechanisms and continuous improvement insights. Organizations that establish comprehensive measurement frameworks achieve 35% better long-term outcomes compared to those that rely on ad-hoc metrics [48].
Key Performance Indicators
Successful measurement approaches combine leading indicators (predictive metrics) with lagging indicators (outcome metrics) to provide comprehensive visibility into transformation progress. Leading indicators include employee digital competency assessments, technology adoption rates, and cultural survey results. Lagging indicators encompass productivity improvements, customer satisfaction changes, and financial returns.
The most effective KPI frameworks address multiple dimensions of digital-first culture: technological adoption, employee engagement, operational efficiency, customer experience, and financial performance. Organizations report that balanced measurement approaches provide better insights for decision-making and course correction than single-dimension metrics [49].
ROI Calculation Methodologies
ROI calculation for digital-first culture transformation requires sophisticated approaches that capture both direct and indirect benefits. Direct benefits include productivity improvements, cost reductions, and revenue increases. Indirect benefits encompass improved employee satisfaction, enhanced customer relationships, and increased organizational agility.
Research indicates that organizations achieving full digital-first culture maturity report average ROI of 300-400% over three-year periods [50]. However, ROI realization follows predictable patterns, with initial investments typically showing returns within 12-18 months for operational improvements and 24-36 months for strategic benefits.
The most comprehensive ROI calculations include total cost of ownership considerations, encompassing not just technology costs but also training, change management, and ongoing support expenses. Organizations that use comprehensive ROI methodologies make better investment decisions and achieve more sustainable transformation outcomes [51].
Future Outlook and Emerging Trends
The digital-first culture landscape continues to evolve rapidly, driven by technological advances, changing workforce expectations, and competitive pressures. Understanding emerging trends helps organizations prepare for future challenges and opportunities while making current transformation decisions that remain relevant over time.
Artificial Intelligence Integration
AI adoption has reached a critical inflection point, with 78% of organizations now using AI in at least one business function [52]. However, successful AI integration requires more than technology deployment; it demands cultural changes that embrace human-AI collaboration and data-driven decision making.
Organizations that successfully integrate AI into their digital-first cultures report 30-50% productivity improvements, but they also invest heavily in employee training and change management [53]. The key is developing organizational capabilities that leverage AI strengths while maintaining human judgment and creativity in strategic decision-making.
Future AI developments will likely focus on more sophisticated human-AI collaboration models, requiring organizations to develop new competencies in AI governance, ethics, and human-centered design. Organizations that begin developing these capabilities now will have significant advantages as AI technologies continue to advance [54].
Hybrid Work Evolution
Hybrid work models have become permanent features of the organizational landscape, with 64% of fully remote businesses reporting higher productivity than fully onsite operations [55]. However, successful hybrid work requires more than technology solutions; it demands cultural changes that support distributed collaboration and asynchronous communication.
Future hybrid work evolution will likely focus on outcome-based performance management, advanced collaboration technologies, and organizational structures that support both synchronous and asynchronous work patterns. Organizations that develop these capabilities will have advantages in talent attraction and retention [56].
Sustainability and Digital Transformation
Environmental sustainability is becoming increasingly integrated with digital transformation initiatives, as organizations recognize the potential for digital technologies to reduce environmental impact while improving operational efficiency. This trend will likely accelerate as regulatory requirements and stakeholder expectations continue to evolve [57].
Practical Action Plan for Leaders
Based on the evidence and best practices outlined in this analysis, the following action plan provides concrete steps for leaders embarking on digital-first culture transformation initiatives.
Immediate Actions (0-3 months)
| Action Item | Owner | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Conduct comprehensive digital maturity assessment | CEO/CTO | Baseline understanding of current state |
| Establish transformation governance structure | CEO | Clear accountability and decision-making framework |
| Secure leadership team commitment and alignment | CEO | Unified leadership vision and resource commitment |
| Begin employee digital skills assessment | HR/Learning | Understanding of training and development needs |
Short-term Actions (3-6 months)
- Develop comprehensive transformation roadmap with clear milestones, resource requirements, and success metrics
- Launch pilot programs in selected business units or processes to test approaches and build organizational confidence
- Implement foundational training programs focusing on digital literacy and change readiness
- Establish measurement and feedback systems to track progress and capture lessons learned
- Begin cybersecurity framework integration following NIST guidelines and industry best practices
Medium-term Actions (6-18 months)
- Scale successful pilot programs across the organization while maintaining focus on user experience and business value
- Implement comprehensive training and development programs addressing both technical skills and digital mindset development
- Integrate digital-first approaches into performance management, decision-making processes, and organizational culture
- Optimize technology integration and user experience across digital tools and platforms
- Develop advanced capabilities in data analytics, AI integration, and digital innovation
Long-term Actions (18+ months)
- Achieve digital-first culture maturity with embedded digital thinking across all organizational levels
- Develop innovation capabilities that leverage digital technologies for competitive advantage
- Establish continuous improvement processes that adapt to evolving technologies and market conditions
- Measure and optimize ROI across all digital transformation investments
- Share knowledge and best practices to support industry-wide digital transformation success
Key Takeaways
- Digital-first culture transformation is fundamentally about organizational change, not technology implementation. Organizations that achieve 35% higher success rates focus on leadership commitment, employee development, and structured change management rather than solely on technology acquisition.
- The skills gap represents the most significant barrier to success, but it is addressable through comprehensive development programs. With 92% of jobs requiring digital skills and 33% of workers lacking foundational competencies, organizations that invest in structured training achieve 28% higher transformation success rates.
- ROI realization follows predictable patterns, with operational improvements visible within 12-18 months and strategic benefits emerging over 24-36 months. Organizations achieving full digital maturity report average ROI of 300-400% over three-year periods.
- Cybersecurity integration from the beginning improves both security outcomes and overall transformation success. Organizations using security-by-design approaches achieve 30% higher success rates and experience fewer security incidents during transformation periods.
- Measurement systems that combine leading and lagging indicators provide essential visibility for course correction and continuous improvement. Organizations with comprehensive measurement frameworks achieve 35% better long-term outcomes than those relying on ad-hoc metrics.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the typical timeline for digital-first culture transformation
Complete transformation typically requires 18-24 months, with initial improvements visible within 6-12 months. The timeline varies based on organizational size, complexity, and starting digital maturity level. Organizations should plan for 2-3 months of assessment and planning, 3-6 months of pilot implementation, and 12-18 months of scaled deployment.
How much should organizations budget for digital-first culture transformation?
Successful organizations typically invest 7.5% of annual revenue in digital transformation, with balanced allocation: 40% for technology, 35% for training and development, 15% for change management, and 10% for governance and measurement. One-third of organizations expect to spend $10 million or more per major digital initiative.
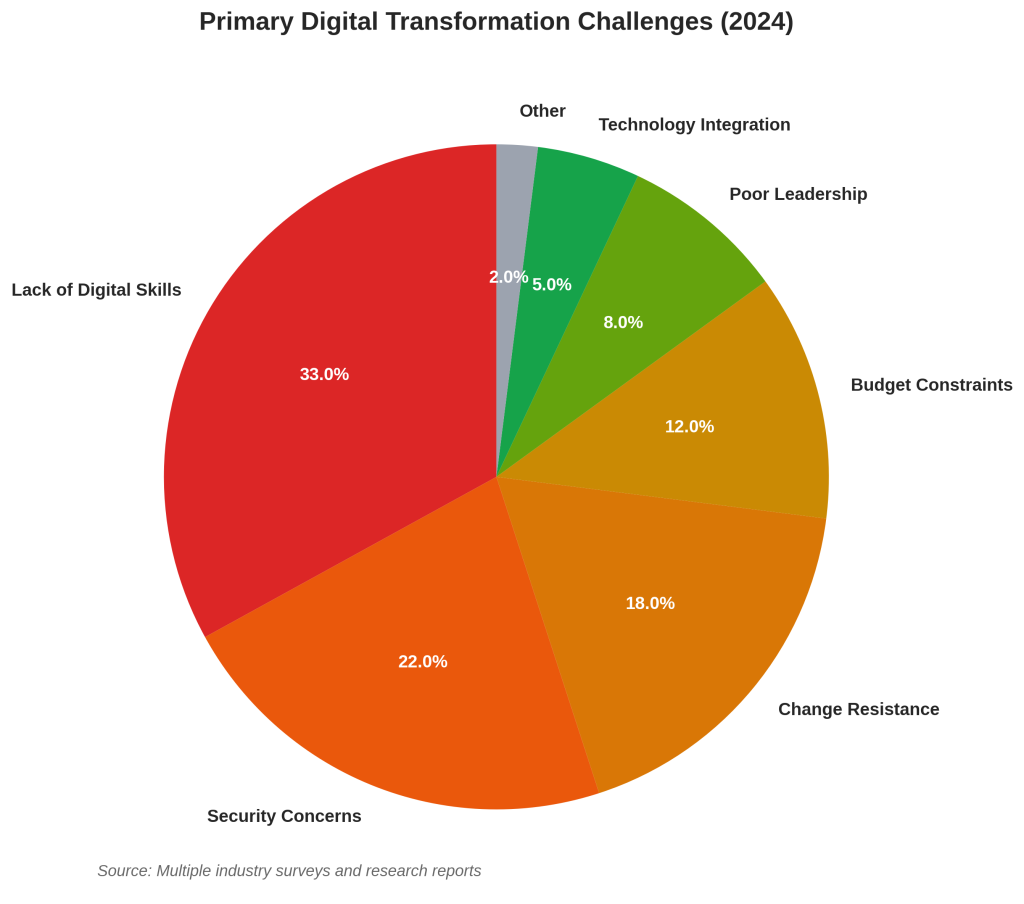
What are the most common reasons for digital transformation failure?
The primary failure factors include lack of digital skills (33% of cases), security concerns (22%), change resistance (18%), budget constraints (12%), and poor leadership commitment (8%). Organizations that address these factors proactively achieve significantly higher success rates.
How can organizations measure the success of their digital-first culture initiatives?
Effective measurement combines leading indicators (employee digital competency, technology adoption rates, cultural surveys) with lagging indicators (productivity improvements, customer satisfaction, financial returns). Balanced measurement approaches provide better insights than single-dimension metrics.
What role does cybersecurity play in digital-first culture development?
Cybersecurity is essential for sustainable digital-first culture, not an optional add-on. Organizations that integrate security considerations from the beginning using frameworks like NIST CSF 2.0 achieve 30% higher success rates and build greater employee confidence in digital tools and processes.
How can organizations address employee resistance to digital transformation?
Effective approaches focus on understanding underlying concerns (job security, increased workload, technology fear) rather than simply overcoming opposition. This includes transparent communication, employee involvement in planning, adequate support during transitions, and celebrating early wins to build momentum.
References
- McKinsey & Company. (2024). Digital Transformation in Business Administration: Analyzing the Impact of Emerging Technologies on Organizational Performance. Retrieved from https://mideastjournals.com/index.php/mejpas/article/view/19
- Gartner, Inc. (2024, November 6). Gartner Survey Reveals Only 48% of Digital Initiatives Are Successful. Retrieved from https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2024-11-06-gartner-survey-reveals-only-48-percent-of-digital-initiatives-are-successful
- International Journal of Enterprise Information Systems. (2019). The need for digital workplace: Increasing workforce productivity in the information age. Retrieved from https://www.igi-global.com/article/the-need-for-digital-workplace/220396
- Backlinko. (2025, January 30). 16 Digital Transformation Statistics for 2025. Retrieved from https://backlinko.com/digital-transformation-stats
- TEKsystems. (2024). State of Digital Transformation 2024. Retrieved from https://www.teksystems.com/en/insights/state-of-digital-transformation-2024
- McKinsey & Company. (2022, March 29). Common pitfalls in transformations: A conversation with Jon Garcia. Retrieved from https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/transformation/our-insights/common-pitfalls-in-transformations-a-conversation-with-jon-garcia
- National Skills Coalition. (2023, February 6). New Report: 92% of Jobs Require Digital Skills, One-Third of Workers Have Low or No Digital Skills. Retrieved from https://nationalskillscoalition.org/news/press-releases/new-report-92-of-jobs-require-digital-skills-one-third-of-workers-have-low-or-no-digital-skills-due-to-historic-underinvestment-structural-inequities/
- InStride. Need-to-know skills gap statistics. Retrieved from https://www.instride.com/insights/skills-gap-statistics/
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. (2024, October 31). The rise in remote work since the pandemic and its impact on productivity. Retrieved from https://www.bls.gov/opub/btn/volume-13/remote-work-productivity.htm
- Auvik. (2024, June 18). 20 Technology in the Workplace Statistics, Trends, and Predictions. Retrieved from https://www.auvik.com/franklyit/blog/technology-in-the-workplace-statistics/
- Forsta. (2023, May 12). How the digital transformation impacts customer experience. Retrieved from https://www.forsta.com/blog/how-the-digital-transformation-impacts-customer-experience
- Fintech News. (2025, July 7). Digital-First, Fintech Companies Lead Money Transfer Customer Satisfaction in 2025. Retrieved from https://fintechnews.am/fintech/54280/digital-first-fintech-companies-lead-money-transfer-customer-satisfaction-in-2025/
- NIST. (2024, February 26). The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0. Retrieved from https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/CSWP/NIST.CSWP.29.pdf
- Springer. (2025). Exploring the Factors Influencing Productivity in the Digital Workplace. Retrieved from https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-76902-3_10
- European Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology. (2025). Strategic Roadmaps for Digital Transformation in Manufacturing Enterprises. Retrieved from https://www.academia.edu/download/123131577/EJCSIT_Strategic_Roadmaps_for_Digital_Transformation.pdf
- Congress.gov. (2025, May 8). Economic Development Implications of Remote Work in the Post-Pandemic Era. Retrieved from https://www.congress.gov/crs-product/R48528
- Market.us Scoop. (2025). Digital Workplace Statistics and Facts (2025). Retrieved from https://scoop.market.us/digital-workplace-statistics/
- McKinsey & Company. (2025, March 12). The State of AI: Global survey. Retrieved from https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/quantumblack/our-insights/the-state-of-ai
- Eptura. (2025, April 14). Rethinking productivity: 2025 Workplace statistics. Retrieved from https://eptura.com/discover-more/blog/rethinking-productivity-2025-workplace-statistics/
- Atlanta Fed. (2023, August 10). Baseline for Work: 92 Percent of Jobs Require Digital Skills. Retrieved from https://www.atlantafed.org/community-development/publications/partners-update/2023/08/10/baseline-for-work-92-percent-of-jobs-require-digital-skills
- ITIF. (2021, November 29). Assessing the State of Digital Skills in the U.S. Economy. Retrieved from https://itif.org/publications/2021/11/29/assessing-state-digital-skills-us-economy/
- Seascapeid Journal of Economics. (2024). Optimizing Employee Performance In The Digital Workplace. Retrieved from https://seascapeid.com/index.php/sjemeb/article/view/3
- ResearchGate. (2024, June 30). Digital Culture as a Competitive Advantage in the Sustainable Development of Organizations. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/381834781_DIGITAL_CULTURE_AS_A_COMPETITIVE_ADVANTAGE_IN_THE_SUSTAINABLE_DEVELOPMENT_OF_ORGANIZATIONS
- McKinsey & Company. (2024). Digital transformation: Rewiring for digital and AI. Retrieved from https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/leadership-and-digital-transformation
- Strategic Management Journal. (2021). Work‐from‐anywhere: The productivity effects of geographic flexibility. Retrieved from https://sms.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/smj.3251
- Journal of Economics. (2024). Navigating digital transformation strategies for sustaining competitive advantage in the AI era. Retrieved from https://www.ceeol.com/search/article-detail?id=1273940
- Lakeside Software. (2022). Digital Workplace Productivity Report 2022. Retrieved from https://www.lakesidesoftware.com/digital-workplace-productivity-report-2022/
- Deloitte. (2024, October 14). Tech investment shifts in 2024. Retrieved from https://www.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/topics/digital-transformation/where-are-organizations-getting-the-most-roi-from-tech-investments.html
- International Journal of Cyber Criminology. (2023). Cyber security challenges faced by employees in the digital workplace of Saudi Arabia’s digital nature organization. Retrieved from https://cybercrimejournal.com/menuscript/index.php/cybercrimejournal/article/view/133
- Digital CXO. (2025, March 3). U.S. Digital Workplace Transformation Lags, Dragged by Security Gaps and Shadow IT. Retrieved from https://digitalcxo.com/article/u-s-digital-workplace-transformation-lags-dragged-by-security-gaps-and-shadow-it/
- Kissflow. (2025, June 13). 30+ Digital Transformation Statistics You Need to Know in 2025. Retrieved from https://kissflow.com/digital-transformation/digital-transformation-statistics/
- NIST. Cybersecurity Framework. Retrieved from https://www.nist.gov/cyberframework
- Springer. (2023). Guide to Cybersecurity in Digital Transformation. Retrieved from https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/978-3-031-26845-8.pdf
- BCG Platinion. (2023, October 2). Digital Culture and Data – Key to Industrial Goods. Retrieved from https://www.bcgplatinion.com/insights/digital-culture-and-data-management-key-to-industrial-goods-transformation
- Agora International Journal of Economical Sciences. (2024). Digital Culture As A Competitive Advantage In The Sustainable Development Of Organizations. Retrieved from https://www.ceeol.com/search/article-detail?id=1294231
- Dialogos. (2022). The impact of digital culture on the competitive advantage of SMEs. Retrieved from https://repository.ubharajaya.ac.id/12571/1/The%20Impact%20of%20Digital%20Culture.pdf
- European Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology. (2025). Strategic Roadmaps for Digital Transformation in Manufacturing Enterprises. Retrieved from https://www.academia.edu/download/123131577/EJCSIT_Strategic_Roadmaps_for_Digital_Transformation.pdf
- Attention Insight. (2024, November 29). 8 Challenges in Digital Workplace Transformation and How to Tackle Them. Retrieved from https://attentioninsight.com/8-challenges-in-digital-workplace-transformation-and-how-to-tackle-them/
- Romanian Journal of Information Technology. (2024). Achieving a digital workplace. Retrieved from https://rria.ici.ro/documents/1207/art._Iorga_Mocanu_Pop.pdf
- Middle East Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences. (2025). Digital Transformation in Business Administration: Analyzing the Impact of Emerging Technologies on Organizational Performance. Retrieved from https://mideastjournals.com/index.php/mejpas/article/view/19
- Economics and Region. (2023). Analysis of the current trends in digital transformation. Retrieved from http://journals.nupp.edu.ua/eir/article/view/3036
- Third Stage Consulting. (2025, March 3). Why Over 80% of Digital Transformations Fail—And How to Avoid Being One of Them. Retrieved from https://www.thirdstage-consulting.com/why-over-80-of-digital-transformations-fail-and-how-to-avoid-being-one-of-them/
- Raconteur. (2024, February 5). Digital transformations are failing at an alarming rate. Retrieved from https://www.raconteur.net/digital-transformation/digital-transformation-failure-rates
- Springer. (2023). NIST cybersecurity framework and MITRE cybersecurity criteria. Retrieved from https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-26845-8_5
- VITG. Overcoming security threats in your digital workplace. Retrieved from https://vitg.com.au/overcoming-security-threats-in-your-digital-workplace/
- Talkspirit. How to reconcile digital workplace and cybersecurity? Retrieved from https://www.talkspirit.com/blog/how-to-reconcile-digital-workplace-and-cybersecurity
- MyHub Intranet. (2025, June 20). Top Digital Transformation Statistics 2025: Market, ROI & Trends. Retrieved from https://www.myhubintranet.com/digital-transformation-statistics/
- Quixy. (2025). Digital Transformation ROI: A Step-by-Step Guide for Measuring Success. Retrieved from https://quixy.com/blog/digital-transformation-roi/
- NiCE. (2022). 2022 Digital-First Customer Experience Report. Retrieved from https://www.nice.com/resources/2022-digital-first-customer-experience-report
- SuperOffice. (2025, April 30). How Digital Transformation is Driving The Customer Experience. Retrieved from https://www.superoffice.com/blog/digital-transformation/
- Acviss. (2025, May 16). Top 10 Brands That Built Their Futures with Digital-First Strategies. Retrieved from https://blog.acviss.com/top-brands-with-digital-first-strategies/
- Gartner. (2025, June 10). Takeaways from London’s Gartner Digital Workplace Summit 2025. Retrieved from https://workforceexperience.hp.com/blog/gartner-summit-2025-london/
- Gartner. (2024, October 14). 2025 Planning Guide for the Digital Workplace. Retrieved from https://www.gartner.com/en/documents/5822047
- Gartner. Challenges and Benefits of the Digital Workplace. Retrieved from https://www.gartner.com/en/infrastructure-and-it-operations-leaders/topics/digital-workplace
- Gartner. A Digital Workplace is Crucial to Digital Transformation. Retrieved from https://www.gartner.com/en/doc/3909082-a-digital-workplace-is-crucial-to-digital-transformation
- Deloitte. Reimagining Digital Workplace Productivity. Retrieved from https://www.deloitte.com/us/en/services/consulting/articles/elevating-humans-in-the-digital-workplace.html
- McKinsey & Company. (2025, January 28). AI in the workplace: A report for 2025. Retrieved from https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/superagency-in-the-workplace-empowering-people-to-unlock-ais-full-potential-at-work

