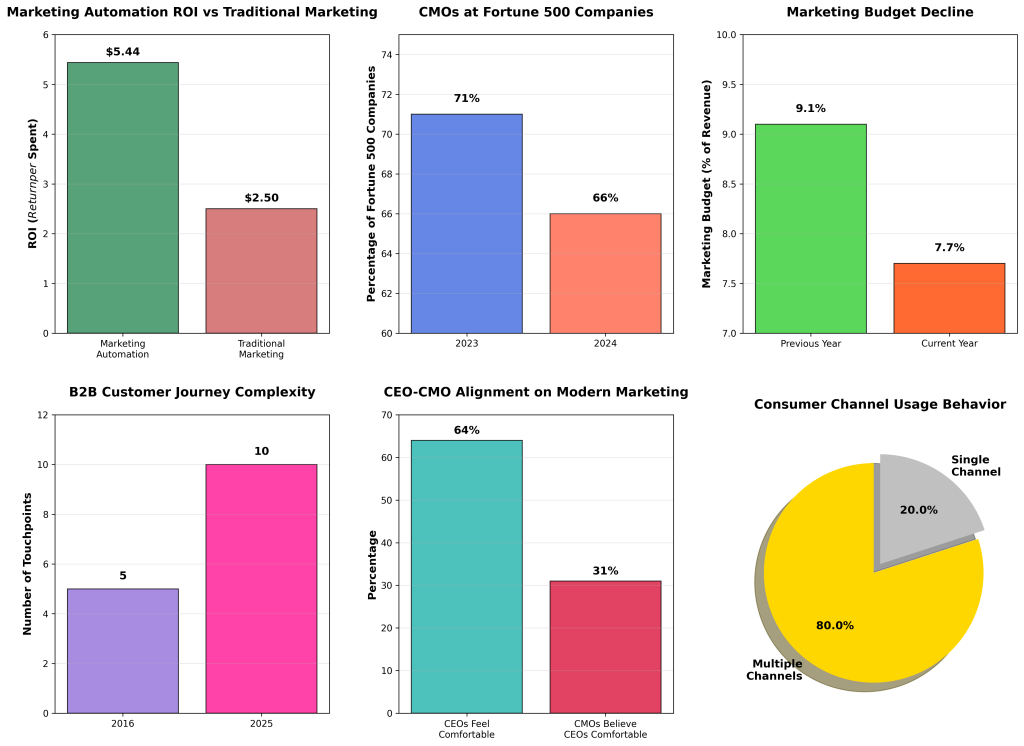
Digital marketing leadership faces an unprecedented crisis of confidence and effectiveness in 2025. While 80% of consumers now use multiple channels for product research and purchase [1], and B2B buyers navigate 10 touchpoints during their typical sales journey (up from just 5 in 2016) [1], marketing leaders struggle to demonstrate tangible business impact. The number of Chief Marketing Officers at Fortune 500 companies has declined from 71% in 2023 to 66% in 2024 [2], while marketing budgets have simultaneously dropped from 9.1% to 7.7% of revenue [1]. Yet organizations implementing marketing automation achieve an average return of $5.44 for every dollar spent over three years [3], suggesting that the challenge lies not in the potential of digital marketing, but in leadership’s ability to bridge the critical gap between strategic vision and effective execution.
The Critical Context: Why Digital Marketing Leadership Matters in 2025
The digital marketing landscape has undergone a fundamental transformation that extends far beyond traditional engagement metrics and conversion optimization. Today’s marketing leaders operate in an environment characterized by unprecedented complexity, where customer expectations have evolved dramatically and organizational structures have become increasingly fragmented. Understanding this context is essential for any marketing leader seeking to drive meaningful business impact in 2025 and beyond.
The modern customer journey represents a paradigm shift from linear, predictable pathways to complex, multi-touchpoint experiences that span numerous channels and platforms. Research from McKinsey & Company reveals that B2B buyers now engage with an average of 10 different touchpoints during their purchasing journey, representing a 100% increase from the 5 touchpoints documented in 2016 [1]. This evolution reflects not merely a change in buyer behavior, but a fundamental restructuring of how business relationships are formed and maintained in the digital age.
Simultaneously, the rise of omnichannel customer expectations has created new challenges for marketing organizations. More than 80% of consumers now utilize multiple channels for product research and purchase decisions [1], demanding seamless, consistent experiences across all touchpoints. This shift has profound implications for marketing leadership, requiring a level of coordination and integration that many organizations struggle to achieve. The challenge is compounded by the fact that each channel often operates with different metrics, timelines, and success criteria, making unified measurement and optimization increasingly complex.
The organizational response to these challenges has often exacerbated rather than resolved the underlying issues. In recent years, many companies have introduced new executive roles such as Chief Digital Officer, Chief Commercial Officer, and Chief Data Officer in an attempt to address specific aspects of digital transformation [1]. While well-intentioned, this proliferation of leadership roles has frequently resulted in organizational fragmentation, with customers receiving inconsistent messages from different departments as each executive views the customer through a different lens.
This fragmentation has created what industry experts describe as a “choppy customer journey,” where the lack of coordination between different organizational functions undermines the very customer experience that digital transformation initiatives are meant to improve. As one chief marketing and sales officer of a global automobile company observes, “Very few companies in our industry have figured out how to clearly delineate the responsibilities of marketing, ownership of the customer journey, and digital efforts” [1].
The implications of this organizational complexity extend beyond customer experience to fundamental questions of accountability and measurement. CEOs today often struggle to identify a single source of truth for customer insights and market intelligence. This challenge is particularly acute given that marketers traditionally serve as the primary custodians of customer understanding within organizations, housing consumer insights and deploying sophisticated qualitative and quantitative research tools to identify customer segments, map buying journeys, and determine preferences [1].
The financial stakes of effective digital marketing leadership have never been higher. Organizations that successfully implement marketing automation technologies achieve substantial returns, with Nucleus Research documenting an average ROI of $5.44 for every dollar invested over the first three years of deployment [3]. The payback period for these investments is typically under six months, with the most significant benefits realized through increased marketer productivity, enhanced campaign efficiency, cost savings from automation, simplified infrastructure, and improved prospect engagement [3].
However, realizing these benefits requires more than technology implementation; it demands sophisticated leadership capable of orchestrating complex organizational change while maintaining focus on measurable business outcomes. The challenge is particularly acute for B2B organizations, where 83% of marketers achieve brand awareness goals through content marketing, and 77% successfully build trust through content initiatives [4]. Yet translating these achievements into quantifiable business impact remains a persistent challenge for many marketing leaders.
The urgency of addressing these leadership challenges is underscored by broader market dynamics. Digital marketing spending continues to grow across all sectors, with B2B companies increasingly prioritizing digital channels over traditional approaches. Research indicates that 64% of new-generation B2B buyers prefer digital channels over traditional ones, while 80% use mobile devices throughout their buying journey [4]. This shift represents not merely a change in channel preference but a fundamental evolution in how business relationships are initiated, developed, and maintained.
For marketing leaders, these trends create both unprecedented opportunities and significant risks. Organizations that successfully navigate this complexity can achieve substantial competitive advantages, while those that fail to adapt risk becoming increasingly irrelevant in their markets. The key differentiator lies not in the adoption of specific technologies or tactics but in the development of leadership capabilities that can effectively bridge the gap between strategic vision and operational execution.
The Marketing Leadership Crisis: Data-Driven Analysis
The current state of marketing leadership reveals a troubling disconnect between the strategic importance of marketing and its organizational influence. Comprehensive analysis of recent research from leading institutions, including McKinsey & Company, Gartner, and Spencer Stuart, reveals multiple dimensions of this crisis, each with significant implications for organizational performance and competitive positioning.

Declining Executive Representation
The most visible manifestation of the marketing leadership crisis is the declining representation of marketing executives in senior leadership positions. According to Spencer Stuart’s executive search data, the percentage of Chief Marketing Officers at Fortune 500 companies decreased from 71% in 2023 to 66% in 2024, representing a concerning 5 percentage point decline in just one year [2]. This trend is further corroborated by Forrester Research, which reports that only 63% of Fortune 500 companies currently have a marketing leader who sits on the leadership team and reports directly to the CEO [1].
This decline in executive representation occurs precisely when marketing’s strategic importance should be increasing. The complexity of modern customer journeys, the proliferation of digital touchpoints, and the need for sophisticated data analysis all suggest that marketing expertise should be more, not less, central to organizational decision-making. The contradiction between marketing’s growing strategic importance and its declining executive representation suggests fundamental misalignment in how organizations perceive and value marketing leadership.
Role Clarity and Strategic Alignment
Beyond representation issues, marketing leadership faces significant challenges related to role clarity and strategic alignment. McKinsey’s research reveals that 20% fewer CEOs (70%, down from 90%) now believe that marketing’s role is clearly defined and understood by the C-suite [1]. This decline in role clarity has profound implications for marketing effectiveness, as unclear expectations and responsibilities inevitably lead to suboptimal resource allocation and strategic misalignment.
The impact of this role ambiguity extends to strategic planning processes, where marketing input is increasingly marginalized. Only 50% of CMOs surveyed believe that marketing executives are involved in the strategic planning process [1]. This exclusion from strategic planning represents a fundamental organizational dysfunction, as marketing leaders possess unique insights into customer behavior, market dynamics, and competitive positioning that are essential for effective strategic decision-making.
The relegation of marketing’s role to primarily advertising and promotional activities further compounds these challenges. When marketing is viewed primarily as a tactical function rather than a strategic capability, organizations miss opportunities to leverage customer insights, market intelligence, and competitive analysis in their broader business planning. This narrow view of marketing’s role also limits CMOs’ ability to demonstrate their impact on broader business objectives, creating a self-reinforcing cycle of diminished influence and reduced strategic involvement.
Budget Constraints and Investment Challenges
The financial dimension of the marketing leadership crisis is equally concerning. Despite widespread recognition of marketing’s importance, marketing budgets have declined from 9.1% of revenue to 7.7% of revenue according to Gartner research [1]. This 1.4 percentage point decrease represents a significant reduction in marketing investment precisely when digital transformation initiatives require substantial resource commitments.
The budget reduction occurs against a backdrop of widespread belief that marketing departments are underfunded. McKinsey’s research indicates that 80% of CEO respondents and 77% of CMOs believe marketing departments lack adequate funding [1]. This consensus on underfunding, combined with actual budget reductions, suggests that organizations are caught in a challenging dynamic where marketing needs are recognized but not adequately addressed through resource allocation.
The implications of these budget constraints extend beyond immediate operational limitations to longer-term strategic positioning. Marketing automation technologies, which deliver an average ROI of $5.44 for every dollar invested [3], require upfront investments that may be difficult to justify in resource-constrained environments. Similarly, the sophisticated analytics capabilities needed to demonstrate marketing ROI often require significant technology and talent investments that may be deferred when budgets are under pressure.
CEO-CMO Alignment Gap
Perhaps the most concerning aspect of the marketing leadership crisis is the growing alignment gap between CEOs and CMOs regarding marketing capabilities and comfort levels. While 64% of CEOs report feeling comfortable with modern marketing (an increase from 48% in the previous year), only 31% of CMOs believe their CEOs are actually comfortable with modern marketing approaches [1]. This represents a 4 percentage point decrease from the previous year and suggests that the perceived improvement in CEO comfort levels may not reflect actual understanding or confidence.
This alignment gap has significant implications for marketing effectiveness and organizational performance. When CEOs lack genuine comfort with modern marketing approaches, they are less likely to provide the support, resources, and strategic backing that marketing leaders need to be successful. The gap also suggests that CMOs may be operating with different assumptions about their CEOs’ expectations and priorities, leading to potential misalignment in strategy development and execution.
The challenge is compounded by the complexity of modern marketing technologies and methodologies. As marketing becomes increasingly data-driven and technologically sophisticated, the knowledge gap between marketing practitioners and other executives may widen. This creates a situation where marketing leaders must not only execute effective strategies but also educate and influence other executives who may lack the technical background to fully appreciate marketing’s potential contributions.
Performance Measurement Challenges
The marketing leadership crisis is further exacerbated by persistent challenges in performance measurement and ROI demonstration. Gartner’s 2025 Tech Marketing Benchmarks Survey identifies “proving ROI with analytics” as a top-three challenge that hinders marketers’ ability to demonstrate success [5]. This challenge is particularly acute for technology marketers in companies with $100 million or more in annual revenue, where complex, difficult-to-quantify activities like positioning, messaging, brand awareness, and sales enablement create measurement difficulties.
The measurement challenge creates a vicious cycle where marketing leaders struggle to demonstrate their value, leading to reduced confidence from other executives, which in turn results in decreased resources and strategic influence. McKinsey’s research reveals that 79% of CMOs understand how marketing KPIs align with overall growth KPIs, representing a decline from 88% in the previous survey [1]. Even more concerning, only 30% of CMOs believe there is a clearly defined view of what constitutes marketing ROI, down from 40% previously [1].
This deterioration in measurement clarity occurs precisely when sophisticated measurement capabilities are becoming more accessible and important. The proliferation of marketing automation platforms, analytics tools, and attribution technologies should theoretically make ROI measurement easier, not more difficult. The fact that measurement challenges are increasing despite technological advances suggests that the issues are more fundamental, relating to organizational alignment, expectation setting, and strategic clarity rather than purely technical limitations.
| Metric | Current State | Previous Period | Change | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMOs at Fortune 500 Companies | 66% | 71% | -5 points | Spencer Stuart [2] |
| Marketing Budget (% of Revenue) | 7.7% | 9.1% | -1.4 points | Gartner [1] |
| CEOs Comfortable with Modern Marketing | 64% | 48% | +16 points | McKinsey [1] |
| CMOs Believe CEOs are Comfortable | 31% | 35% | -4 points | McKinsey [1] |
| Marketing Role Clearly Defined | 70% | 90% | -20 points | McKinsey [1] |
| CMOs Understand KPI Alignment | 79% | 88% | -9 points | McKinsey [1] |
The data presented in this analysis reveals a marketing leadership function under significant pressure from multiple directions. The combination of declining executive representation, reduced budgets, unclear role definitions, and measurement challenges creates a perfect storm that threatens marketing’s ability to contribute effectively to organizational success. However, this crisis also represents an opportunity for marketing leaders who can successfully navigate these challenges and demonstrate clear business value through effective strategy development and execution.
Strategic Framework: From Vision to Execution
Effective digital marketing leadership requires a systematic approach that bridges the gap between strategic vision and operational execution. The framework presented here synthesizes best practices from leading organizations and research findings from authoritative sources to provide a comprehensive roadmap for marketing leaders seeking to drive measurable business impact.
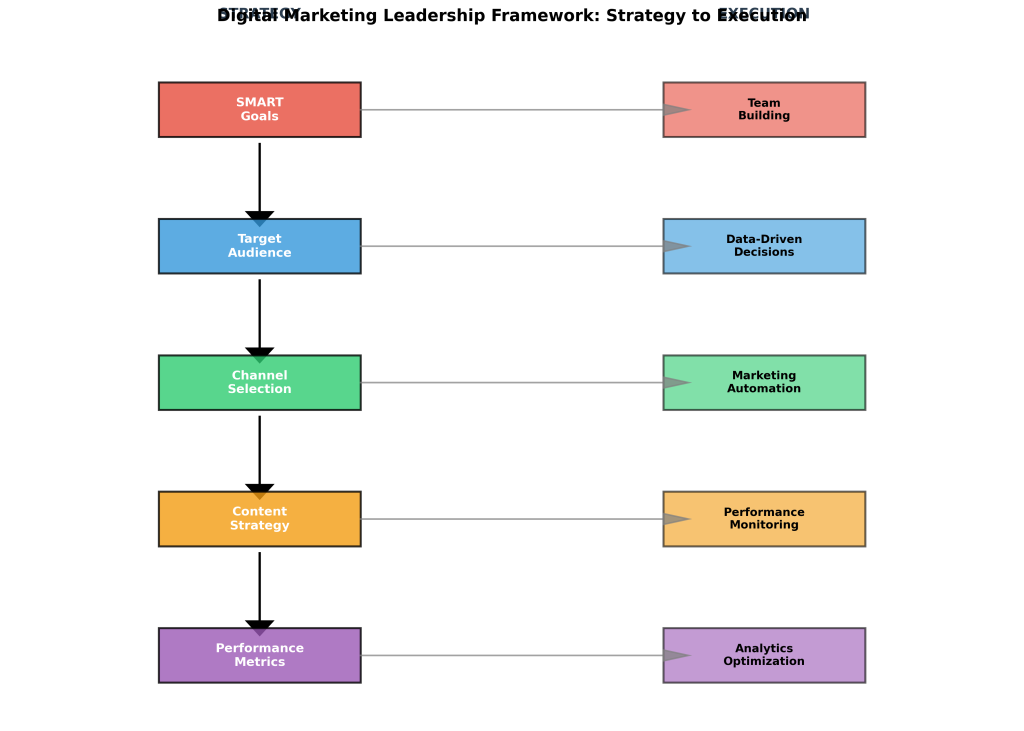
Foundation: SMART Goals and Strategic Alignment
The foundation of effective digital marketing leadership lies in the establishment of SMART goals that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. However, the application of SMART criteria in digital marketing contexts requires sophisticated understanding of both short-term tactical metrics and long-term strategic outcomes. Research consistently demonstrates that organizations with clearly defined, measurable objectives achieve superior performance compared to those operating with vague or aspirational goals.
The challenge for marketing leaders lies not in understanding the SMART framework itself, but in selecting appropriate metrics that accurately reflect marketing’s contribution to broader business objectives. McKinsey’s research reveals that 70% of CEOs measure marketing’s impact based on year-over-year revenue growth and margin, while only 35% of CMO respondents track this as a top metric [1]. This disconnect suggests that many marketing organizations are optimizing for metrics that do not align with executive expectations and business priorities.
Effective goal setting in digital marketing requires a hierarchical approach that connects tactical activities to strategic outcomes. At the tactical level, marketers might focus on metrics such as click-through rates, conversion rates, and engagement levels. At the operational level, these metrics should aggregate to measures such as lead quality, customer acquisition cost, and lifetime value. At the strategic level, marketing goals should directly connect to business outcomes such as revenue growth, market share expansion, and customer retention.
The temporal dimension of goal setting is equally important. While some marketing activities produce immediate, measurable results, others require longer time horizons to demonstrate their full impact. Brand awareness campaigns, thought leadership initiatives, and customer education programs may not produce immediate revenue impact, but can significantly influence long-term business performance. Effective marketing leaders develop goal frameworks that account for both immediate and long-term impacts, ensuring that short-term pressures do not undermine long-term strategic positioning.
Target Audience Research and Segmentation
Contemporary target audience research extends far beyond traditional demographic and psychographic analysis to encompass behavioral data, intent signals, and dynamic preference mapping. The proliferation of digital touchpoints has created unprecedented opportunities for audience understanding, but it has also increased the complexity of audience analysis and segmentation.
Modern audience research must account for the reality that B2B buyers now engage with an average of 10 touchpoints during their purchasing journey [1], each providing different types of information and serving different functions in the decision-making process. This complexity requires marketing leaders to develop sophisticated understanding of how different audience segments navigate these touchpoints and what information or experiences they seek at each stage.
The integration of first-party data, third-party data sources, and emerging signals such as intent data and community interactions provides marketing leaders with unprecedented insight into audience behavior and preferences. However, leveraging these data sources effectively requires sophisticated analytical capabilities and clear frameworks for data integration and interpretation. Gartner’s research emphasizes the importance of combining new B2B customer data signals with traditional data sources to achieve comprehensive, high-quality data collection [5].
Persona development in digital marketing contexts must evolve beyond static profiles to dynamic, data-driven representations that reflect changing behaviors and preferences. Effective personas incorporate not only demographic and psychographic information but also behavioral patterns, technology preferences, content consumption habits, and decision-making processes. These enhanced personas serve as the foundation for personalized messaging, channel selection, and content strategy development.
The challenge of audience research is compounded by privacy regulations and changing data availability. Marketing leaders must develop audience understanding strategies that are both effective and compliant with evolving privacy requirements. This often requires greater emphasis on first-party data collection, direct customer feedback, and observational research methods that respect customer privacy while providing actionable insights.
Channel Selection and Integration
Channel selection in digital marketing has evolved from a relatively straightforward decision between a limited number of options to a complex optimization problem involving dozens of potential touchpoints, each with different characteristics, audiences, and performance metrics. The fact that 80% of consumers now use multiple channels for product research and purchase [1] means that channel selection cannot be viewed as an either-or decision but rather as an integration challenge.
Effective channel selection requires deep understanding of where target audiences engage most actively and effectively, but it also requires consideration of how different channels work together to create cohesive customer experiences. The goal is not to be present on every available channel but to select and integrate channels that collectively provide comprehensive coverage of the customer journey while maintaining message consistency and brand coherence.
The integration challenge is particularly acute for B2B organizations, where decision-making processes often involve multiple stakeholders with different information needs and channel preferences. A single B2B purchase decision might involve research conducted through search engines, social media engagement, content consumption, webinar attendance, sales conversations, and peer recommendations. Marketing leaders must orchestrate these touchpoints to ensure that each interaction builds upon previous ones and moves prospects closer to purchase decisions.
Channel performance measurement requires sophisticated attribution modeling that accounts for the complex, non-linear nature of modern customer journeys. Traditional last-click attribution models are inadequate for understanding how different channels contribute to business outcomes. Marketing leaders must implement multi-touch attribution approaches that provide accurate assessment of each channel’s contribution to overall performance.
The emergence of new channels and the evolution of existing ones requires continuous evaluation and adaptation of channel strategies. Social media platforms regularly introduce new features and advertising options, search engines modify their algorithms and ad formats, and new technologies create entirely new channel opportunities. Marketing leaders must balance the need for strategic consistency with the imperative to adapt to changing channel landscapes.
Content Strategy and Calendar Management
Content strategy in digital marketing has evolved from a supporting function to a central organizing principle that drives audience engagement, thought leadership, and conversion optimization. The recognition that 83% of B2B marketers achieve brand awareness goals through content marketing, while 77% build trust through content initiatives [4], underscores the strategic importance of sophisticated content planning and execution.

Effective content strategy requires alignment between content types, audience preferences, channel characteristics, and business objectives. Different content formats serve different functions in the customer journey, and marketing leaders must develop content portfolios that provide comprehensive support for prospects and customers at every stage of their engagement with the organization.
The data reveals that blog posts represent 19.47% of content formats used by marketers in 2024, making them the fourth most popular format following short-form video (29.18%), images (28.95%), and interviews [4]. This distribution suggests that successful content strategies must incorporate multiple formats and adapt to changing audience preferences for content consumption.
Content calendar management has become increasingly complex as organizations seek to maintain consistent messaging across multiple channels while adapting content for different audience segments and engagement contexts. Effective calendar management requires sophisticated planning tools, clear approval processes, and flexible execution capabilities that can respond to changing market conditions and emerging opportunities.
The measurement of content performance requires metrics that go beyond traditional engagement measures to assess content’s contribution to business objectives. While metrics such as views, shares, and comments provide useful feedback on content resonance, marketing leaders must also track how content consumption influences lead generation, sales progression, and customer retention.
Performance Metrics and Measurement Framework
The development of effective performance measurement frameworks represents one of the most critical challenges facing digital marketing leaders. The complexity of modern marketing activities, combined with the proliferation of available metrics, creates both opportunities and risks for marketing measurement and optimization.
Gartner’s research emphasizes the importance of focusing on strategic, operational, and tactical metrics that align with key business and marketing objectives across customer journey stages, including awareness, consideration, purchase, adoption, and retention [5]. This hierarchical approach ensures that measurement efforts provide actionable insights at multiple organizational levels while maintaining clear connections between tactical activities and strategic outcomes.
The challenge of leading metrics alignment is particularly important for marketing activities that do not produce an immediate revenue impact. When introducing new products or services, marketing leaders must track visitor and account-level engagement as precursors to pipeline generation [5]. This requires a sophisticated understanding of how early-stage metrics correlate with later-stage business outcomes and the ability to communicate these relationships to other executives who may be focused primarily on immediate results.
The integration of qualitative and quantitative metrics provides a more comprehensive view of marketing performance than either approach alone. While quantitative metrics such as conversion rates and revenue attribution provide clear performance indicators, qualitative insights from customer feedback, sales team observations, and market research provide context and explanation for quantitative trends.
Benchmarking and competitive analysis add another dimension to performance measurement by providing external reference points for internal performance assessment. Marketing leaders must develop benchmarking approaches that account for industry differences, competitive positioning, and organizational maturity while providing actionable insights for performance improvement.
| Framework Component | Key Activities | Success Metrics | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMART Goals | Define specific, measurable objectives aligned with business goals | Goal clarity score, stakeholder alignment | Quarterly |
| Target Audience | Conduct research, develop personas, map customer journeys | Audience engagement rates, conversion by segment | Bi-annually |
| Channel Selection | Evaluate channel performance, optimize mix, ensure integration | Channel ROI, cross-channel attribution | Monthly |
| Content Strategy | Develop content calendar, create diverse formats, measure performance | Content engagement, lead generation | Weekly |
| Performance Metrics | Establish KPIs, implement tracking, conduct regular reviews | Measurement accuracy, reporting efficiency | Ongoing |
Execution Excellence: Building High-Performance Teams
The transition from strategic planning to effective execution represents the most critical challenge facing digital marketing leaders. While developing sophisticated strategies is essential, the ability to execute those strategies consistently and effectively determines ultimate success. Research consistently demonstrates that execution capabilities, rather than strategic sophistication, often differentiate high-performing marketing organizations from their competitors.
Building Diverse, Collaborative Teams
Modern digital marketing execution requires teams that combine creativity, analytical rigor, and technical expertise in ways that were not necessary in traditional marketing environments. The complexity of contemporary marketing technologies, the sophistication of data analysis requirements, and the need for rapid adaptation to changing market conditions all demand team compositions that go far beyond traditional marketing skill sets.
Effective digital marketing teams require expertise across multiple disciplines, including content production, search engine optimization, data analysis, campaign management, marketing automation, customer experience design, and performance measurement. However, simply assembling individuals with these skills is insufficient; the key lies in creating collaborative structures that enable these diverse capabilities to work together effectively.
The challenge of team building is compounded by the rapid evolution of marketing technologies and methodologies. Skills that were cutting-edge two years ago may now be considered basic requirements, while entirely new capabilities emerge regularly. Marketing leaders must develop team structures that are both stable enough to execute consistent strategies and flexible enough to adapt to changing requirements and opportunities.
Clear role definition and responsibility allocation are essential for avoiding the overlaps and gaps that can undermine team effectiveness. When team members are unclear about their responsibilities or when multiple individuals believe they are responsible for the same outcomes, execution suffers. Conversely, when critical activities fall between defined roles, important work may be neglected or executed inconsistently.
The geographic distribution of modern teams adds another layer of complexity to team building and management. Many marketing organizations now operate with team members distributed across multiple locations, time zones, and cultural contexts. This distribution can provide access to diverse perspectives and specialized expertise, but it also requires sophisticated coordination and communication capabilities.
Regular training and mentorship programs are essential for maintaining team capabilities in rapidly evolving environments. The half-life of marketing skills continues to decrease as new technologies, platforms, and methodologies emerge. Organizations that invest in continuous learning and development maintain competitive advantages over those that rely on static skill sets.

Data-Driven Decision Making
The foundation of execution excellence in digital marketing lies in the systematic use of data to guide decision-making processes. However, becoming truly data-driven requires more than simply collecting and analyzing data; it requires developing organizational cultures and processes that consistently prioritize evidence over intuition and measurable outcomes over subjective preferences.
The proliferation of analytics tools and data sources has created both opportunities and challenges for marketing leaders. While more data is available than ever before, the ability to extract actionable insights from this data requires sophisticated analytical capabilities and clear frameworks for data interpretation and application. Google Analytics, social media analytics platforms, marketing automation systems, and customer relationship management tools each provide different types of insights that must be integrated to create a comprehensive understanding of marketing performance.
Understanding customer behavior patterns through data analysis enables marketing teams to optimize timing, messaging, and channel selection in ways that significantly improve performance. For example, analyzing when target audiences are most active on social media platforms allows teams to schedule content for maximum engagement. Similarly, understanding which content types generate the highest conversion rates enables teams to allocate resources more effectively across different content formats.
The development of data-driven cultures requires more than technical capabilities; it requires organizational commitment to evidence-based decision making and willingness to challenge assumptions and conventional wisdom when data suggests alternative approaches. This cultural transformation often represents the most significant challenge in developing data-driven marketing capabilities.
Data quality and integrity are fundamental prerequisites for effective data-driven decision making. Poor data quality can lead to incorrect conclusions and suboptimal decisions that undermine marketing effectiveness. Marketing leaders must implement data governance processes that ensure accuracy, completeness, and consistency across all data sources and analytical processes.
The integration of different data sources presents both technical and analytical challenges. Customer data from CRM systems, engagement data from marketing automation platforms, website analytics, social media metrics, and sales performance data must be combined to create comprehensive views of marketing performance. This integration often requires sophisticated technical infrastructure and analytical expertise.
Marketing Automation and Technology Integration
Marketing automation represents one of the most significant opportunities for improving execution efficiency and effectiveness. Nucleus Research’s findings that organizations achieve an average ROI of $5.44 for every dollar spent on marketing automation [3] demonstrate the substantial value potential of these technologies. However, realizing this value requires sophisticated implementation and management approaches that go beyond simple technology deployment.
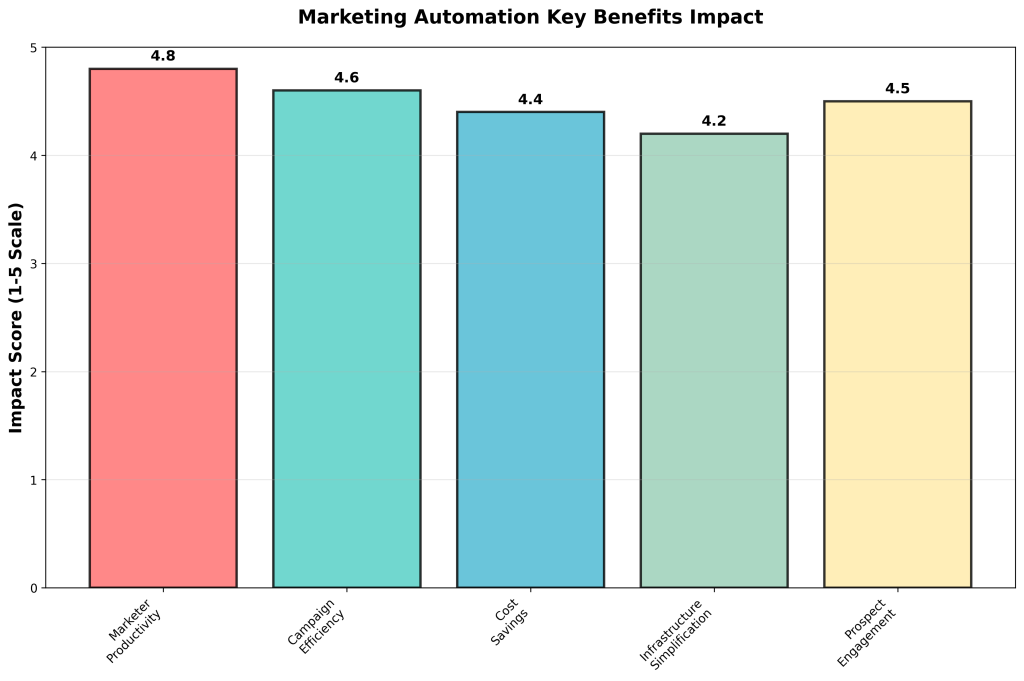
The key benefits of marketing automation include increased marketer productivity, enhanced campaign efficiency, cost savings from automation, simplified infrastructure, and improved prospect engagement [3]. These benefits are achieved through the automation of repetitive tasks, the personalization of customer communications, and the optimization of campaign timing and targeting based on customer behavior and preferences.
Effective marketing automation implementation requires careful consideration of customer journey mapping, content development, lead scoring, and nurturing workflows. The automation of inappropriate or poorly designed processes can actually harm marketing effectiveness by creating impersonal or irrelevant customer experiences. Marketing leaders must ensure that automation enhances rather than replaces human insight and creativity.
The integration of marketing automation with other business systems, particularly customer relationship management and sales force automation platforms, is essential for creating seamless customer experiences and accurate performance measurement. When these systems operate in isolation, organizations miss opportunities for optimization and may create inconsistent customer experiences.
Training and capability development are critical success factors for marketing automation implementation. The sophistication of modern marketing automation platforms requires team members who understand both the technical capabilities of these systems and the strategic principles that should guide their use. Organizations that invest in comprehensive training programs achieve better results from their automation investments.
The measurement of automation impact requires metrics that go beyond traditional campaign performance indicators to assess the broader organizational benefits of automation. While campaign-specific metrics such as open rates and click-through rates provide useful feedback, marketing leaders must also track how automation affects overall team productivity, lead quality, and sales conversion rates.
Performance Monitoring and Optimization
Continuous performance monitoring and optimization represent the operational heart of execution excellence. The dynamic nature of digital marketing environments requires real-time monitoring capabilities and rapid response mechanisms that can identify and address performance issues before they significantly impact business outcomes.
Dashboard development and visualization are essential tools for effective performance monitoring. Well-designed dashboards provide quick, easy-to-understand visualizations of critical metrics that enable marketing teams to identify trends, spot anomalies, and make rapid adjustments to ongoing campaigns. However, dashboard effectiveness depends on careful selection of metrics, appropriate visualization techniques, and regular review and updating of dashboard content.
The frequency and scope of performance reviews must balance the need for timely response with the practical limitations of analysis and optimization activities. Daily monitoring may be appropriate for high-volume, short-duration campaigns, while monthly or quarterly reviews may be sufficient for longer-term brand-building activities. Marketing leaders must develop review schedules that provide adequate oversight without creating an excessive administrative burden.
Performance optimization requires systematic approaches to testing and experimentation. A/B testing, multivariate testing, and other experimental methodologies enable marketing teams to identify the most effective approaches to messaging, design, timing, and targeting. However, effective testing requires careful experimental design, adequate sample sizes, and rigorous analysis of results.
The communication of performance insights to stakeholders throughout the organization is essential for maintaining support and alignment for marketing activities. Regular performance updates build transparency and accountability while providing opportunities to educate other executives about marketing’s contributions to business objectives. The format and frequency of these communications should be tailored to the needs and preferences of different stakeholder groups.
Budget reallocation based on performance insights enables marketing teams to optimize resource allocation continuously. When certain campaigns or channels demonstrate superior performance, resources should be shifted to maximize overall impact. However, this reallocation must be balanced against the need for strategic consistency and long-term positioning.
Cross-Functional Collaboration and Integration
Digital marketing execution increasingly requires sophisticated collaboration with other organizational functions, including sales, customer service, product development, and information technology. The complexity of modern customer journeys means that marketing activities must be coordinated with other customer-facing functions to ensure consistent, high-quality customer experiences.
Sales and marketing alignment represents one of the most critical collaboration challenges. The fact that B2B buyers now engage with 10 touchpoints during their purchasing journey [1] means that handoffs between marketing and sales must be seamless and well-coordinated. Poor alignment between these functions can result in lost opportunities, inconsistent messaging, and suboptimal customer experiences.
Lead qualification and scoring processes require close collaboration between marketing and sales teams to ensure that leads are properly prioritized and followed up appropriately. Marketing teams must understand sales team capabilities and preferences, while sales teams must provide feedback on lead quality and conversion rates to enable marketing optimization.
Customer service integration enables marketing teams to leverage customer feedback and support interactions to improve messaging, identify new opportunities, and address potential issues before they become widespread problems. Customer service teams often have the most direct and frequent contact with customers, providing valuable insights that can inform marketing strategy and execution.
Product development collaboration ensures that marketing activities accurately reflect product capabilities and roadmaps while providing product teams with market feedback that can inform development priorities. This collaboration is particularly important for technology companies where product capabilities evolve rapidly and marketing messages must remain current and accurate.
Information technology partnership is essential for implementing and maintaining the sophisticated technology infrastructure that modern digital marketing requires. Marketing automation platforms, analytics tools, customer data platforms, and other marketing technologies require ongoing technical support and integration with other business systems.
Measurement and Optimization: The ROI Imperative
The ability to measure and demonstrate return on investment has become the defining challenge for digital marketing leadership in 2025. As marketing budgets face increasing scrutiny and CMOs struggle to maintain their positions in executive leadership, the imperative to prove marketing’s business impact has never been more critical. However, effective measurement requires more than simply tracking metrics; it demands a sophisticated understanding of how marketing activities contribute to business outcomes and the ability to communicate these contributions clearly to other executives.
Establishing Measurement Building Blocks
Gartner’s research emphasizes that quantifying marketing impact requires establishing measurement “building blocks” consisting of metrics, data, processes, technology, and resources that enable continuous monitoring, optimization, and demonstration of marketing activities that support business objectives [5]. This systematic approach ensures that measurement efforts are comprehensive, consistent, and aligned with organizational priorities.
The selection of appropriate metrics represents the foundation of effective measurement. Marketing leaders must focus on strategic, operational, and tactical metrics that align with key business and marketing objectives across all customer journey stages, including awareness, consideration, purchase, adoption, and retention [5]. This hierarchical approach ensures that measurement provides actionable insights at multiple organizational levels while maintaining clear connections between day-to-day activities and long-term business outcomes.
Leading metrics play a particularly important role in marketing measurement because many marketing activities do not produce an immediate revenue impact. When introducing new products or services, marketing teams must track visitor and account-level engagement with websites and content as precursors to pipeline generation [5]. This requires a sophisticated understanding of how early-stage metrics correlate with later-stage business outcomes and the ability to communicate these relationships to executives who may be focused primarily on immediate results.
The integration of traditional and emerging data sources provides marketing leaders with unprecedented opportunities for comprehensive measurement. Combining new B2B customer data signals such as product usage, buyer intent, and community interactions with traditional first- and third-party data sources enables a more accurate and complete assessment of marketing performance [5]. However, this integration requires sophisticated data management capabilities and clear frameworks for data interpretation and application.
Data quality and governance are fundamental prerequisites for effective measurement. Poor data quality can lead to incorrect conclusions and suboptimal decisions that undermine marketing effectiveness. Marketing leaders must implement data governance processes that ensure accuracy, completeness, and consistency across all data sources while maintaining compliance with privacy regulations and ethical data use standards.
Technology and Tools for ROI Measurement
The technology infrastructure supporting marketing measurement has evolved dramatically, providing marketing leaders with sophisticated tools for tracking, analyzing, and reporting marketing performance. B2B marketing automation platforms, account-based marketing systems, specialized dashboard tools, multitouch attribution solutions, business intelligence platforms, and artificial intelligence capabilities all contribute to comprehensive measurement ecosystems [5].
Marketing automation platforms provide detailed tracking of customer interactions across multiple touchpoints, enabling marketing teams to understand how prospects engage with different types of content and communications. These platforms typically include built-in analytics capabilities that track email open rates, click-through rates, website visits, content downloads, and other engagement metrics that provide insights into campaign effectiveness and customer preferences.
Account-based marketing platforms offer specialized measurement capabilities for B2B organizations that focus on specific target accounts rather than broad lead generation. These platforms track account-level engagement across multiple stakeholders and touchpoints, providing insights into how entire organizations progress through purchasing processes rather than focusing solely on individual lead behavior.
Multitouch attribution tools address one of the most significant challenges in digital marketing measurement by providing an accurate assessment of how different channels and touchpoints contribute to business outcomes. Traditional last-click attribution models are inadequate for understanding the complex, non-linear customer journeys that characterize modern B2B purchasing processes. Advanced attribution modeling enables marketing leaders to understand the true contribution of each marketing activity to overall performance.
Business intelligence platforms integrate marketing data with other business data sources to provide comprehensive views of how marketing activities affect broader business outcomes. These platforms enable marketing leaders to demonstrate connections between marketing activities and metrics such as revenue growth, customer retention, and market share expansion that are of primary interest to other executives.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities are increasingly being integrated into marketing measurement tools to automate analysis, identify patterns, and generate insights that would be difficult or impossible to discover through manual analysis. These capabilities can augment human analysis and automate routine reporting tasks, freeing marketing teams to focus on strategic interpretation and optimization activities.
Addressing the ROI Measurement Challenge
Despite the availability of sophisticated measurement tools and methodologies, many marketing leaders continue to struggle with ROI demonstration. Gartner’s 2025 Tech Marketing Benchmarks Survey identifies “proving ROI with analytics” as a top-three challenge that hinders marketers’ ability to demonstrate success [5]. This challenge is particularly acute for complex, difficult-to-quantify activities such as positioning and messaging, brand awareness, competitive analysis, and sales enablement.
The measurement challenge is compounded by the collaborative nature of many marketing activities. Pipeline creation programs such as product-led growth, account-based marketing, and demand generation involve heavy collaboration with sales, customer success, and product teams [5]. When multiple functions contribute to business outcomes, isolating marketing’s specific contribution becomes more difficult but also more important for demonstrating value.
Standard processes and methodologies are essential for consistent and credible ROI measurement. Marketing leaders must define campaign tracking standards for all marketing and sales channels, select appropriate analysis and modeling techniques, develop data storytelling approaches that effectively communicate marketing value, and establish data privacy compliance standards [5]. These standardized approaches ensure that measurement efforts are consistent, comparable, and credible to other executives.
The resource requirements for effective ROI measurement are often underestimated. Marketing measurement programs require both monetary and non-monetary resources, and marketing leaders may need to make business cases for analytics capabilities that are not available with existing tools [5]. When internal teams lack necessary skills, organizations may need to access expertise from business analytics, IT, or data science functions or invest in external resources and training.
Communicating ROI to Stakeholders
The ability to communicate marketing ROI effectively to other executives represents a critical leadership skill that often determines marketing’s organizational influence and resource allocation. McKinsey’s research reveals significant disconnects between how CEOs and CMOs view marketing performance, with 70% of CEOs measuring marketing impact based on year-over-year revenue growth and margin while only 35% of CMOs track this as a top metric [1].
This measurement disconnect suggests that many marketing leaders are optimizing for metrics that do not align with executive expectations and business priorities. Effective ROI communication requires understanding what metrics matter most to different stakeholder groups and developing reporting approaches that clearly demonstrate marketing’s contribution to those metrics.
Data storytelling has emerged as an essential capability for marketing leaders who must translate complex analytical findings into compelling narratives that resonate with non-marketing executives. Effective data storytelling combines quantitative analysis with qualitative context to explain not just what happened, but why it happened and what it means for future business performance.
The frequency and format of ROI communication should be tailored to the needs and preferences of different stakeholder groups. CEOs and CFOs may prefer high-level summaries that focus on business impact, while sales leaders may want detailed information about lead quality and conversion rates. Marketing leaders must develop communication strategies that provide appropriate levels of detail for different audiences while maintaining consistency in core messages.
Transparency about limitations and challenges builds credibility and trust with other executives. Rather than presenting only positive results, effective marketing leaders acknowledge areas where performance falls short of expectations and explain what steps are being taken to address these issues. This transparency demonstrates accountability and professional maturity that enhances rather than undermines marketing’s credibility.
Continuous Optimization and Improvement
ROI measurement is most valuable when it drives continuous optimization and improvement rather than simply providing historical reporting. The dynamic nature of digital marketing environments requires ongoing testing, experimentation, and refinement of strategies and tactics based on performance data and market feedback.
A/B testing and multivariate testing provide systematic approaches to optimization that enable marketing teams to identify the most effective approaches to messaging, design, timing, and targeting. However, effective testing requires careful experimental design, adequate sample sizes, and rigorous analysis of results. Marketing leaders must develop testing capabilities that balance the need for rapid optimization with the requirements for statistical validity.
The integration of testing results into broader optimization strategies requires a sophisticated understanding of how different variables interact and affect overall performance. Individual test results must be interpreted within the context of broader marketing strategies and business objectives to ensure that optimization efforts support rather than undermine long-term positioning and brand building.
Competitive benchmarking provides external reference points for performance assessment and optimization. Understanding how marketing performance compares to industry standards and competitive benchmarks helps marketing leaders identify areas for improvement and set realistic performance targets. However, benchmarking must account for differences in business models, target markets, and competitive positioning.
The documentation and sharing of optimization insights across the organization enables broader learning and improvement. When marketing teams discover effective approaches or identify common pitfalls, sharing these insights with other functions can improve overall organizational performance. This knowledge sharing also demonstrates marketing’s analytical capabilities and strategic thinking to other executives.
| Measurement Component | Key Metrics | Reporting Frequency | Primary Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic Impact | Revenue growth, market share, customer lifetime value | Quarterly | CEO, CFO, Board |
| Operational Performance | Lead generation, conversion rates, cost per acquisition | Monthly | Sales, Marketing |
| Tactical Execution | Campaign performance, engagement rates, channel ROI | Weekly | Marketing Team |
| Customer Experience | Satisfaction scores, retention rates, advocacy metrics | Monthly | Customer Success |
Technology Enablement: Automation and Analytics
The technological foundation of modern digital marketing leadership extends far beyond simple tool adoption to encompass sophisticated integration of automation, analytics, and artificial intelligence capabilities that amplify human expertise and enable scalable execution. The strategic deployment of marketing technology represents a critical differentiator between organizations that achieve sustainable competitive advantages and those that struggle to keep pace with market evolution.
Marketing automation technologies have demonstrated substantial value potential, with Nucleus Research documenting an average ROI of $5.44 for every dollar invested over the first three years of deployment [3]. However, realizing this value requires sophisticated implementation approaches that go beyond technology deployment to encompass process redesign, team training, and cultural transformation.
The key benefit areas identified by Nucleus Research include increased marketer productivity, enhanced campaign efficiency, cost savings from automation, simplified infrastructure, and improved prospect engagement [3]. These benefits are achieved through the systematic automation of repetitive tasks, the personalization of customer communications at scale, and the optimization of campaign timing and targeting based on real-time customer behavior and preferences.
Analytics and business intelligence platforms provide the data foundation necessary for informed decision-making and continuous optimization. The integration of customer data from multiple sources, including CRM systems, marketing automation platforms, website analytics, social media metrics, and sales performance data, creates comprehensive views of marketing performance that enable sophisticated analysis and optimization.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities are increasingly being integrated into marketing technology stacks to automate analysis, identify patterns, and generate insights that would be difficult or impossible to discover through manual analysis. These capabilities can augment human expertise and automate routine tasks, enabling marketing teams to focus on strategic thinking and creative problem-solving.
Visual Framework: Dashboard and Metrics
Effective visualization of marketing performance data is essential for enabling rapid decision-making, facilitating stakeholder communication, and maintaining organizational alignment around marketing objectives. Well-designed dashboards and reporting frameworks provide the visual foundation for data-driven marketing leadership.
Dashboard design principles must balance comprehensiveness with usability, ensuring that critical information is immediately accessible while providing drill-down capabilities for detailed analysis. The most effective dashboards present information hierarchically, with high-level summaries supported by detailed breakdowns that enable users to understand both overall performance and specific contributing factors.
Real-time monitoring capabilities enable marketing teams to identify and respond to performance issues before they significantly impact business outcomes. However, the frequency of monitoring must be balanced against the practical limitations of analysis and response capabilities to avoid creating excessive administrative burden or analysis paralysis.
| Dashboard Section | Key Metrics | Update Frequency | Primary Users |
|---|---|---|---|
| Executive Summary | Revenue impact, ROI, goal progress | Daily | Leadership team |
| Campaign Performance | Conversion rates, cost per acquisition, engagement | Real-time | Marketing managers |
| Channel Analysis | Channel ROI, attribution, traffic sources | Weekly | Channel specialists |
| Customer Journey | Funnel conversion, touchpoint analysis, retention | Monthly | Strategy team |
Actionable Implementation Plan
Transforming digital marketing leadership from its current state to a high-performance, strategically aligned function requires systematic implementation of the frameworks and practices outlined in this analysis. The following action plan provides a structured approach to implementation that balances the need for rapid improvement with the practical constraints of organizational change management.
Phase 1: Foundation Building (Months 1-3)
The foundation phase focuses on establishing the basic infrastructure and capabilities necessary for effective digital marketing leadership. This phase includes goal setting, team assessment, technology audit, and initial process development.
- Conduct comprehensive marketing audit: Assess current capabilities, technologies, processes, and performance metrics to establish a baseline understanding
- Define SMART goals and KPIs: Establish specific, measurable objectives that align with business priorities and executive expectations
- Evaluate team capabilities: Identify skill gaps, training needs, and organizational structure requirements
- Audit technology stack: Assess current marketing technologies and identify integration, upgrade, or replacement needs
- Establish measurement framework: Implement basic tracking and reporting capabilities for essential metrics
Phase 2: Capability Development (Months 4-9)
The capability development phase focuses on building the skills, processes, and technologies necessary for advanced digital marketing execution. This phase includes team training, technology implementation, and process optimization.
- Implement marketing automation: Deploy and configure marketing automation platforms to support lead nurturing and campaign management
- Develop content strategy: Create comprehensive content planning and production processes aligned with customer journey mapping
- Enhance analytics capabilities: Implement advanced analytics tools and develop data analysis competencies
- Optimize channel integration: Develop coordinated approaches to multi-channel campaign execution and measurement
- Establish testing protocols: Implement systematic A/B testing and optimization processes
Phase 3: Performance Optimization (Months 10-12)
The performance optimization phase focuses on refining and scaling successful approaches while addressing remaining gaps and challenges. This phase includes advanced optimization, stakeholder alignment, and strategic planning for continued improvement.
- Implement advanced attribution: Deploy sophisticated attribution modeling to understand true marketing impact
- Optimize automation workflows: Refine marketing automation processes based on performance data and customer feedback
- Enhance stakeholder communication: Develop comprehensive reporting and communication strategies for different executive audiences
- Scale successful programs: Expand high-performing campaigns and strategies while maintaining quality and consistency
- Plan for continuous improvement: Establish ongoing optimization processes and strategic planning capabilities
| Phase | Duration | Key Deliverables | Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foundation Building | 3 months | Audit report, goal framework, team plan | Baseline established, goals defined |
| Capability Development | 6 months | Technology implementation, process documentation | Automation ROI, team productivity |
| Performance Optimization | 3 months | Advanced analytics, stakeholder alignment | Revenue impact, executive satisfaction |
Future Outlook: Trends and Challenges
The future of digital marketing leadership will be shaped by several converging trends that present both opportunities and challenges for marketing leaders. Understanding these trends and preparing for their implications is essential for maintaining competitive advantage and organizational relevance.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning will continue to transform marketing capabilities, enabling more sophisticated personalization, predictive analytics, and automated optimization. However, the successful deployment of these technologies will require marketing leaders who understand both their capabilities and limitations and who can integrate AI-driven insights with human creativity and strategic thinking.
Privacy regulations and changing data availability will require marketing leaders to develop new approaches to customer understanding and targeting that respect privacy while maintaining effectiveness. The deprecation of third-party cookies and increasing privacy restrictions will accelerate the importance of first-party data collection and customer relationship building.
The continued evolution of customer expectations will require marketing organizations to become more agile and responsive while maintaining consistency and quality. The pace of change in customer preferences, technology capabilities, and competitive dynamics will continue to accelerate, requiring marketing leaders who can balance strategic consistency with tactical flexibility.
Cross-functional collaboration will become increasingly important as customer experiences span multiple organizational functions and touchpoints. Marketing leaders will need to develop sophisticated partnership and influence skills to coordinate activities across sales, customer service, product development, and other functions.
The measurement and demonstration of marketing ROI will remain a critical challenge and opportunity. Marketing leaders who can effectively quantify and communicate their business impact will gain increased organizational influence and resource allocation, while those who cannot may find their roles further marginalized.
Key Takeaways
- Marketing leadership faces a crisis of confidence: CMO representation at Fortune 500 companies declined from 71% to 66% in 2024, while marketing budgets dropped from 9.1% to 7.7% of revenue, despite widespread recognition of marketing’s strategic importance.
- Customer complexity demands sophisticated coordination: B2B buyers now engage with 10 touchpoints during their purchasing journey (up from 5 in 2016), while 80% of consumers use multiple channels for research and purchase, requiring unprecedented levels of coordination and integration.
- Marketing automation delivers substantial ROI when properly implemented: Organizations achieve an average return of $5.44 for every dollar spent on marketing automation over three years, with payback periods under six months and benefits including increased productivity, campaign efficiency, and prospect engagement.
- Measurement capabilities determine organizational influence: Only 30% of CMOs believe there is a clearly defined view of marketing ROI (down from 40%), while 70% of CEOs measure marketing impact based on revenue growth compared to only 35% of CMOs tracking this metric.
- Execution excellence requires systematic approaches: Success depends on building diverse teams, implementing data-driven decision making, leveraging marketing automation effectively, and maintaining continuous performance monitoring and optimization processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary cause of the marketing leadership crisis?
The crisis stems from multiple factors, including unclear role definitions, measurement challenges, budget constraints, and misalignment between CEO and CMO expectations. Only 70% of CEOs believe marketing’s role is clearly defined (down from 90%), while significant gaps exist in how marketing performance is measured and communicated.
How can marketing leaders demonstrate ROI more effectively?
Effective ROI demonstration requires establishing measurement building blocks, including appropriate metrics, data integration, standardized processes, and technology infrastructure. Marketing leaders must focus on strategic, operational, and tactical metrics that align with business objectives while developing clear communication strategies for different stakeholder groups.
What are the most important capabilities for digital marketing teams?
Modern digital marketing teams require diverse capabilities, including content production, search optimization, data analysis, campaign management, marketing automation, customer experience design, and performance measurement. However, the key is creating collaborative structures that enable these capabilities to work together effectively.
How should organizations approach marketing automation implementation?
Successful marketing automation implementation requires careful consideration of customer journey mapping, content development, lead scoring, and nurturing workflows. Organizations should focus on automating appropriate processes while ensuring that automation enhances rather than replaces human insight and creativity.
What trends will shape the future of digital marketing leadership?
Key trends include the continued evolution of AI and machine learning capabilities, changing privacy regulations and data availability, increasing customer expectations for personalized experiences, greater need for cross-functional collaboration, and ongoing pressure to demonstrate measurable business impact.
References
- McKinsey & Company. (2025, June 16). The CMO’s comeback: Aligning the C-suite to drive customer-centric growth. Retrieved from https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/growth-marketing-and-sales/our-insights/the-cmos-comeback-aligning-the-c-suite-to-drive-customer-centric-growth
- Spencer Stuart. (2024). Fortune 500 CMO Study. Referenced in McKinsey research on marketing leadership trends.
- Nucleus Research. (2021, March 26). Marketing automation returns $5.44 for every dollar spent. Retrieved from https://nucleusresearch.com/research/single/marketing-automation-returns-5-44-for-every-dollar-spent/
- Lead Forensics. (2025). 29 Must-Know B2B Marketing Statistics for 2025. Retrieved from https://www.leadforensics.com/blog/24-must-know-b2b-marketing-statistics-for-2025/
- Gartner. (2024, November 20). Marketing ROI Metrics to Quantify Impact. Retrieved from https://www.gartner.com/en/articles/marketing-roi-metrics
- Forrester Research. (2024). Marketing leadership representation study. Referenced in McKinsey research on C-suite marketing representation.
- HubSpot. (2025). 2025 Marketing Statistics, Trends & Data. Retrieved from https://www.hubspot.com/marketing-statistics
- WordStream. (2025, May 19). 180+ Powerful Digital Marketing Statistics for 2025. Retrieved from https://www.wordstream.com/blog/ws/2022/04/19/digital-marketing-statistics

