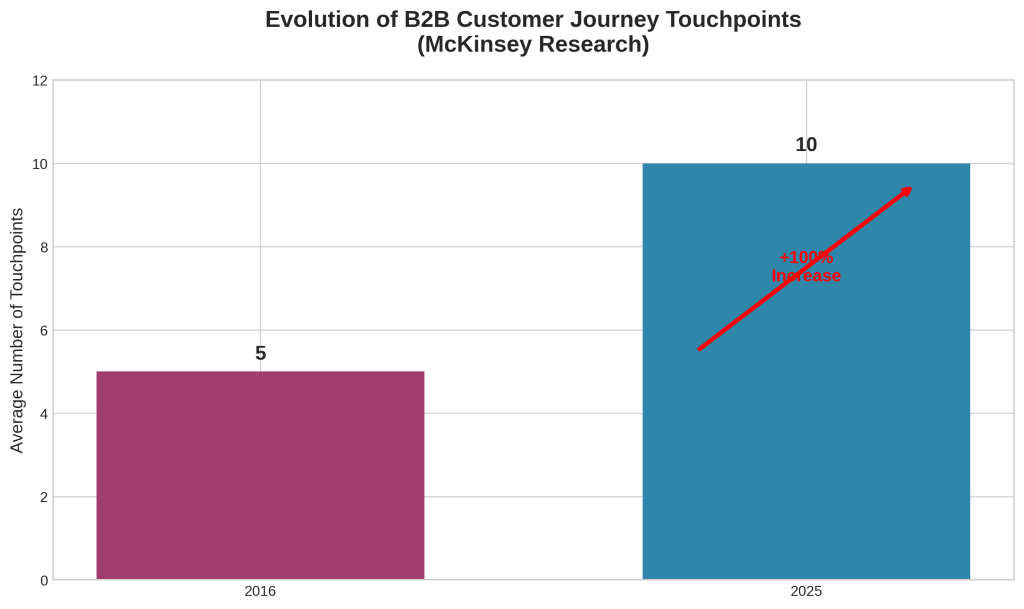
The digital marketing landscape has evolved dramatically, with modern consumers interacting with brands across an average of 10 touchpoints during their buying journey—double the number from 2016 [1]. This fundamental shift demands a holistic approach to digital marketing that integrates all channels and touchpoints into a cohesive, customer-centric strategy. Research from McKinsey reveals that companies with a single customer-focused executive role achieve up to 2.3 times more growth than those with fragmented marketing responsibilities [2].
This comprehensive analysis examines the critical components of holistic digital marketing strategy, drawing from authoritative sources including the U.S. International Trade Administration, McKinsey’s 2025 CMO Growth Research Survey, HubSpot’s State of Marketing Report, and Deloitte’s Government Marketing Trends research. The evidence demonstrates that integrated marketing approaches not only improve customer experience but also deliver measurable business results, with email marketing achieving conversion rates of 2.8% for B2C brands and video marketing providing positive ROI for 93% of businesses [3].
However, implementing holistic marketing strategies presents significant challenges. Many organizations struggle with fragmented customer ownership, unclear marketing impact measurement, and the complexity of coordinating multiple channels. This article provides a balanced examination of both opportunities and limitations, offering evidence-based recommendations for building sustainable, integrated marketing strategies that drive measurable growth in 2025 and beyond.
The Critical Need for Holistic Marketing in 2025
The digital marketing ecosystem has reached an unprecedented level of complexity, fundamentally altering how businesses must approach customer engagement and growth strategies. According to the U.S. International Trade Administration, digital marketing now encompasses “an online marketing program that boosts cross channel promotion of a brand, product, or service” [4]. This definition, while comprehensive, understates the strategic imperative that has emerged in recent years.
The economic landscape of 2025 presents unique challenges that make integrated marketing approaches not just beneficial, but essential for survival. McKinsey’s latest research indicates that economic uncertainty, unpredictable consumer behavior, fluctuating markets, and rapid geopolitical change have created a daunting environment for business leaders [2]. In this context, fragmented marketing efforts become not just inefficient, but potentially destructive to brand coherence and customer trust.
The scale of digital marketing investment underscores its critical importance. Industry data shows that the global digital advertising and marketing market reached $667 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to $786.2 billion by 2026 [5]. This massive investment demands strategic coordination to ensure maximum return on investment and sustainable competitive advantage.
The Fragmentation Crisis in Modern Organizations
A significant challenge facing modern organizations is the fragmentation of customer ownership across multiple departments and executive roles. McKinsey’s analysis of Fortune 500 companies reveals a troubling trend: the average size of executive teams increased by 50% between 2020 and 2022 alone [2]. This expansion has led to a diffusion of responsibility where, as McKinsey researchers note, “when everyone is responsible for acquiring customers and driving growth, no one is.”
The consequences of this fragmentation are measurable and significant. Companies have added new executive roles such as chief digital officer, chief commercial officer, and chief data officer in response to evolving market demands. However, this proliferation of roles has resulted in what McKinsey describes as “a choppy customer journey, with customers receiving different messages from different departments because each executive looks at the customer through a different lens” [2].
Perhaps most concerning is the decline in chief marketing officer representation at the highest levels of corporate leadership. According to Spencer Stuart, the number of CMOs at Fortune 500 companies declined from 71% in 2023 to 66% in 2024 [2]. Forrester Research reports an even more dramatic figure, indicating that only 63% of Fortune 500 companies currently have CMOs [2]. This trend suggests that at precisely the moment when integrated marketing leadership is most needed, many organizations are moving in the opposite direction.
Government and Public Sector Recognition
The importance of holistic marketing approaches has gained recognition even within government and public sector organizations. Deloitte’s 2023 Government & Public Services Marketing Trends report identifies “a solid shift toward people-centric marketing and communication strategies” driven by the need for government agencies to influence and shape resident behavior while building deeper trust [6].
This shift reflects broader recognition that effective communication and engagement require integrated approaches. The report emphasizes that successful government marketing involves “innovative strategies that are rooted in data and creativity,” focusing on transparent communication, reliable results, and prioritizing the resident experience [6]. These principles directly parallel the requirements for effective holistic marketing in the private sector.
The U.S. government’s emphasis on digital marketing effectiveness is further evidenced by Executive Order 14058, “Transforming Federal Customer Experience and Service Delivery to Rebuild Trust in Government,” issued in December 2021 [7]. This order mandates improved customer experience across federal agencies, recognizing that fragmented communication approaches undermine public trust and effectiveness.
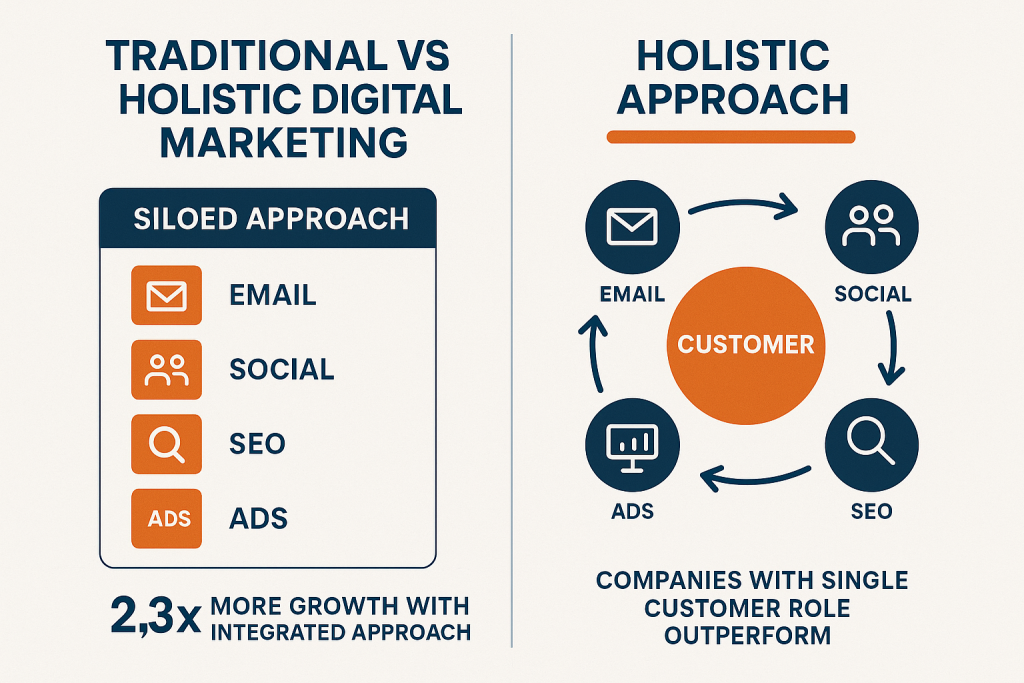
Understanding Marketing Fragmentation and Its Impact
The fragmentation of marketing responsibilities represents one of the most significant barriers to effective customer engagement in modern organizations. This fragmentation manifests in multiple dimensions: organizational structure, technology systems, data management, and strategic decision-making processes. Understanding these dimensions is crucial for developing effective holistic marketing strategies.
Organizational Structure Challenges
McKinsey’s research reveals that the rush to modernize and meet customers across multiple touchpoints has resulted in organizational fragmentation that undermines rather than enhances customer experience [2]. The proliferation of specialized roles—while individually valuable—has created coordination challenges that many organizations struggle to address effectively.
The data supporting this concern is compelling. McKinsey’s analysis of Fortune 500 companies demonstrates that organizations with a single customer- or growth-oriented role in their executive committee (such as a CMO, chief commercial officer, chief revenue officer, or chief growth officer) achieve up to 2.3 times more growth than those with multiple, potentially competing roles [2]. This finding suggests that clarity of responsibility and unified strategic direction significantly outweigh the theoretical benefits of specialized expertise.
However, the challenge extends beyond simple organizational charts. Even when companies have designated a single customer-focused executive, McKinsey notes that “that doesn’t necessarily mean they have also given that person full ownership and responsibility for the customer” [2]. This distinction between title and authority represents a critical implementation challenge that many organizations fail to address adequately.
The Measurement and Attribution Problem
One of the most significant consequences of marketing fragmentation is the difficulty in measuring and attributing marketing impact across channels. HubSpot’s 2025 State of Marketing Report reveals that 87% of marketers report that data is their company’s most under-utilized asset [3]. This statistic becomes even more concerning when considered alongside Gartner research showing that 26% of marketers report that decision-makers do not review the information provided by marketing analytics teams, and 24% report that decision-makers reject analytics recommendations in favor of gut instincts [8].
The measurement challenge is compounded by the complexity of modern customer journeys. With consumers using multiple channels for product research and purchase—more than 80% according to industry research [2]—traditional attribution models become inadequate. Single-touch attribution models, which assign credit to either the first or last interaction, fail to capture the cumulative impact of integrated marketing efforts.
This measurement gap creates a vicious cycle where marketing teams struggle to demonstrate value, leading to reduced investment and further fragmentation of efforts. As one CFO quoted in McKinsey’s research noted, “CFOs often view marketing as a cost center rather than an investment” [2]. This perspective, while understandable given measurement challenges, undermines the strategic potential of integrated marketing approaches.
Technology Integration Barriers
The technology landscape presents both opportunities and challenges for holistic marketing implementation. While advanced marketing technology stacks offer unprecedented capabilities for customer data integration and campaign coordination, many organizations struggle with what industry experts term “martech sprawl”—the proliferation of disconnected marketing technology tools that create rather than solve integration challenges.
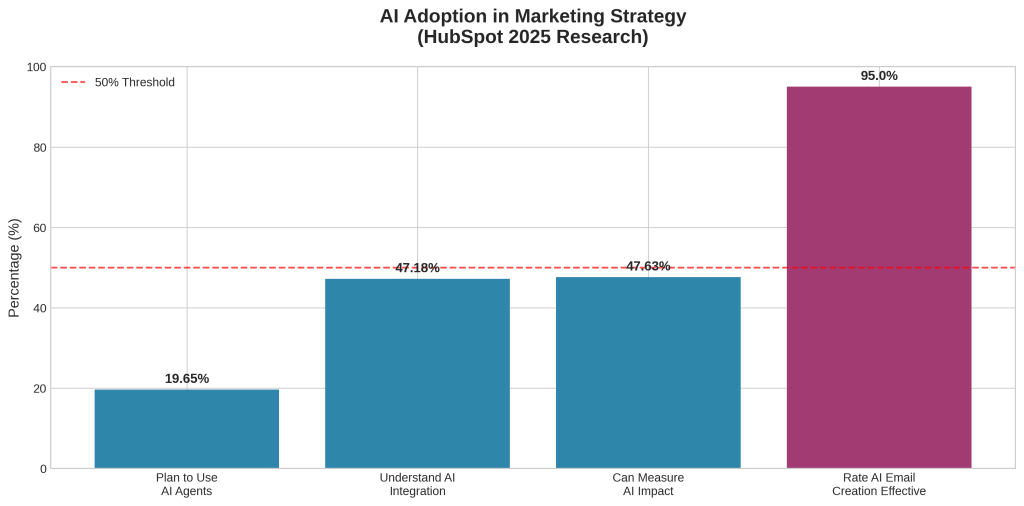
HubSpot’s research indicates that 47.18% of marketers say they understand how to incorporate AI into their marketing strategy, while 47.63% say they know how to measure AI’s impact [3]. These relatively low percentages suggest that even as organizations invest in advanced technologies, many lack the strategic framework necessary to leverage these tools effectively within a holistic marketing approach.
The challenge is particularly acute in data integration and customer identity resolution. Without unified customer data platforms, organizations struggle to create the single customer view that is essential for holistic marketing. This technical fragmentation mirrors and reinforces organizational fragmentation, creating compound barriers to effective integration.
| Fragmentation Type | Impact on Performance | Measurement Challenge | Solution Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organizational Structure | 2.3x lower growth potential | Unclear accountability | Single customer-focused executive |
| Data and Analytics | 87% under-utilization of data assets | 26% of insights ignored by leadership | Integrated measurement framework |
| Technology Systems | Disconnected customer experience | 47% lack AI measurement capability | Unified customer data platform |
| Channel Coordination | Inconsistent messaging across touchpoints | Attribution across 10+ touchpoints | Cross-channel campaign orchestration |
The Customer Experience Consequence
The ultimate consequence of marketing fragmentation is degraded customer experience. When different departments deliver different messages through different channels, customers receive what McKinsey describes as “a choppy customer journey” [2]. This inconsistency not only confuses customers but also undermines brand trust and reduces conversion effectiveness.
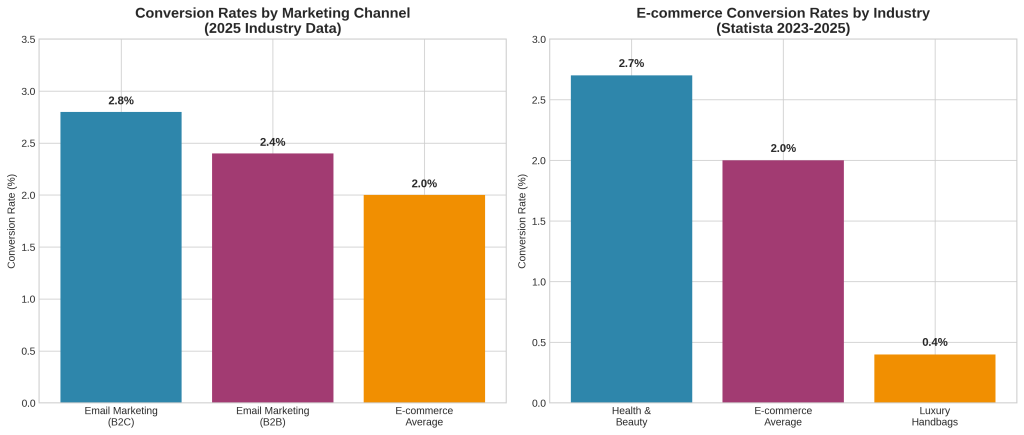
The impact on customer experience is measurable through conversion rate data. Industry research shows that the average conversion rate across all e-commerce sites remains under 2% [3], with significant variation by industry—from 2.7% for health and beauty to just 0.4% for luxury handbags [3]. While multiple factors influence these rates, the consistency of messaging and experience across touchpoints plays a crucial role in conversion optimization.
Email marketing provides a compelling example of how integration can improve performance. Segmented emails drive 30% more opens and 50% more clickthroughs than unsegmented ones [3]. This improvement demonstrates the value of coordinated, data-driven approaches that consider customer behavior across multiple touchpoints rather than treating each channel in isolation.
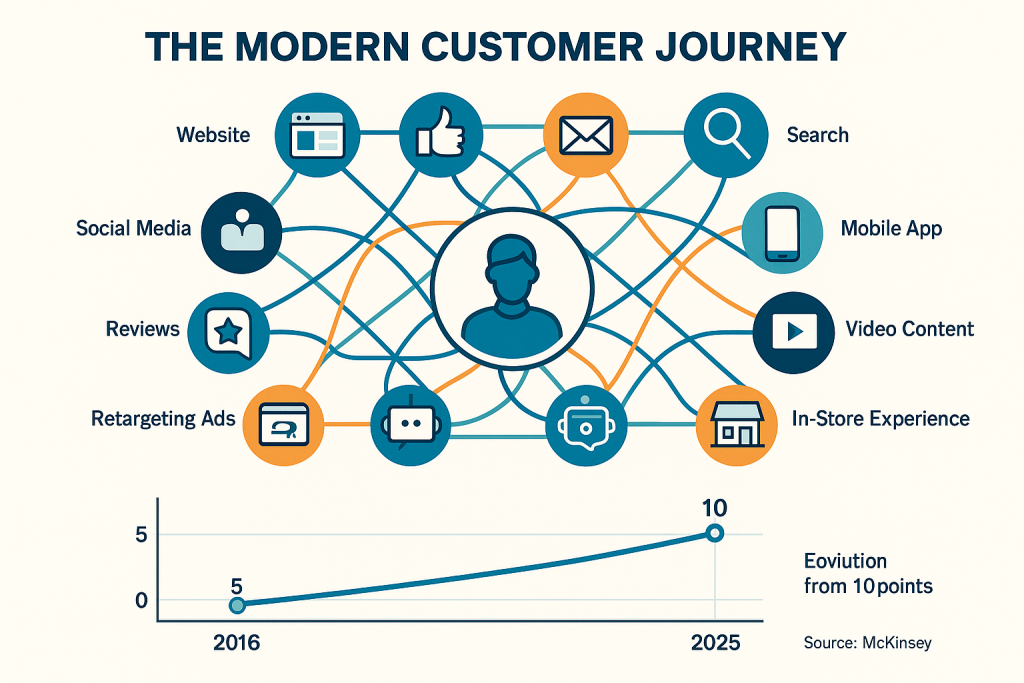
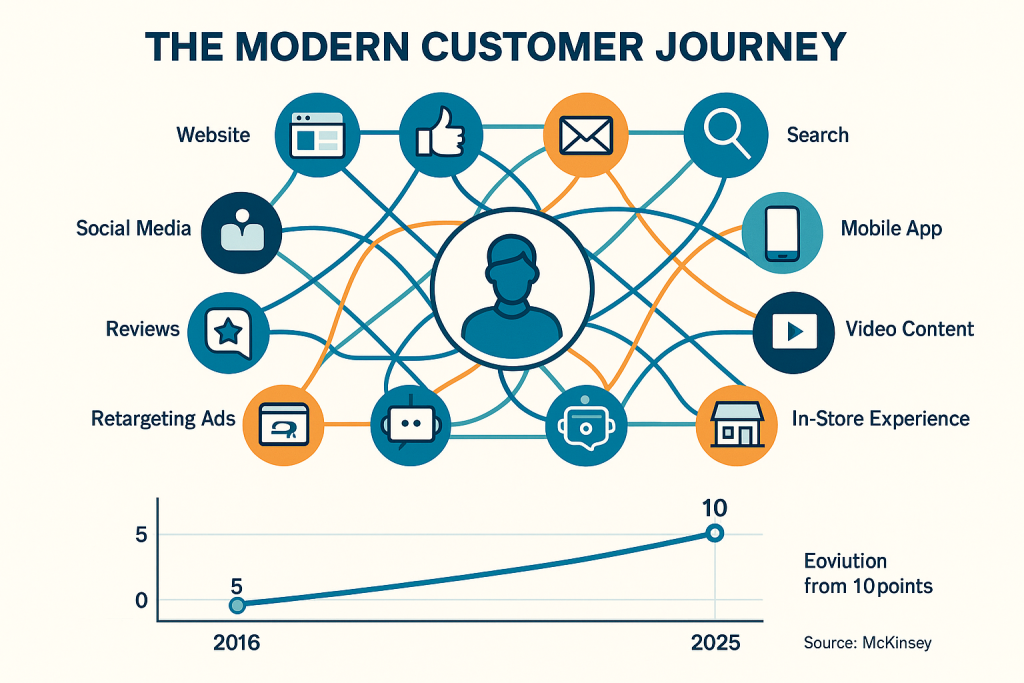
The Evolution of Customer Journey Complexity
The modern customer journey has evolved into a complex, multi-touchpoint experience that challenges traditional linear marketing models. McKinsey’s research documents a fundamental shift in B2B buyer behavior: customers now use an average of 10 points of interaction during a typical sales journey, compared to only 5 in 2016 [2]. This 100% increase in touchpoint complexity represents more than a quantitative change—it reflects a qualitative transformation in how customers research, evaluate, and purchase products and services.
The Omnichannel Reality
The concept of omnichannel customer experience has evolved from marketing buzzword to operational necessity. Research indicates that more than 80% of consumers use multiple channels for product research or purchase [2]. This behavior pattern creates both opportunities and challenges for marketers seeking to create cohesive brand experiences.
The omnichannel reality extends beyond simple multi-channel presence. Customers expect seamless transitions between channels, consistent messaging across touchpoints, and personalized experiences that acknowledge their previous interactions regardless of channel. This expectation places significant demands on organizational capabilities, requiring not just technological integration but also strategic coordination across all customer-facing functions.
The U.S. International Trade Administration recognizes this complexity in its guidance for businesses, noting that digital marketing should be “used in conjunction with planned calls to action” and emphasizing the importance of “measurable traffic towards your website and other online sales channels” [4]. This government perspective underscores the strategic importance of coordinated, multi-channel approaches even for basic business development activities.
Touchpoint Proliferation and Its Implications
The proliferation of customer touchpoints reflects broader changes in media consumption, technology adoption, and consumer behavior. Modern customers interact with brands through traditional channels such as websites, email, and search, but also through newer touchpoints including social media platforms, mobile applications, video content, online reviews, chatbots, retargeting advertisements, and even in-store experiences that integrate digital elements.
Each additional touchpoint creates both opportunity and complexity. On the positive side, more touchpoints provide more opportunities to engage customers, deliver value, and influence purchase decisions. However, each touchpoint also represents a potential point of failure where inconsistent messaging, poor user experience, or technical problems can damage brand perception and reduce conversion likelihood.
The challenge is compounded by the non-linear nature of modern customer journeys. Unlike traditional funnel models that assumed customers moved through predictable stages from awareness to purchase, modern customers move fluidly between touchpoints, often revisiting earlier stages or jumping directly to purchase decisions based on immediate needs or compelling offers.
Industry-Specific Journey Variations
Customer journey complexity varies significantly across industries, reflecting differences in purchase consideration time, product complexity, and regulatory requirements. Conversion rate data illustrates these variations: health and beauty products achieve 2.7% conversion rates, while luxury handbags achieve only 0.4% [3]. These differences reflect varying customer journey lengths and complexity levels.
B2B customer journeys tend to be longer and more complex than B2C journeys, involving multiple decision-makers, extended evaluation periods, and higher stakes purchase decisions. However, B2C journeys in certain categories—particularly high-involvement purchases like automobiles, real estate, or financial services—can be equally complex and extended.
The implications for holistic marketing strategy are significant. Organizations must develop customer journey maps that accurately reflect their specific industry dynamics while maintaining flexibility to adapt to evolving customer behaviors. This requires ongoing research, testing, and optimization rather than static strategic planning.
The Role of Digital Transformation
Digital transformation has been both a driver and enabler of customer journey complexity. Forrester research indicates that 15% of surveyed companies have prioritized digital transformation, while Gartner reports that digital transformation is an organizational priority for 87% of senior business leaders [9]. This widespread focus on digital transformation reflects recognition that customer expectations have fundamentally shifted.
However, digital transformation efforts often focus on individual touchpoints or channels rather than the holistic customer experience. Organizations may excel at social media engagement while struggling with email marketing integration, or they may have sophisticated e-commerce platforms that don’t connect effectively with in-store experiences. These gaps create the “choppy customer journey” that McKinsey identifies as a key challenge in modern marketing [2].
The solution requires what industry experts term “customer experience orchestration”—the strategic coordination of all touchpoints to create seamless, valuable customer experiences. This orchestration goes beyond technology integration to include organizational alignment, process standardization, and cultural change management.
Measurement and Attribution Challenges
The complexity of modern customer journeys creates significant challenges for marketing measurement and attribution. Traditional last-click attribution models become inadequate when customers interact with brands across 10 or more touchpoints before making purchase decisions. Similarly, first-click attribution fails to account for the nurturing and conversion activities that occur throughout extended customer journeys.
Advanced attribution models, including algorithmic and data-driven approaches, offer improved accuracy but require sophisticated analytics capabilities and clean, integrated data. Many organizations struggle with these requirements, leading to what HubSpot identifies as the under-utilization of data assets [3].
The measurement challenge extends beyond attribution to include customer lifetime value calculation, cross-channel performance optimization, and return on investment analysis. Organizations need measurement frameworks that can capture the cumulative impact of integrated marketing efforts while providing actionable insights for ongoing optimization.
Core Components of Holistic Digital Marketing
Effective holistic digital marketing requires the strategic integration of multiple components that work synergistically to create superior customer experiences and business outcomes. Based on analysis of authoritative research and industry best practices, eight core components emerge as essential for comprehensive digital marketing integration: customer-centric strategy foundation, content marketing and SEO integration, social media engagement, email marketing automation, paid advertising coordination, data analytics and measurement, customer relationship management, and emerging technology adoption.
Customer-Centric Strategy Foundation
The foundation of holistic digital marketing is a genuinely customer-centric strategic approach that places customer needs, behaviors, and outcomes at the center of all marketing decisions. This approach goes beyond customer segmentation or persona development to encompass what McKinsey terms “customer experience orchestration”—the strategic coordination of all touchpoints to create seamless, valuable customer experiences [2].
Customer-centricity requires organizations to shift from product-focused or channel-focused thinking to customer journey-focused thinking. This shift has measurable implications: companies with strong customer experience programs achieve revenue growth rates 4-8% above their market average, according to Bain & Company research. However, achieving genuine customer-centricity requires organizational changes that extend far beyond marketing departments.
The U.S. International Trade Administration emphasizes the importance of understanding your audience and “how they get information to help you determine achievable, measurable goals” [4]. This government guidance reflects broader recognition that effective marketing begins with deep customer understanding rather than channel or tactic selection.
Practical implementation of customer-centric strategy requires several key capabilities: comprehensive customer research and insights, detailed customer journey mapping, cross-functional collaboration processes, and continuous feedback and optimization mechanisms. Organizations that excel in these areas create sustainable competitive advantages that are difficult for competitors to replicate.
Content Marketing and SEO Integration
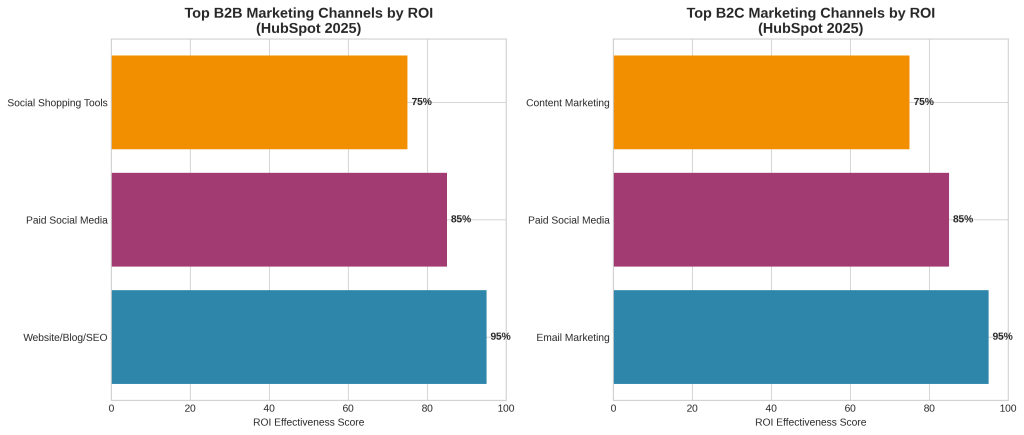
Content marketing and search engine optimization represent one of the most powerful combinations in holistic digital marketing when properly integrated. HubSpot’s 2025 research identifies website, blog, and SEO efforts as the top marketing channel driving ROI for B2B brands [3]. This finding reflects the compounding value of content that serves both immediate customer needs and long-term organic visibility.
Effective content marketing integration requires strategic alignment between content creation, search optimization, and customer journey stages. Content must serve multiple purposes simultaneously: attracting organic search traffic, educating and nurturing prospects, supporting sales conversations, and reinforcing brand positioning. This multi-purpose approach maximizes the return on content investment while creating more cohesive customer experiences.
The integration extends beyond keyword optimization to include content format diversification, distribution channel coordination, and performance measurement alignment. Modern content marketing encompasses blog posts, video content, infographics, podcasts, interactive tools, and other formats that serve different customer preferences and consumption contexts.
However, content marketing integration faces significant challenges. Many organizations struggle with content quality consistency, production scalability, and performance measurement across different content types and distribution channels. Success requires both strategic planning and operational excellence in content creation and distribution processes.
Social Media Engagement and Community Building
Social media engagement has evolved from a supplementary marketing activity to a core component of holistic digital marketing strategy. HubSpot research identifies paid social media content as the second-highest ROI channel for both B2B and B2C brands [3]. This performance reflects the unique capabilities of social media platforms for audience targeting, engagement, and conversion.
Effective social media integration requires coordination across multiple platforms, content types, and engagement strategies. Organizations must balance organic community building with paid advertising, brand awareness objectives with direct response goals, and platform-specific content with cross-platform consistency. This balance requires sophisticated strategic planning and execution capabilities.
The social media landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with new platforms, features, and advertising options emerging regularly. Video content has become particularly important, with TikTok projected to generate $33.1 billion in advertising revenue in 2025 [3]. Organizations must maintain strategic flexibility while building sustainable social media capabilities.
Community building represents a particularly valuable aspect of social media integration. Organizations that successfully build engaged communities around their brands create sustainable competitive advantages through increased customer loyalty, reduced acquisition costs, and enhanced brand advocacy. However, community building requires long-term commitment and authentic engagement rather than purely promotional approaches.
Email Marketing Automation and Personalization
Email marketing remains one of the most effective channels for customer engagement and conversion, achieving 2.8% conversion rates for B2C brands and 2.4% conversion rates for B2B brands [3]. For B2C organizations, email marketing ranks as the top ROI-driving channel [3]. These performance levels reflect email marketing’s unique capabilities for personalization, automation, and direct customer communication.
The effectiveness of email marketing increases significantly when integrated with other marketing channels and customer data sources. Segmented emails drive 30% more opens and 50% more clickthroughs than unsegmented ones [3]. This improvement demonstrates the value of data integration and customer insights in email marketing optimization.
Modern email marketing automation extends beyond simple drip campaigns to include behavioral triggers, dynamic content personalization, and cross-channel coordination. Advanced email marketing systems can trigger emails based on website behavior, social media engagement, purchase history, and other customer actions, creating more relevant and timely communications.
However, email marketing faces increasing challenges from inbox competition, privacy regulations, and changing customer expectations. HubSpot research indicates that 59% of Americans say that most emails they receive are not useful to them [3]. This statistic underscores the importance of relevance, value, and strategic integration in email marketing programs.
Paid Advertising Coordination and Optimization
Paid advertising represents a critical component of holistic digital marketing, providing capabilities for precise audience targeting, immediate market entry, and scalable customer acquisition. However, the effectiveness of paid advertising depends heavily on its integration with other marketing channels and customer touchpoints.
The paid advertising landscape has become increasingly complex, with options spanning search advertising, social media advertising, display advertising, video advertising, and emerging formats such as connected TV and audio advertising. Video ad spending alone is projected to reach over $207.5 billion in 2025 and more than $268 billion by 2029 [3].
Effective paid advertising integration requires coordination across multiple platforms, campaign types, and optimization objectives. Organizations must balance brand awareness campaigns with direct response campaigns, prospecting efforts with retargeting campaigns, and short-term performance with long-term brand building. This coordination requires sophisticated campaign management and optimization capabilities.
Attribution and measurement represent particular challenges in paid advertising integration. With customers interacting across multiple touchpoints before converting, traditional last-click attribution models often undervalue the contribution of upper-funnel advertising activities. Organizations need advanced attribution models and measurement frameworks to optimize paid advertising within holistic marketing strategies.
Data Analytics and Customer Intelligence
Data analytics serves as the foundation for effective holistic digital marketing, providing the insights necessary for strategic decision-making, campaign optimization, and customer experience improvement. However, HubSpot research reveals that 87% of marketers report that data is their company’s most under-utilized asset [3]. This under-utilization represents a significant opportunity for organizations that can effectively leverage their data assets.
The challenge extends beyond data collection to include data integration, analysis, and activation. Many organizations collect vast amounts of customer data across multiple systems but struggle to create unified customer views or actionable insights. Gartner research indicates that 26% of marketers report that decision-makers do not review marketing analytics information, while 24% report that decision-makers reject analytics recommendations in favor of gut instincts [8].
Effective data analytics integration requires several key capabilities: unified customer data platforms, advanced analytics and modeling capabilities, real-time reporting and dashboards, and organizational processes for data-driven decision making. Organizations that excel in these areas can optimize marketing performance continuously and respond quickly to changing market conditions.
The emergence of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies offers new opportunities for data analytics integration. However, HubSpot research indicates that only 47.18% of marketers understand how to incorporate AI into their marketing strategy, and 47.63% know how to measure AI’s impact [3]. These relatively low percentages suggest significant opportunities for organizations that can effectively leverage AI capabilities.
| Component | Primary Function | Integration Points | Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer-Centric Strategy | Foundation and coordination | All components | Customer satisfaction, retention |
| Content Marketing & SEO | Organic visibility and education | Social media, email, paid ads | Organic traffic, engagement |
| Social Media Engagement | Community building and awareness | Content, email, paid advertising | Engagement rate, reach |
| Email Marketing | Direct communication and nurturing | CRM, content, social media | 2.8% B2C, 2.4% B2B conversion |
| Paid Advertising | Targeted acquisition and retargeting | All channels for attribution | ROAS, customer acquisition cost |
| Data Analytics | Insights and optimization | All components for measurement | Data utilization, decision speed |
Channel Performance and ROI Analysis
Understanding the relative performance and return on investment of different marketing channels is crucial for effective resource allocation and strategic planning within holistic digital marketing frameworks. However, channel performance analysis in integrated marketing environments requires sophisticated measurement approaches that account for cross-channel interactions, attribution complexity, and varying optimization objectives across different business contexts.
B2B vs. B2C Channel Performance Differences
HubSpot’s 2025 State of Marketing Report reveals significant differences in channel effectiveness between B2B and B2C organizations, reflecting fundamental differences in customer behavior, purchase processes, and decision-making dynamics [3]. For B2B brands, the top three marketing channels driving ROI are: (1) website, blog, and SEO efforts, (2) paid social media content, and (3) social media shopping tools. In contrast, B2C brands achieve the highest ROI from: (1) email marketing, (2) paid social media content, and (3) content marketing.
These differences reflect the distinct characteristics of B2B and B2C customer journeys. B2B customers typically engage in extended research processes, often spending significant time on company websites and educational content before engaging with sales teams. The prominence of SEO and content marketing in B2B ROI rankings reflects this research-intensive behavior pattern.
B2C customers, while also conducting research, often have shorter consideration periods and more direct paths to purchase. The effectiveness of email marketing for B2C brands reflects the channel’s capabilities for personalized communication, promotional offers, and direct conversion facilitation. Email marketing achieves 2.8% conversion rates for B2C brands compared to 2.4% for B2B brands [3], demonstrating its particular effectiveness in consumer contexts.
However, these channel performance differences should not be interpreted as prescriptive recommendations for channel selection. Effective holistic marketing requires understanding how channels work together rather than optimizing individual channels in isolation. The synergistic effects of integrated channel strategies often exceed the sum of individual channel contributions.
Video Marketing Performance and Growth Trajectory
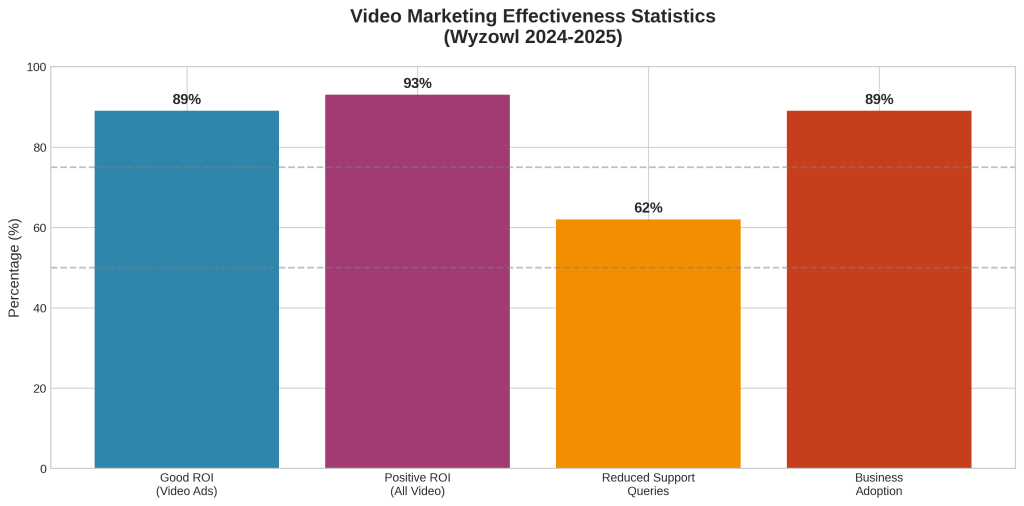
Video marketing has emerged as one of the most effective and rapidly growing components of digital marketing strategies. Research from Wyzowl indicates that 89% of video marketers report that video advertising provides good ROI, while 93% of video marketers report that video gives them positive ROI [3]. These high satisfaction rates reflect video’s unique capabilities for engagement, storytelling, and conversion.
The business adoption of video marketing continues to accelerate, with 89% of businesses currently using video marketing and 68% of non-adopters planning to start in 2025 [3]. This widespread adoption reflects both the effectiveness of video content and the increasing accessibility of video production and distribution technologies.
The financial scale of video marketing investment underscores its strategic importance. Video ad spending is projected to reach over $207.5 billion in 2025 and more than $268 billion by 2029 [3]. TikTok alone is projected to generate $33.1 billion in advertising revenue in 2025 [3], demonstrating the rapid growth of short-form video advertising.
Beyond direct advertising revenue, video marketing provides operational benefits that contribute to overall marketing efficiency. Wyzowl research indicates that 62% of video marketers say video has decreased the number of support queries they receive [3]. This reduction in support volume demonstrates video’s effectiveness for customer education and self-service enablement.
Conversion Rate Analysis Across Channels and Industries
Conversion rate analysis provides crucial insights into channel effectiveness and optimization opportunities within holistic marketing strategies. Industry data reveals significant variation in conversion performance across different channels and industry sectors, reflecting the complex interplay of customer behavior, product characteristics, and competitive dynamics.
Email marketing demonstrates consistently strong conversion performance across different business contexts, achieving 2.8% conversion rates for B2C brands and 2.4% conversion rates for B2B brands [3]. These rates significantly exceed the average e-commerce conversion rate of under 2% [3], demonstrating email marketing’s effectiveness for qualified audience engagement.
However, conversion rates vary dramatically across industry sectors, reflecting differences in product complexity, purchase consideration time, and customer behavior patterns. Health and beauty products achieve the highest e-commerce conversion rates at 2.7%, while luxury handbags achieve only 0.4% [3]. These differences highlight the importance of industry-specific benchmarking and optimization strategies.
The variation in conversion rates also reflects different stages of customer journey optimization. Industries with higher conversion rates often have more mature digital marketing capabilities, better customer experience design, and more effective integration between marketing and sales processes. Organizations in lower-converting industries can often achieve significant improvements through holistic marketing optimization.
Segmentation significantly improves conversion performance across all channels. HubSpot research demonstrates that segmented emails drive 30% more opens and 50% more clickthroughs than unsegmented ones [3]. This improvement illustrates the value of customer data integration and personalization capabilities within holistic marketing frameworks.
Attribution Challenges and Multi-Touch Analysis
Accurate attribution analysis represents one of the most significant challenges in channel performance measurement, particularly within holistic marketing frameworks where customers interact with multiple touchpoints before converting. Traditional single-touch attribution models—whether first-click or last-click—fail to capture the cumulative impact of integrated marketing efforts.
The complexity of modern customer journeys exacerbates attribution challenges. With B2B customers using an average of 10 touchpoints during their buying journey [2], and more than 80% of consumers using multiple channels for product research or purchase [2], single-touch attribution models become increasingly inadequate for strategic decision-making.
Advanced attribution models, including algorithmic attribution, data-driven attribution, and marketing mix modeling, offer improved accuracy but require sophisticated analytics capabilities and clean, integrated data. Many organizations struggle with these requirements, contributing to what HubSpot identifies as the under-utilization of data assets [3].
The attribution challenge extends beyond technical measurement to include organizational alignment and decision-making processes. Gartner research indicates that 26% of marketers report that decision-makers do not review marketing analytics information, while 24% report that decision-makers reject analytics recommendations in favor of gut instincts [8]. These statistics suggest that attribution challenges are as much organizational as technical.
Emerging Channel Performance Trends
Several emerging trends are reshaping channel performance dynamics and creating new opportunities for holistic marketing optimization. Artificial intelligence and automation technologies are enabling more sophisticated personalization and optimization capabilities across all channels.
HubSpot research indicates that 19.65% of marketers plan to use AI agents to automate marketing in 2025 [3]. While this percentage may seem modest, it represents early adoption of technologies that are likely to become mainstream rapidly. Organizations that develop AI capabilities early may achieve sustainable competitive advantages in channel optimization and customer experience delivery.
The effectiveness of AI-powered marketing tools is already demonstrable in specific applications. HubSpot research shows that 95% of marketers who use generative AI for email creation rate it as “effective,” with 54% rating it as “very effective” [3]. Additionally, 43% of marketers who use generative AI say it’s most helpful for creating email copy [3].
However, AI adoption faces significant challenges related to understanding, measurement, and integration. Only 47.18% of marketers say they understand how to incorporate AI into their marketing strategy, and 47.63% say they know how to measure AI’s impact [3]. These relatively low percentages suggest that while AI offers significant potential, most organizations are still in early stages of AI integration.
| Channel | B2B Performance | B2C Performance | Optimization Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Email Marketing | 2.4% conversion rate | 2.8% conversion rate, #1 ROI | Segmentation (+50% CTR) |
| Website/Blog/SEO | #1 ROI channel | #3 ROI channel | Content integration |
| Paid Social Media | #2 ROI channel | #2 ROI channel | Cross-platform coordination |
| Video Marketing | 93% positive ROI | 89% good ROI | Multi-format strategy |
| E-commerce Average | Varies by industry | Under 2% conversion | Journey optimization |
Technology and AI in Integrated Marketing
The integration of artificial intelligence and advanced marketing technologies represents both the greatest opportunity and the most significant challenge in modern holistic digital marketing. While these technologies offer unprecedented capabilities for personalization, automation, and optimization, their effective implementation requires strategic planning, organizational change, and sophisticated measurement frameworks that many organizations struggle to develop.
Current State of AI Adoption in Marketing
HubSpot’s 2025 research reveals a complex picture of AI adoption in marketing, with significant opportunities for organizations that can effectively leverage these technologies. Currently, 19.65% of marketers plan to use AI agents to automate marketing in 2025 [3]. While this percentage may appear modest, it represents early adoption of technologies that are likely to become mainstream rapidly as capabilities improve and costs decrease.
The effectiveness of AI applications in marketing is already demonstrable in specific use cases. HubSpot research shows that 95% of marketers who use generative AI for email creation rate it as “effective,” with 54% rating it as “very effective” [3]. This high satisfaction rate suggests that AI technologies can deliver immediate value when applied to appropriate marketing tasks.
Email marketing represents the most mature application of AI in marketing, with 43% of marketers who use generative AI saying it’s most helpful for creating email copy [3]. This application leverages AI’s strengths in content generation while operating within the structured environment of email marketing campaigns, making it relatively straightforward to implement and measure.
However, broader AI adoption faces significant barriers related to understanding, measurement, and strategic integration. Only 47.18% of marketers say they understand how to incorporate AI into their marketing strategy, and 47.63% say they know how to measure AI’s impact [3]. These relatively low percentages suggest that while AI offers significant potential, most organizations are still in early stages of AI integration.
Data Integration and Customer Intelligence Platforms
The foundation of effective AI implementation in holistic marketing is robust data integration and customer intelligence capabilities. However, HubSpot research reveals that 87% of marketers report that data is their company’s most under-utilized asset [3]. This under-utilization represents a significant barrier to AI effectiveness and holistic marketing optimization.
The challenge extends beyond data collection to include data quality, integration, and activation. Many organizations collect vast amounts of customer data across multiple systems but struggle to create unified customer views or actionable insights. This fragmentation undermines both AI effectiveness and holistic marketing coordination.
Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) and similar technologies offer solutions for data integration challenges, but their implementation requires significant technical and organizational capabilities. Successful CDP implementation involves not just technology deployment but also data governance, privacy compliance, and cross-functional collaboration processes.
The measurement challenge is compounded by the complexity of modern customer journeys and the limitations of traditional attribution models. Organizations need advanced analytics capabilities that can capture cross-channel interactions, long-term customer value, and the cumulative impact of integrated marketing efforts. These requirements often exceed the capabilities of traditional marketing analytics tools.
Marketing Automation and Orchestration
Marketing automation technologies enable the coordination and optimization of complex, multi-channel marketing campaigns at scale. However, effective automation requires strategic planning that goes beyond individual channel optimization to encompass customer journey orchestration and cross-channel coordination.
The most effective marketing automation implementations focus on customer experience optimization rather than operational efficiency alone. This approach requires understanding customer behavior patterns, preference signals, and engagement contexts across multiple touchpoints. Organizations that excel in this area create more relevant, timely, and valuable customer experiences.
However, marketing automation also presents risks related to over-automation, reduced personalization, and customer experience degradation. The challenge is balancing efficiency gains with authentic customer engagement and relationship building. This balance requires ongoing testing, optimization, and human oversight of automated processes.
Cross-channel orchestration represents the most advanced application of marketing automation, enabling coordinated campaigns that adapt to customer behavior across multiple touchpoints. This capability requires sophisticated technology integration, data management, and strategic planning that many organizations struggle to achieve effectively.
Privacy, Compliance, and Ethical Considerations
The integration of AI and advanced marketing technologies must address growing privacy regulations, ethical considerations, and customer expectations regarding data use and personalization. These requirements create both constraints and opportunities for holistic marketing strategies.
Privacy regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and emerging state-level privacy laws require organizations to implement privacy-by-design approaches in their marketing technology implementations. This requirement affects data collection, storage, processing, and activation across all marketing channels and touchpoints.
However, privacy compliance can also create competitive advantages for organizations that implement transparent, customer-centric data practices. Customers increasingly prefer brands that demonstrate responsible data stewardship and provide clear value in exchange for personal information. Organizations that excel in this area can build stronger customer relationships and sustainable competitive advantages.
Ethical AI considerations extend beyond legal compliance to include fairness, transparency, and accountability in automated decision-making processes. Marketing AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate biases, exclude certain customer segments, or make decisions that customers perceive as unfair or manipulative. Organizations need governance frameworks that address these risks proactively.
Implementation Challenges and Success Factors
The implementation of AI and advanced marketing technologies faces several common challenges that organizations must address to achieve successful holistic marketing integration. These challenges span technical, organizational, and strategic dimensions.
Technical challenges include data quality and integration issues, system compatibility problems, and the complexity of managing multiple technology vendors and platforms. Many organizations underestimate the technical requirements for effective AI implementation, leading to disappointing results and reduced confidence in technology investments.
Organizational challenges include skills gaps, change management resistance, and the need for new processes and governance frameworks. AI implementation often requires new roles, responsibilities, and collaboration patterns that can be difficult to establish within existing organizational structures.
Strategic challenges include the need for clear objectives, appropriate success metrics, and long-term commitment to technology development and optimization. Many organizations approach AI implementation tactically rather than strategically, limiting their ability to achieve sustainable competitive advantages.
Success factors for AI implementation in holistic marketing include executive leadership commitment, cross-functional collaboration, customer-centric design principles, and continuous learning and optimization approaches. Organizations that excel in these areas are more likely to achieve meaningful business results from their technology investments.
| Implementation Stage | Key Activities | Success Metrics | Common Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foundation | Data integration, governance, privacy compliance | Data quality scores, integration completeness | 87% data under-utilization |
| Pilot Implementation | Email AI, basic automation, testing | 95% effectiveness rating for email AI | 47% lack strategic understanding |
| Scale and Integration | Cross-channel orchestration, advanced analytics | Customer experience improvement, ROI | 47% can’t measure AI impact |
| Optimization | Continuous learning, strategic refinement | Competitive advantage, customer loyalty | Organizational change management |
Visual Framework and Implementation Models
Effective holistic digital marketing requires visual frameworks and implementation models that help organizations understand complex relationships, coordinate activities, and measure progress toward strategic objectives. These frameworks serve both strategic planning and operational coordination functions, providing shared mental models that enable cross-functional collaboration and decision-making.
The Customer-Centric Integration Model
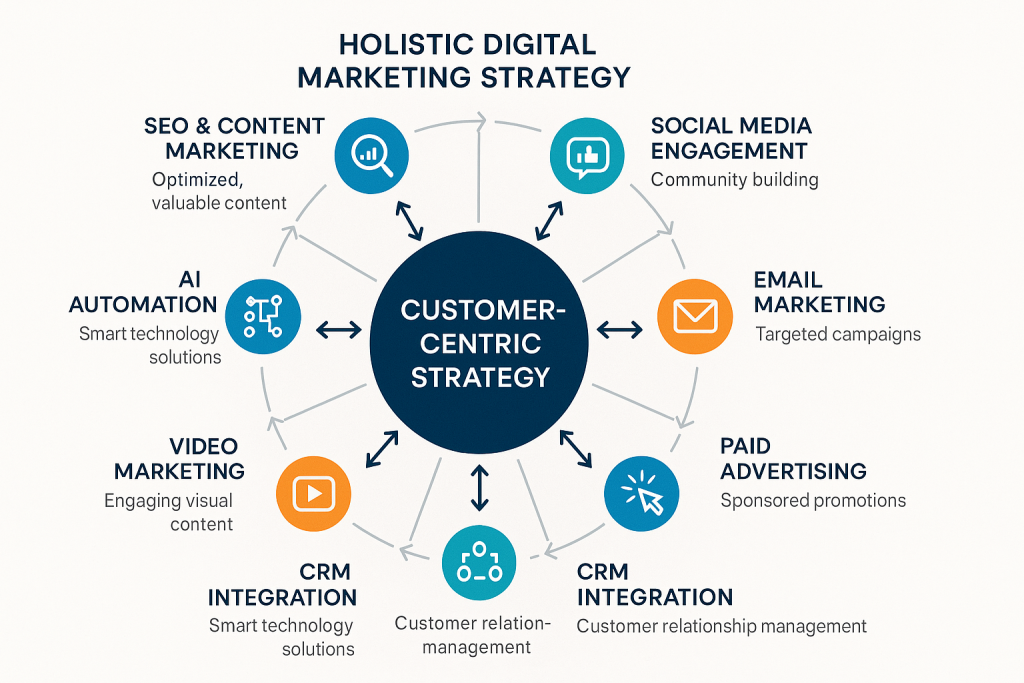
The customer-centric integration model places customer needs, behaviors, and outcomes at the center of all marketing activities, with eight core components arranged around this central focus. This model reflects the fundamental principle that effective holistic marketing begins with deep customer understanding rather than channel or technology selection.
The eight core components—SEO and content marketing, social media engagement, email marketing, paid advertising, video marketing, AI automation, CRM integration, and data analytics—are interconnected through customer data, shared objectives, and coordinated execution. The model emphasizes that success depends not on individual component performance but on the synergistic effects of integrated implementation.
This framework addresses the fragmentation challenges identified in McKinsey research by providing a clear structure for coordination and accountability. Organizations can use this model to assess their current capabilities, identify integration gaps, and plan systematic improvements that enhance customer experience and business results.
The customer-centric approach also addresses the measurement challenges that plague many marketing organizations. By focusing on customer outcomes rather than channel metrics, organizations can develop measurement frameworks that capture the cumulative impact of integrated marketing efforts while providing actionable insights for optimization.
The Traditional vs. Holistic Comparison Framework
The comparison between traditional, siloed approaches and holistic, integrated approaches provides a powerful visual representation of the strategic choice facing modern marketing organizations. This framework illustrates both the structural differences and the performance implications of different organizational approaches.
Traditional siloed approaches organize marketing activities by channel or function, with limited coordination between different areas. This structure often reflects organizational history, budget allocation processes, and individual expertise areas. However, McKinsey research demonstrates that this approach significantly limits growth potential, with integrated approaches achieving 2.3 times more growth [2].
Holistic integrated approaches organize marketing activities around customer needs and journey stages, with extensive coordination between different channels and functions. This structure requires more sophisticated planning and execution capabilities but delivers superior customer experiences and business results.
The framework helps organizations understand that the choice between siloed and integrated approaches is not merely tactical but strategic, with significant implications for competitive positioning, customer relationships, and long-term business success.
Customer Journey Complexity Visualization
The modern customer journey visualization illustrates the dramatic increase in touchpoint complexity that has occurred over the past decade. This framework helps organizations understand why traditional linear marketing models have become inadequate and why holistic approaches are necessary for effective customer engagement.
The visualization shows customers at the center of a complex network of touchpoints including websites, social media, email, search, mobile applications, video content, online reviews, chatbots, retargeting advertisements, and in-store experiences. The interconnected nature of these touchpoints reflects the non-linear, multi-channel behavior patterns that characterize modern customer journeys.
The timeline component of the visualization demonstrates the evolution from 5 touchpoints in 2016 to 10 touchpoints in 2025, based on McKinsey research [2]. This 100% increase in complexity underscores the urgency of developing holistic marketing capabilities that can coordinate effectively across multiple touchpoints.
Organizations can use this framework to map their own customer journeys, identify coordination gaps, and prioritize integration efforts that will have the greatest impact on customer experience and business results.
Implementation Roadmap and Maturity Model
The implementation roadmap provides a structured approach for organizations to develop holistic marketing capabilities systematically. This framework recognizes that holistic marketing transformation is a complex, multi-stage process that requires careful planning, resource allocation, and change management.
The roadmap includes four primary stages: foundation building, pilot implementation, scale and integration, and optimization and innovation. Each stage has specific objectives, activities, success metrics, and prerequisites that guide organizations through the transformation process.
Foundation building focuses on establishing the organizational, technical, and strategic prerequisites for holistic marketing. This stage includes customer research and journey mapping, data integration and governance, organizational alignment, and measurement framework development. Success in this stage is measured by data quality, organizational readiness, and strategic clarity.
Pilot implementation involves testing integrated approaches in controlled environments to validate strategies, refine processes, and build organizational confidence. This stage typically focuses on high-impact, low-risk integration opportunities such as email and content marketing coordination or social media and paid advertising alignment.
Scale and integration expand successful pilot approaches across all marketing channels and customer touchpoints. This stage requires sophisticated project management, change management, and performance monitoring capabilities. Success is measured by customer experience improvement, operational efficiency gains, and business result enhancement.
Optimization and innovation focus on continuous improvement, advanced capability development, and competitive advantage building. This stage involves advanced analytics, AI implementation, and strategic innovation that creates sustainable differentiation in the marketplace.
Strategic Implementation Roadmap
Implementing holistic digital marketing requires a systematic, phased approach that addresses organizational, technical, and strategic challenges while building sustainable capabilities for long-term competitive advantage. The following roadmap provides a structured framework for organizations to develop integrated marketing capabilities, based on analysis of successful implementations and industry best practices.
Phase 1: Foundation and Assessment (Months 1-3)
The foundation phase establishes the organizational, technical, and strategic prerequisites necessary for successful holistic marketing implementation. This phase requires significant investment in planning, research, and capability building, but provides the foundation for all subsequent implementation activities.
Customer research and journey mapping represent the most critical activities in this phase. Organizations must develop a comprehensive understanding of customer behaviors, preferences, and journey patterns across all touchpoints. This research should leverage both quantitative data analysis and qualitative customer insights to create detailed customer personas and journey maps that guide strategic decision-making.
The U.S. International Trade Administration emphasizes the importance of understanding “your audience and how they get information to help you determine achievable, measurable goals” [4]. This government guidance reflects the fundamental principle that effective marketing begins with customer understanding rather than channel or technology selection.
Data audit and integration planning address the technical prerequisites for holistic marketing. Organizations must assess their current data assets, identify integration requirements, and develop plans for creating unified customer views across all marketing channels. This assessment should address data quality, privacy compliance, and technical integration requirements.
Organizational alignment activities ensure that all stakeholders understand the strategic importance of holistic marketing and their roles in successful implementation. This includes executive leadership alignment, cross-functional team formation, and change management planning that addresses potential resistance and coordination challenges.
| Activity Category | Key Activities | Deliverables | Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Research | Journey mapping, persona development, touchpoint analysis | Customer journey maps, detailed personas | Research completeness, stakeholder alignment |
| Data Assessment | Data audit, integration planning, privacy compliance | Data integration roadmap, compliance framework | Data quality scores, integration feasibility |
| Organizational Alignment | Stakeholder engagement, team formation, change planning | Implementation team, change management plan | Leadership commitment, team readiness |
| Strategic Planning | Objective setting, measurement framework, resource planning | Strategic plan, measurement framework | Objective clarity, measurement readiness |
Phase 2: Pilot Implementation (Months 4-8)
The pilot implementation phase tests integrated marketing approaches in controlled environments to validate strategies, refine processes, and build organizational confidence. This phase focuses on high-impact, low-risk integration opportunities that can demonstrate value quickly while providing learning opportunities for broader implementation.
Email marketing and content integration represents an ideal pilot opportunity for most organizations. HubSpot research demonstrates that segmented emails drive 30% more opens and 50% more clickthroughs than unsegmented ones [3], providing clear value from integration efforts. Organizations can integrate email marketing with content marketing, social media, and website activities to create coordinated campaigns that deliver superior customer experiences.
Social media and paid advertising coordination offers another high-value pilot opportunity. HubSpot research identifies paid social media content as the second-highest ROI channel for both B2B and B2C brands [3]. Organizations can coordinate organic social media content with paid advertising campaigns to create more effective audience engagement and conversion strategies.
The pilot phase should include rigorous testing and measurement to validate integration approaches and identify optimization opportunities. This testing should compare integrated approaches with traditional siloed approaches to demonstrate value and build organizational confidence in holistic marketing strategies.
Change management activities during the pilot phase focus on building organizational capabilities and addressing resistance to new approaches. This includes training programs, process documentation, and communication strategies that help team members understand and embrace integrated marketing approaches.
Phase 3: Scale and Integration (Months 9-18)
The scale and integration phase expands successful pilot approaches across all marketing channels and customer touchpoints. This phase requires sophisticated project management, change management, and performance monitoring capabilities to coordinate complex, multi-channel integration efforts.
Technology integration becomes critical during this phase, as organizations implement customer data platforms, marketing automation systems, and analytics tools that enable holistic marketing coordination. The technical complexity of this phase often requires external expertise and significant resource investment.
Cross-channel campaign orchestration represents the most advanced capability developed during this phase. Organizations learn to coordinate campaigns across email, social media, content marketing, paid advertising, and other channels to create seamless customer experiences that guide customers through complex, multi-touchpoint journeys.
Performance measurement and optimization become increasingly sophisticated during this phase, as organizations develop attribution models and analytics capabilities that can capture the cumulative impact of integrated marketing efforts. This measurement sophistication is essential for ongoing optimization and strategic decision-making.
The scale phase also addresses the organizational challenges identified in McKinsey research, including the need for clear customer ownership and accountability. Organizations may need to restructure marketing teams, redefine roles and responsibilities, and implement new governance processes that support holistic marketing coordination.
Phase 4: Optimization and Innovation (Months 19+)
The optimization and innovation phase focuses on continuous improvement, advanced capability development, and competitive advantage building. This phase involves advanced analytics, AI implementation, and strategic innovation that creates sustainable differentiation in the marketplace.
AI and automation implementation accelerates during this phase, as organizations develop the data integration and analytics capabilities necessary for effective AI deployment. HubSpot research indicates that 95% of marketers using generative AI for email creation rate it as effective [3], suggesting significant opportunities for organizations that can implement AI capabilities effectively.
Advanced personalization and customer experience optimization become key focus areas during this phase. Organizations leverage their integrated data and analytics capabilities to create highly personalized customer experiences that adapt to individual customer behaviors and preferences across all touchpoints.
Competitive intelligence and market adaptation capabilities enable organizations to respond quickly to changing market conditions, customer behaviors, and competitive threats. This agility becomes a sustainable competitive advantage in rapidly evolving digital marketing environments.
The optimization phase also includes strategic innovation activities that explore new channels, technologies, and approaches for customer engagement. Organizations that excel in this phase often become market leaders in their industries, setting standards that competitors struggle to match.
Implementation Success Factors and Risk Mitigation
Successful holistic marketing implementation requires attention to several critical success factors that span organizational, technical, and strategic dimensions. Organizations that address these factors proactively are more likely to achieve their strategic objectives and avoid common implementation pitfalls.
Executive leadership commitment represents the most critical success factor, as holistic marketing transformation requires significant resource investment, organizational change, and long-term strategic commitment. Leaders must champion integration efforts, provide necessary resources, and maintain focus through inevitable implementation challenges.
Cross-functional collaboration capabilities enable organizations to coordinate complex, multi-channel marketing efforts effectively. This collaboration requires new processes, communication systems, and governance frameworks that may be unfamiliar to organizations accustomed to siloed marketing approaches.
Customer-centric design principles ensure that integration efforts focus on customer value creation rather than operational efficiency alone. Organizations that maintain customer focus throughout implementation are more likely to achieve sustainable competitive advantages and long-term business success.
Continuous learning and optimization approaches enable organizations to adapt their strategies based on performance data, customer feedback, and changing market conditions. This adaptability is essential in rapidly evolving digital marketing environments where customer behaviors and competitive dynamics change frequently.
Risk mitigation strategies should address common implementation challenges including technology integration difficulties, organizational resistance, resource constraints, and measurement complexity. Organizations that plan for these challenges proactively are more likely to maintain implementation momentum and achieve their strategic objectives.
| Phase | Duration | Key Milestones | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foundation | Months 1-3 | Customer research complete, data audit finished, team aligned | Strategic clarity, organizational readiness |
| Pilot | Months 4-8 | Email-content integration, social-paid coordination | 30% email improvement, proven integration value |
| Scale | Months 9-18 | Full channel integration, technology deployment | Coordinated campaigns, improved customer experience |
| Optimization | Months 19+ | AI implementation, advanced personalization | Competitive advantage, sustainable growth |
Future Trends and Market Evolution
The future of holistic digital marketing will be shaped by several converging trends that promise to both enhance opportunities and increase complexity for marketing organizations. Understanding these trends is crucial for strategic planning and competitive positioning, as organizations that anticipate and prepare for future developments will be better positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities while avoiding potential disruptions.
Artificial Intelligence and Automation Acceleration
The integration of artificial intelligence and automation technologies in marketing will accelerate significantly over the next three to five years, driven by improving technology capabilities, decreasing costs, and increasing competitive pressure. Current adoption rates suggest that organizations are still in early stages of AI implementation, creating significant opportunities for competitive advantage.
HubSpot research indicates that only 19.65% of marketers plan to use AI agents to automate marketing in 2025 [3], suggesting that AI adoption will accelerate rapidly as capabilities improve and success stories emerge. Organizations that develop AI capabilities early will likely achieve sustainable competitive advantages in personalization, optimization, and customer experience delivery.
The effectiveness of AI applications will continue to improve as organizations develop better data integration capabilities and more sophisticated implementation approaches. Current success rates—such as the 95% effectiveness rating for AI-powered email creation [3]—suggest that AI technologies can deliver immediate value when properly implemented.
However, AI implementation will also create new challenges related to privacy, ethics, and customer trust. Organizations will need to develop governance frameworks that ensure responsible AI use while maximizing business value. The organizations that excel in this balance will likely emerge as market leaders in their respective industries.
Privacy and Data Governance Evolution
Privacy regulations and customer expectations regarding data use will continue to evolve, creating both constraints and opportunities for holistic marketing strategies. Organizations that develop privacy-first approaches to marketing will likely achieve competitive advantages through enhanced customer trust and regulatory compliance.
The trend toward privacy-first marketing will accelerate the development of first-party data strategies and customer data platforms that enable personalization without relying on third-party data sources. Organizations that excel in first-party data collection and activation will be better positioned for long-term success.
Consent management and transparency will become increasingly important competitive differentiators, as customers gravitate toward brands that demonstrate responsible data stewardship. Organizations that can provide clear value in exchange for customer data while maintaining transparent data practices will build stronger customer relationships.
The technical complexity of privacy compliance will drive consolidation in marketing technology, as organizations seek integrated platforms that can manage privacy requirements across all marketing channels and touchpoints. This consolidation will favor organizations that can implement comprehensive, integrated marketing technology stacks.
Customer Experience and Personalization Sophistication
Customer expectations for personalized, relevant marketing experiences will continue to increase, driven by exposure to sophisticated personalization from leading digital platforms. Organizations will need to develop more advanced personalization capabilities to meet these evolving expectations.
Real-time personalization and dynamic content optimization will become standard requirements rather than competitive advantages. Organizations will need to develop technical capabilities that can adapt marketing messages, content, and experiences based on immediate customer behavior and context.
Cross-channel personalization consistency will become increasingly important as customers interact with brands across more touchpoints. Organizations will need to develop customer identity resolution and experience orchestration capabilities that ensure consistent personalization across all channels.
The measurement of personalization effectiveness will become more sophisticated, with organizations developing advanced analytics capabilities that can capture the cumulative impact of personalized experiences on customer lifetime value and business outcomes.
Channel Evolution and Emerging Touchpoints
The digital marketing channel landscape will continue to evolve rapidly, with new platforms, formats, and interaction models emerging regularly. Organizations will need to maintain strategic flexibility while building sustainable capabilities that can adapt to changing channel dynamics.
Video content will continue to grow in importance, with video ad spending projected to reach over $268 billion by 2029 [3]. Organizations will need to develop sophisticated video marketing capabilities that span multiple platforms, formats, and optimization objectives.
Voice and conversational interfaces will become increasingly important marketing touchpoints, requiring organizations to develop new content strategies and optimization approaches. The integration of voice interactions with traditional marketing channels will create new opportunities for customer engagement.
Augmented reality and virtual reality technologies will create new opportunities for immersive marketing experiences, particularly in industries such as retail, real estate, and entertainment. Organizations that can effectively integrate these technologies with traditional marketing channels will create unique competitive advantages.
The Internet of Things and connected devices will create new data sources and interaction opportunities that organizations can leverage for more sophisticated customer understanding and engagement strategies.
Organizational and Skills Evolution
The organizational structures and skill requirements for effective holistic marketing will continue to evolve, driven by technological advancements, changes in customer expectations, and competitive pressure. Organizations will need to adapt their talent strategies and organizational designs to remain competitive.
The trend toward customer-centric organizational structures will accelerate, with more organizations adopting the single customer-focused executive model that McKinsey research shows delivers 2.3 times more growth [2]. This structural change will require significant organizational transformation and change management capabilities.
Cross-functional collaboration skills will become increasingly important as marketing integration requires coordination across multiple departments and expertise areas. Organizations will need to develop new collaboration processes and governance frameworks that enable effective integration.
Technical skills requirements will continue to increase, with marketing professionals needing to understand data analysis, technology integration, and AI implementation. Organizations will need to invest in training and development programs that build these capabilities.
Strategic thinking and customer empathy will become even more important as marketing becomes more complex and technology-driven. Organizations will need to maintain focus on customer value creation while leveraging advanced technologies and analytics capabilities.
Challenges and Risk Factors
Several challenges and risk factors could impede the development of holistic marketing capabilities and create competitive disadvantages for organizations that fail to address them proactively.
Technology complexity and integration challenges will continue to create barriers for many organizations, particularly smaller companies that lack sophisticated technical capabilities. The organizations that can navigate this complexity effectively will achieve sustainable competitive advantages.
Skills gaps and talent shortages in key areas such as data analysis, AI implementation, and customer experience design will create competitive advantages for organizations that can attract and retain top talent in these areas.
Privacy regulations and customer trust issues could create significant constraints on marketing effectiveness if not managed properly. Organizations that fail to develop privacy-first approaches may face regulatory penalties and customer backlash.
Economic uncertainty and budget constraints could limit investment in holistic marketing capabilities, creating opportunities for organizations that maintain strategic focus and investment during challenging periods.
Competitive pressure and market saturation in some channels could reduce the effectiveness of traditional marketing approaches, requiring organizations to develop more sophisticated and differentiated strategies.
Key Takeaways and Success Metrics
The analysis of holistic digital marketing strategy reveals several critical insights that organizations must understand and act upon to achieve competitive advantage in increasingly complex digital marketing environments. These takeaways synthesize research from authoritative sources, including McKinsey, HubSpot, government agencies, and academic institutions, to provide evidence-based guidance for strategic decision-making.
Strategic Imperatives for Holistic Marketing Success
- Organizational Structure Drives Performance: Companies with a single customer-focused executive role achieve up to 2.3 times more growth than those with fragmented marketing responsibilities, according to McKinsey’s Fortune 500 analysis [2]. This finding underscores the critical importance of clear accountability and unified strategic direction in marketing leadership.
- Customer Journey Complexity Demands Integration: Modern B2B customers use an average of 10 touchpoints during their buying journey, compared to 5 in 2016 [2]. This 100% increase in complexity makes integrated marketing approaches essential rather than optional for effective customer engagement.
- Channel Integration Delivers Measurable Results: Segmented emails drive 30% more opens and 50% more clickthroughs than unsegmented approaches [3], demonstrating the tangible value of data integration and coordinated marketing efforts across channels.
- Data Utilization Represents Significant Opportunity: 87% of marketers report that data is their company’s most under-utilized asset [3], while 26% report that decision-makers ignore marketing analytics recommendations [8]. Organizations that can effectively leverage data assets will achieve substantial competitive advantages.
- AI Implementation Offers Early-Mover Advantages: 95% of marketers using generative AI for email creation rate it as effective [3], yet only 47% understand how to incorporate AI into their marketing strategy [3]. This gap creates opportunities for organizations that can implement AI capabilities effectively.
Performance Benchmarks and Success Metrics
Effective measurement of holistic marketing success requires comprehensive metrics that capture both individual channel performance and integrated campaign effectiveness. The following benchmarks provide guidance for performance evaluation and optimization:
| Metric Category | Key Metrics | Industry Benchmarks | Excellence Targets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Channel Performance | Email conversion rates, video ROI, social engagement | 2.8% B2C email, 93% video positive ROI | 30% above segmentation baseline |
| Integration Effectiveness | Cross-channel attribution, customer journey completion | 10 touchpoint average journey | Seamless cross-channel experience |
| Customer Experience | Customer satisfaction, retention, lifetime value | Industry-specific baselines | Top quartile performance |
| Business Impact | Revenue growth, market share, competitive position | Market average growth | 2.3x growth advantage |
Implementation Success Factors
Organizations that successfully implement holistic marketing strategies demonstrate consistent patterns in their approach, resource allocation, and execution capabilities. These success factors provide guidance for organizations planning their own holistic marketing transformations:
Executive Leadership Commitment: Successful implementations require sustained executive support, adequate resource allocation, and clear strategic direction. Leaders must champion integration efforts and maintain focus through inevitable implementation challenges.
Customer-Centric Design Principles: Organizations that maintain focus on customer value creation throughout their integration efforts achieve superior results compared to those that prioritize operational efficiency or technology implementation alone.
Data Integration and Analytics Capabilities: Effective holistic marketing requires sophisticated data management and analytics capabilities that enable unified customer views, cross-channel attribution, and continuous optimization.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Integration success depends on effective collaboration across marketing, sales, technology, and other departments. Organizations must develop new processes and governance frameworks that enable this collaboration.
Continuous Learning and Optimization: Holistic marketing requires ongoing testing, measurement, and refinement. Organizations that embrace continuous improvement approaches achieve better long-term results than those that treat integration as a one-time project.
Risk Mitigation and Challenge Management
Holistic marketing implementation faces several common challenges that organizations must address proactively to ensure success. Understanding these challenges and developing mitigation strategies is crucial for maintaining implementation momentum and achieving strategic objectives.
Technology Integration Complexity: The technical challenges of integrating multiple marketing systems and data sources can overwhelm organizations that lack adequate technical capabilities. Success requires careful planning, appropriate expertise, and realistic timelines.
Organizational Resistance and Change Management: Holistic marketing often requires significant changes in roles, responsibilities, and processes. Organizations must invest in change management and training to ensure successful adoption.
Measurement and Attribution Challenges: The complexity of measuring integrated marketing effectiveness can create confusion and reduce confidence in holistic approaches. Organizations need sophisticated measurement frameworks and clear success metrics.
Resource and Budget Constraints: Holistic marketing transformation requires significant investment in technology, training, and process development. Organizations must secure adequate resources and maintain investment through implementation challenges.
Competitive and Market Pressures: Rapidly changing market conditions and competitive pressures can disrupt implementation efforts. Organizations need strategic flexibility and adaptive capabilities to maintain progress despite external challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary difference between traditional marketing and holistic digital marketing?
Traditional marketing typically operates in silos, with different channels and campaigns managed independently. Holistic digital marketing integrates all marketing channels and touchpoints around a customer-centric strategy, creating coordinated experiences across the entire customer journey. McKinsey research shows that companies with integrated approaches achieve 2.3 times more growth than those with fragmented marketing responsibilities [2].
How long does it typically take to implement a holistic marketing strategy?
Implementation typically requires 18-24 months for full integration, divided into four phases: Foundation (3 months), Pilot Implementation (5 months), Scale and Integration (10 months), and ongoing Optimization. However, organizations can begin seeing results from pilot integrations within 4-6 months, particularly in areas like email marketing and content coordination.
What are the most common barriers to holistic marketing implementation?
The most significant barriers include organizational fragmentation (87% of marketers report data under-utilization), technology integration complexity, skills gaps in data analysis and AI implementation, and resistance to change management. Additionally, 26% of organizations report that decision-makers ignore marketing analytics recommendations [8].
Which marketing channels provide the highest ROI in integrated strategies?
Channel effectiveness varies by business type. For B2B organizations, the top ROI channels are website/blog/SEO efforts, paid social media, and social shopping tools. For B2C brands, email marketing leads with 2.8% conversion rates, followed by paid social media and content marketing [3]. However, the synergistic effects of integration often exceed individual channel performance.
How important is AI in holistic digital marketing strategies?
AI is becoming increasingly important, with 95% of marketers using generative AI for email creation rating it as effective [3]. However, only 47% of marketers understand how to incorporate AI strategically, and 47% know how to measure AI’s impact [3]. Organizations that develop AI capabilities early will likely achieve competitive advantages in personalization and optimization.
What role does customer data play in holistic marketing success?
Customer data is fundamental to holistic marketing effectiveness, enabling personalization, attribution, and optimization across all channels. However, 87% of marketers report that data is their company’s most under-utilized asset [3]. Success requires unified customer data platforms, advanced analytics capabilities, and organizational processes for data-driven decision making.
How do privacy regulations affect holistic marketing strategies?
Privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA require privacy-by-design approaches in marketing technology implementation. However, privacy compliance can create competitive advantages through enhanced customer trust and first-party data strategies. Organizations that demonstrate responsible data stewardship while providing clear value for customer information will build stronger relationships.
What organizational structure works best for holistic marketing?
McKinsey research demonstrates that companies with a single customer-focused executive role (CMO, chief commercial officer, chief revenue officer, or chief growth officer) achieve up to 2.3 times more growth than those with multiple, potentially competing roles [2]. Clear accountability and unified strategic direction are essential for integration success.
How should organizations measure holistic marketing effectiveness?
Effective measurement requires comprehensive frameworks that capture both individual channel performance and integrated campaign effectiveness. Key metrics include cross-channel attribution, customer journey completion rates, customer lifetime value, and business impact measures. Segmented approaches show 30% more email opens and 50% more clickthroughs [3], demonstrating the value of integrated measurement.
What are the biggest risks in holistic marketing implementation?
Primary risks include technology integration complexity, organizational resistance to change, inadequate resource allocation, and measurement challenges. Additionally, rapidly changing customer behaviors and competitive pressures can disrupt implementation efforts. Success requires careful planning, adequate expertise, realistic timelines, and strategic flexibility to adapt to changing conditions.
References and Sources
- McKinsey & Company. (2025). “The CMO’s comeback: Aligning the C-suite to drive customer-centric growth.” McKinsey Growth, Marketing & Sales Research. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/growth-marketing-and-sales/our-insights/the-cmos-comeback-aligning-the-c-suite-to-drive-customer-centric-growth
- McKinsey & Company. (2025). “Fortune 500 Analysis: Customer-Centric Growth Strategies.” McKinsey Growth, Marketing & Sales Research Survey. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/growth-marketing-and-sales/our-insights/the-cmos-comeback-aligning-the-c-suite-to-drive-customer-centric-growth
- HubSpot. (2025). “State of Marketing Report 2025: Marketing Statistics and Trends.” HubSpot Research. https://www.hubspot.com/marketing-statistics
- U.S. International Trade Administration. (2024). “Understanding Digital Marketing for Business Growth.” U.S. Department of Commerce. https://www.trade.gov/understanding-digital-marketing
- Statista. (2024). “Digital Advertising and Marketing Market Size Worldwide.” Statista Market Research. https://www.statista.com/outlook/dmo/digital-advertising/worldwide
- Deloitte. (2023). “Government & Public Services Marketing Trends 2023.” Deloitte Consulting. https://www.deloitte.com/us/en/services/consulting/services/government-and-public-services-global-marketing-trends.html
- The White House. (2021). “Executive Order 14058: Transforming Federal Customer Experience and Service Delivery to Rebuild Trust in Government.” Federal Register. https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2021/12/16/2021-27380/transforming-federal-customer-experience-and-service-delivery-to-rebuild-trust-in-government
- Gartner, Inc. (2024). “Marketing Analytics and Decision-Making Research.” Gartner Marketing Research. https://www.gartner.com/en/marketing/research
- Forrester Research. (2024). “Digital Transformation Priorities Survey.” Forrester Consulting. https://www.forrester.com/research/digital-transformation/

