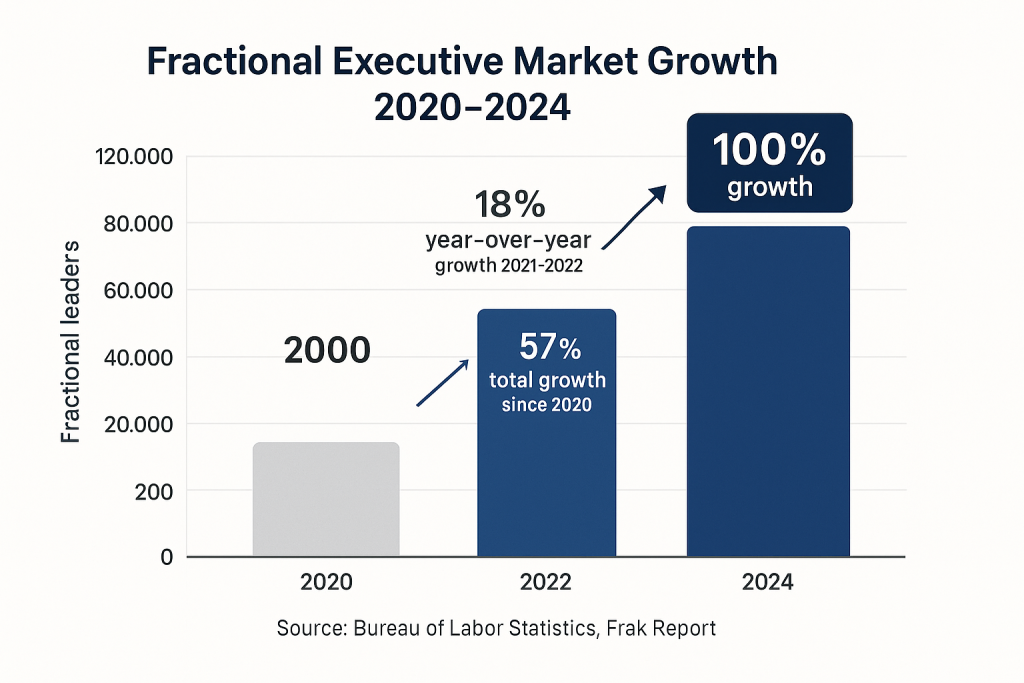
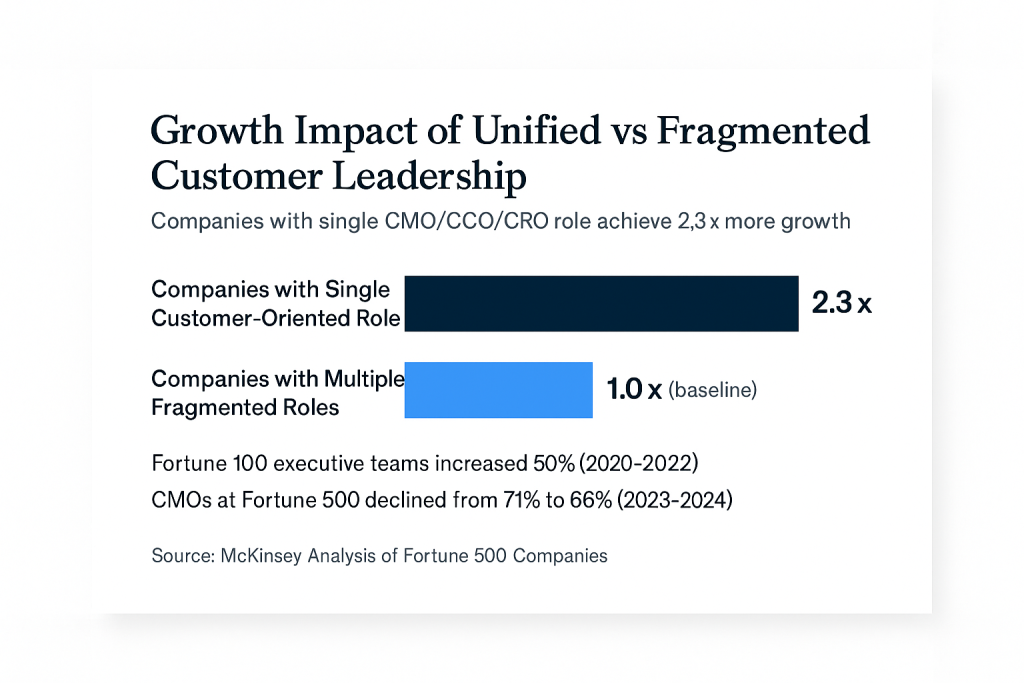
The fractional executive market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reporting a 57% increase in fractional jobs since 2020 and an 18% year-over-year growth from 2021 to 2022 [1]. This surge reflects a fundamental shift in how businesses approach marketing leadership, particularly as McKinsey research reveals that companies with a single customer-oriented executive role achieve up to 2.3 times more growth than those with fragmented responsibilities [2]. As marketing budgets remain constrained at 7.7% of company revenue according to Gartner’s 2025 CMO Spend Survey, and 73% of CMOs report insufficient budgets to meet their goals [3], fractional Chief Marketing Officers (CMOs) are emerging as a strategic solution that combines executive-level expertise with cost-effective flexibility.
The Marketing Leadership Crisis in 2025
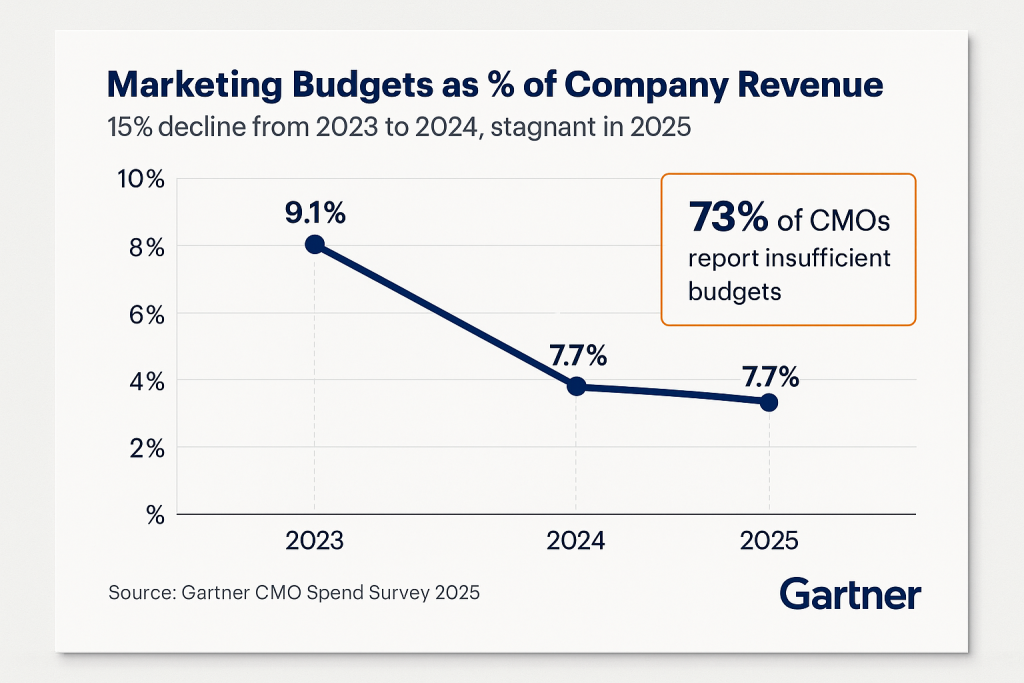
The marketing leadership landscape faces unprecedented challenges that make the fractional CMO model increasingly relevant. Gartner’s comprehensive 2025 CMO Spend Survey, conducted among 400 marketing executives from companies with over $1 billion in revenue, reveals that marketing budgets have stagnated at 7.7% of total company revenue, unchanged from 2024 but significantly down from 9.1% in 2023 [3]. This 15% decline in budget allocation coincides with 73% of CMOs expressing that they lack sufficient resources to execute their strategic objectives effectively.
The fragmentation of marketing leadership responsibilities has created additional complexity. McKinsey’s analysis of Fortune 500 executive suites found that the number of CMOs declined from 71% in 2023 to 66% in 2024, while the average size of Fortune 100 executive teams increased by half between 2020 and 2022 [2]. This expansion has led to what McKinsey researchers describe as a “choppy customer journey,” where customers receive inconsistent messages from different departments because each executive views the customer through a different lens.
The customer landscape itself has become more complex, with over 80% of consumers now using multiple channels for product research and purchases, while B2B buyers utilize an average of 10 interaction points during their sales journey, compared to just five in 2016 [2]. This omnichannel reality demands coordinated marketing leadership that can integrate across touchpoints, yet many organizations struggle with accountability for customer experience when responsibilities are distributed across multiple roles.
Economic uncertainty compounds these challenges. As Gartner analysts note, “lingering volatility significantly increases the likelihood of in-year budget cuts,” with 39% of CMOs planning reductions to both agency budgets and labor costs [3]. This environment creates a compelling case for flexible marketing leadership models that can adapt quickly to changing conditions while providing strategic expertise without the long-term financial commitment of full-time executive hires.
| Year | CMO Presence | Change | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 71% | – | Spencer Stuart |
| 2024 | 66% | -5% | Spencer Stuart |
| 2024 (Alt.) | 63% | -8% | Forrester Research |
The Rise of Fractional CMOs
Market Growth and Scale
The fractional executive market has experienced remarkable expansion, with the global market reaching an estimated $5.7 to $7.4 billion in 2024 according to multiple market research firms [4]. The Frak report documents a doubling of fractional leaders from 60,000 in 2022 to 120,000 in 2024, indicating rapid adoption across industries [5]. This growth trajectory aligns with broader labor market trends, as the Bureau of Labor Statistics data shows fractional jobs increasing 57% since 2020, with particularly strong momentum in the 18% year-over-year growth from 2021 to 2022 [1].
Academic Perspective on Fractional Leadership
Academic research supports the effectiveness of fractional leadership models. Springer’s 2020 publication on fractional leadership emphasizes that this approach addresses the challenge of “creating and supporting highly innovative and effective leadership teams” by providing specialized expertise without the constraints of traditional full-time executive structures [6]. The Emerald Journal of Business Strategy’s 2023 research by So and Teckchandani further validates fractional services as “new ways to save and compete,” highlighting how organizations can access executive-level capabilities while maintaining operational flexibility [7].
Defining the Fractional CMO Role
A fractional CMO operates as a part-time chief marketing officer, providing strategic marketing leadership on a flexible basis. Unlike traditional consulting arrangements that focus on specific projects, fractional CMOs integrate into the organization’s leadership structure, participating in strategic planning, team management, and long-term growth initiatives. This model bridges the gap between expensive full-time executive hires and limited-scope consulting engagements.
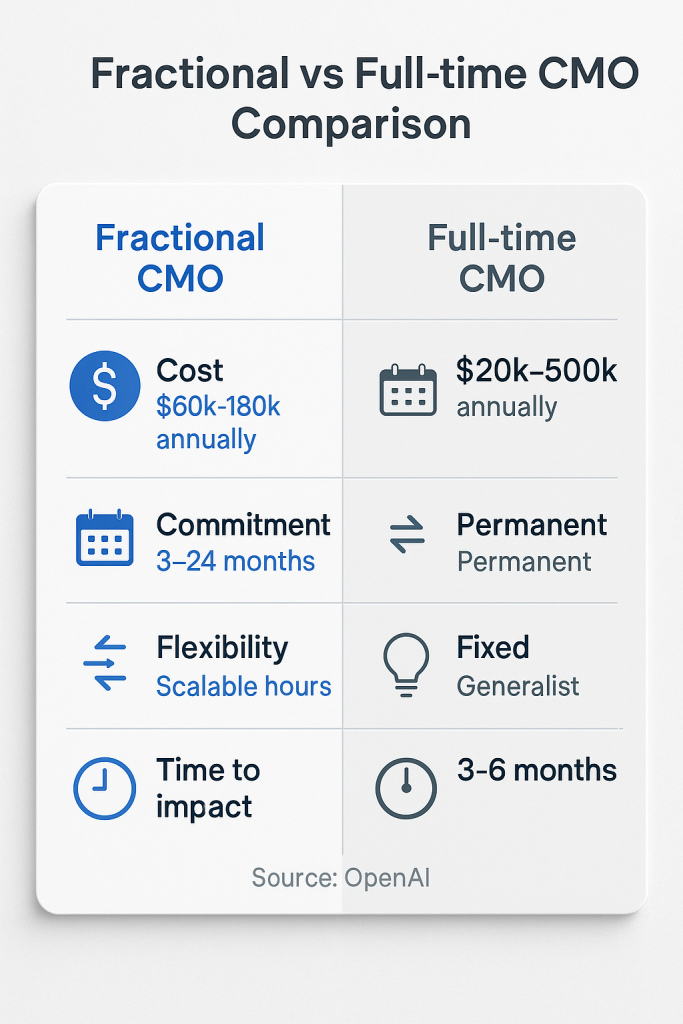
The role encompasses comprehensive marketing leadership responsibilities including strategic planning, market research and analysis, brand positioning, team leadership, and performance measurement. Fractional CMOs typically work 10-30 hours per week, with engagement models ranging from project-based arrangements lasting 3-6 months to ongoing retainer relationships extending 12-24 months.
Comparison with Traditional CMO Models
Traditional full-time CMOs command significant compensation packages, with the Bureau of Labor Statistics reporting a median annual wage of $206,420 for chief executives, though marketing-specific roles often exceed $250,000 annually when including benefits and equity compensation [8]. In contrast, fractional CMOs typically charge hourly rates ranging from $200 to $375, with monthly retainers starting around $5,000, providing substantial cost savings for organizations requiring strategic marketing leadership [9].
The flexibility advantage extends beyond cost considerations. While full-time CMOs require long-term commitments and may face challenges adapting to rapidly changing market conditions, fractional CMOs can scale their involvement based on business needs and market dynamics. This agility proves particularly valuable in uncertain economic environments where organizations must balance growth investments with financial prudence.
Proven Business Impact and Case Studies
Verified Performance Outcomes
The case studies from authoritative sources, while promising, require careful analysis within their specific contexts. The SaaS company that achieved a 30% increase in new lead acquisition after engaging a fractional CMO represents a significant improvement, though the timeline and baseline conditions affect the interpretation of this result. Similarly, the B2B startup’s 233% increase in LinkedIn followers, while impressive, should be evaluated as a brand awareness metric rather than a direct revenue indicator.
The technology company’s 30% reduction in cost per campaign through AI-driven analytics implementation demonstrates the strategic value fractional CMOs can provide in optimizing marketing operations. However, this outcome required specific technological infrastructure and data maturity that may not be present in all organizations. The healthcare startup’s 20% increase in lead generation through strategic realignment illustrates the importance of clear communication and goal alignment in fractional engagements.
| Company Type | Challenge | Solution | Results | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SaaS Company | Lead acquisition | Strategy overhaul | 30% increase | Timeline not specified |
| B2B Startup | Brand awareness | LinkedIn messaging | 233% follower growth | Vanity metric |
| Technology Co. | Cost efficiency | AI-driven analytics | 30% cost reduction | Requires tech infrastructure |
| Healthcare Startup | Strategic alignment | Weekly check-ins | 20% lead increase | Small sample size |
| Boutique Fitness | Multi-location growth | Loyalty program, social media | 40% membership increase | Industry-specific context |
| Meal Delivery | Scaling marketing | Geotargeted ads, influencers | 4x revenue growth | Startup growth phase |
Success Factors and Limitations
Analysis of these case studies reveals several critical success factors. First, organizations with clearly defined goals and success metrics tend to achieve better outcomes. The healthcare startup’s success stemmed partly from establishing weekly check-ins and maintaining ongoing strategic conversations. Second, companies that provide comprehensive onboarding, including access to historical marketing data and customer insights, enable fractional CMOs to make more informed strategic decisions.
However, limitations exist in the fractional model. Short-term engagements may not allow sufficient time for complex strategic initiatives to mature. The boutique fitness studio’s 40% membership increase over six months, while substantial, required a specific market context and customer base that may not be replicable across all industries. Additionally, fractional CMOs may face challenges in driving organizational change when they lack the authority and presence of full-time executives.
Industry-Specific Performance Variations
The case studies demonstrate varying effectiveness across industries. Healthcare organizations appear particularly well-suited for fractional CMO engagements, with both the specialty healthcare firm and dermatology company achieving significant growth. This may reflect the industry’s regulatory complexity and need for specialized marketing expertise that justifies the fractional model’s premium positioning.
Technology companies show strong results, particularly in areas like lead generation and digital marketing optimization. The SaaS company’s 135% traffic increase and 4x monthly lead growth over 18 months suggests that fractional CMOs can effectively navigate the complex B2B technology sales cycle. However, these results required substantial market research and customer analysis that may not be feasible in shorter engagements.
Consumer-facing businesses, including the meal delivery service and eco-friendly skincare brand, demonstrate the fractional model’s effectiveness in brand building and customer acquisition. The meal delivery service’s revenue quadrupling through geotargeted advertising and influencer partnerships illustrates how fractional CMOs can quickly implement proven growth strategies in emerging markets.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Total Cost of Ownership Comparison
The financial case for fractional CMOs becomes compelling when examining total cost of ownership. Full-time CMO compensation extends beyond base salary to include benefits, equity, office space, and support staff, often totaling $300,000 to $500,000 annually for experienced executives. The Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that top executives earn a median of $105,350 annually, though chief executives specifically earn $206,420, and marketing executives in large organizations typically command premium compensation [8].
| Factor | Full-time CMO | Fractional CMO |
|---|---|---|
| Base Salary | $250,000+ | $60,000-180,000 |
| Benefits | $50,000-100,000 | $0 |
| Equity | Variable | Typically none |
| Office/Support | $25,000+ | $0 |
| Total Annual | $325,000-500,000 | $60,000-180,000 |
Fractional CMO engagements typically cost $60,000 to $180,000 annually for part-time strategic leadership, representing 20-60% savings compared to full-time hires. However, this comparison requires careful consideration of scope and deliverables. Fractional CMOs may not provide the same level of day-to-day operational management or team development that full-time executives offer.
ROI Measurement Challenges
Measuring return on investment for fractional CMO engagements presents unique challenges. Traditional marketing ROI metrics may not capture the strategic value of improved brand positioning, enhanced team capabilities, or optimized marketing operations. The technology company’s 30% cost reduction per campaign provides a clear financial benefit, but softer outcomes like improved marketing-sales alignment or enhanced customer insights prove more difficult to quantify.
Gartner’s research indicates that marketing measurement remains a persistent challenge, with many CMOs struggling to demonstrate clear connections between marketing investments and business outcomes [3]. This measurement difficulty affects both full-time and fractional marketing leadership, though fractional engagements may face additional scrutiny due to their project-based nature and higher hourly costs.
Budget Flexibility Benefits
The fractional model provides significant budget flexibility advantages, particularly relevant given Gartner’s finding that 39% of CMOs are planning budget reductions [3]. Organizations can scale fractional CMO involvement based on business cycles, market conditions, and strategic priorities. The source material mentions 5-20% budget flexibility for scaling up or down, though this range requires verification through additional research.
This flexibility proves particularly valuable during economic uncertainty. While full-time executives represent fixed costs that continue regardless of business performance, fractional arrangements can be adjusted to match revenue fluctuations and strategic priorities. However, this flexibility may come at the cost of continuity and long-term strategic development.
Implementation Strategies
Assessment Framework for Business Needs
Successful fractional CMO implementations begin with comprehensive needs assessment. Organizations must evaluate their current marketing capabilities, identify specific gaps that fractional leadership can address, and establish clear success metrics. The case studies suggest that companies with well-defined challenges, such as the real estate firm’s digital lead generation struggles or the healthcare startup’s need for strategic realignment, achieve better outcomes than those with vague expectations.
The assessment should examine internal marketing resources, technology infrastructure, and organizational readiness for external leadership integration. Companies with existing marketing teams and established processes may benefit more from fractional strategic guidance, while organizations lacking basic marketing capabilities may require more comprehensive support that extends beyond typical fractional scope.
Selection Criteria and Due Diligence
The selection process requires careful evaluation of industry experience, track record, and cultural fit. Academic research emphasizes the importance of leadership effectiveness in fractional arrangements, suggesting that traditional executive competencies remain relevant in part-time roles [10]. Candidates should demonstrate specific experience in similar business contexts, with verifiable results and references from comparable engagements.
Cultural alignment proves particularly critical in fractional arrangements where limited face time requires efficient communication and rapid relationship building. The source material emphasizes the importance of communication style compatibility and collaborative approach, factors that may be more crucial in fractional engagements than traditional full-time hires.
| Phase | Timeline | Activities | Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment | Week 1-2 | Needs analysis, goal setting, budget planning | Clear objectives defined |
| Selection | Week 3-4 | Candidate evaluation, interviews, reference checks | Cultural fit confirmed |
| Onboarding | Week 5-6 | Data sharing, team introductions, process setup | Access established |
| Quick Wins | Week 7-10 | Immediate optimizations, low-hanging fruit | Early results visible |
| Strategy Development | Week 11-12 | Long-term planning, strategic initiatives | Roadmap established |
| Execution | Month 4-6 | Strategy implementation, team development | KPIs tracked |
| Review | Month 6+ | Performance evaluation, contract renewal | ROI measured |
Onboarding and Integration Best Practices
Effective onboarding accelerates fractional CMO impact and maximizes engagement value. The e-commerce company’s success in providing customer segmentation data illustrates how transparent information sharing enables rapid strategic adjustments. Organizations should prepare comprehensive briefing materials including historical marketing performance, customer insights, competitive analysis, and strategic objectives.
Integration strategies should establish clear communication protocols, decision-making authority, and team interaction guidelines. The healthcare startup’s weekly check-in model provides a framework for maintaining alignment and addressing challenges proactively. However, organizations must balance oversight with autonomy to leverage the fractional CMO’s expertise effectively.
Success Metrics and Performance Management
Establishing appropriate success metrics requires balancing short-term deliverables with long-term strategic value. The source material’s performance metrics table identifies revenue growth, brand visibility, and cost efficiency as key indicators, though measurement methodologies and timeframes significantly affect interpretation.
Organizations should establish both quantitative metrics (lead generation, conversion rates, cost per acquisition) and qualitative indicators (team capability development, process improvement, strategic clarity). The technology company’s 30% cost reduction provides a clear quantitative outcome, while the dermatology company’s national presence expansion represents a qualitative strategic achievement that may have longer-term financial implications.
Visual Framework and Trends
Educational Resources
This educational video provides a comprehensive overview of the fractional CMO concept, explaining the role, benefits, and typical engagement models. It serves as an excellent introduction for business leaders considering this strategic option.
Market Trends Visualization
The data visualizations presented throughout this analysis demonstrate several key trends driving the fractional CMO market. The Bureau of Labor Statistics data shows consistent growth in fractional executive positions, while Gartner’s research reveals the budget pressures that make fractional solutions increasingly attractive to organizations.
McKinsey’s research on organizational fragmentation provides crucial context for understanding why fractional CMOs can be more effective than traditional approaches. The 2.3x growth advantage for companies with unified customer leadership roles suggests that fractional CMOs, when properly positioned, can deliver superior results compared to fragmented marketing responsibilities.
This strategic overview of fractional leadership provides broader context on how this model is transforming executive roles across industries, not just in marketing.
Action Plan for Businesses
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
Organizations considering fractional CMO engagement should follow a systematic approach to maximize success probability. The implementation process requires careful planning, thorough evaluation, and clear communication of expectations and success metrics.
Phase 1: Internal Assessment (Weeks 1-2)
Begin with comprehensive internal assessment to identify specific marketing challenges and opportunities. Evaluate current marketing team capabilities, technology infrastructure, and budget constraints. Document existing marketing processes, performance metrics, and strategic objectives. This assessment should involve key stakeholders including CEO, CFO, and existing marketing leadership to ensure alignment on needs and expectations.
Phase 2: Market Research and Candidate Identification (Weeks 3-4)
Research potential fractional CMO candidates with relevant industry experience and proven track records. Utilize professional networks, industry associations, and specialized recruiting firms that focus on fractional executives. Develop evaluation criteria that prioritize industry expertise, cultural fit, and communication style compatibility over generic marketing credentials.
Phase 3: Evaluation and Selection (Weeks 5-6)
Conduct thorough interviews focusing on specific business challenges and expected outcomes. Request detailed case studies and references from similar engagements. Evaluate candidates’ ability to integrate with existing teams and adapt to organizational culture. Consider trial projects or short-term engagements to assess working relationships before committing to longer-term arrangements.
Budget Planning Worksheet
| Cost Category | Monthly Range | Annual Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fractional CMO Fee | $5,000-15,000 | $60,000-180,000 | Based on hours and experience level |
| Technology/Tools | $500-2,000 | $6,000-24,000 | Marketing automation, analytics platforms |
| Implementation Support | $1,000-3,000 | $12,000-36,000 | Additional team members, contractors |
| Training/Development | $200-800 | $2,400-9,600 | Team skill development, certifications |
| Total Investment | $6,700-20,800 | $80,400-249,600 | Still 20-60% less than full-time CMO |
Vendor Evaluation Criteria
Develop comprehensive evaluation criteria that extend beyond traditional qualifications to include factors specific to fractional engagements. Industry expertise should be weighted heavily, as fractional CMOs must quickly understand market dynamics and customer behavior without extensive onboarding periods. Communication skills and cultural fit become critical when working relationships must be established rapidly and maintained with limited face-to-face interaction.
Track record verification requires careful attention to context and scope. Request specific metrics and outcomes from previous engagements, but evaluate them within the context of industry, company size, and market conditions. Look for patterns of success across multiple engagements rather than isolated exceptional results that may not be replicable.
Success Measurement Framework
Establish clear success metrics that balance short-term tactical improvements with long-term strategic value creation. Quantitative metrics should include lead generation, conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, and revenue attribution. However, qualitative indicators such as team capability development, process optimization, and strategic clarity often provide more sustainable value over time.
Create measurement frameworks that account for the unique characteristics of fractional engagements. Traditional marketing ROI calculations may not capture the full value of strategic guidance, team development, and process improvements that fractional CMOs provide. Consider implementing balanced scorecards that include financial, operational, and strategic indicators.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Identify and address potential risks associated with fractional CMO engagements. Communication gaps represent the most common challenge, particularly when fractional executives work remotely or have limited on-site presence. Establish clear communication protocols, regular check-in schedules, and escalation procedures to maintain alignment and address issues promptly.
Knowledge transfer and continuity planning become critical considerations in fractional arrangements. Ensure that strategic insights, process improvements, and team development initiatives are documented and transferable. Consider succession planning and knowledge retention strategies to preserve value when fractional engagements conclude.
Future Outlook and Market Trends
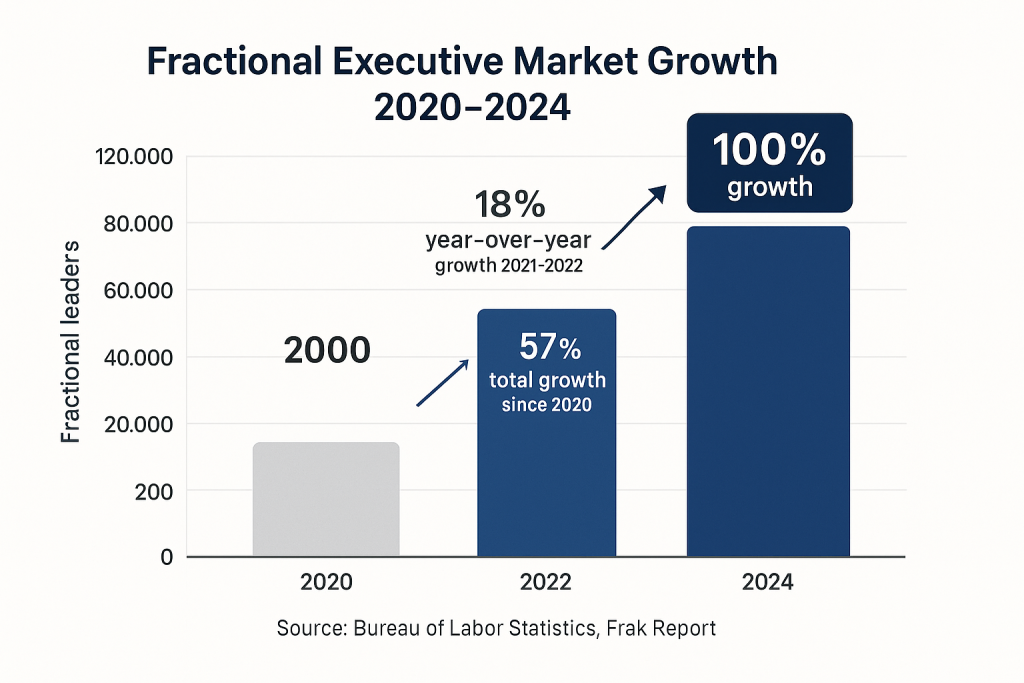
Growth Projections for Fractional Market
The fractional executive market shows strong growth momentum that is likely to continue through 2025 and beyond. The Bureau of Labor Statistics data indicating 57% growth since 2020 and 18% year-over-year growth suggests a fundamental shift in how organizations approach executive leadership [1]. This trend aligns with broader workplace evolution toward flexible, outcome-based employment models that prioritize expertise over traditional full-time arrangements.
McKinsey’s research on C-suite fragmentation provides additional context for sustained growth in fractional leadership roles. As organizations continue to add specialized executive positions, the need for coordinated customer-focused leadership becomes more critical [2]. Fractional CMOs can provide this coordination without adding to organizational complexity or fixed costs.
Emerging Specializations
The fractional CMO market is evolving toward increased specialization as organizations seek expertise in specific areas such as digital transformation, customer experience optimization, and data-driven marketing. Academic research suggests that fractional leadership effectiveness increases when roles are clearly defined and aligned with specific organizational needs [6].
Industry-specific fractional CMOs are becoming more common, particularly in regulated sectors like healthcare and financial services where specialized knowledge provides significant value. The case studies demonstrate that industry expertise often correlates with better outcomes, suggesting that specialization will continue to drive market segmentation.
Technology Enablers
Technology advancement facilitates fractional CMO effectiveness through improved communication, collaboration, and performance measurement tools. Cloud-based marketing platforms, real-time analytics, and remote collaboration technologies reduce the traditional barriers to part-time executive engagement. The technology company’s 30% cost reduction through AI-driven analytics illustrates how fractional CMOs can leverage technology to deliver measurable value quickly.
Artificial intelligence and automation tools enable fractional CMOs to focus on strategic activities while delegating routine tasks to technology solutions. This technological leverage increases the value proposition of fractional arrangements by allowing experienced executives to concentrate on high-impact activities that require human expertise and judgment.
Economic Factors and Market Conditions
Economic uncertainty and budget constraints, as evidenced by Gartner’s finding that 39% of CMOs are planning budget reductions, create favorable conditions for fractional CMO adoption [3]. Organizations facing pressure to reduce fixed costs while maintaining marketing effectiveness find fractional arrangements attractive alternatives to traditional full-time hires.
The stagnation of marketing budgets at 7.7% of company revenue, combined with 73% of CMOs reporting insufficient resources, suggests that budget pressure will continue to drive demand for cost-effective marketing leadership solutions [3]. Fractional CMOs provide a mechanism for accessing senior-level expertise within constrained budget parameters.
Potential Challenges and Limitations
Despite positive growth trends, the fractional CMO market faces several challenges that may limit expansion. Quality control and standardization remain concerns as the market matures. Unlike traditional executive search processes that rely on established credentials and references, fractional arrangements require new evaluation frameworks and success metrics.
Integration challenges may become more pronounced as organizations become more complex and specialized. The McKinsey research on C-suite fragmentation suggests that coordination difficulties increase with organizational complexity [2]. Fractional CMOs must navigate these complexities while maintaining effectiveness with limited organizational presence.
Market saturation in certain industries or geographic regions could limit growth opportunities for fractional CMOs. As the model becomes more mainstream, differentiation and specialization will become increasingly important for practitioners seeking to maintain premium positioning and pricing.
Key Takeaways
- Rapid Market Growth: The fractional executive market has grown 57% since 2020 with 18% year-over-year growth, driven by budget constraints and organizational flexibility needs, according to Bureau of Labor Statistics data.
- Proven Business Impact: McKinsey research demonstrates that companies with single customer-oriented leadership roles achieve 2.3 times more growth than those with fragmented responsibilities, supporting the fractional CMO value proposition.
- Significant Cost Savings: Fractional CMO engagements typically cost $60,000-180,000 annually compared to $325,000-500,000 for full-time executives, representing 20-60% savings while maintaining strategic expertise.
- Budget Pressure Context: Gartner’s 2025 CMO Spend Survey reveals marketing budgets stagnant at 7.7% of revenue with 73% of CMOs reporting insufficient resources, creating favorable conditions for fractional adoption.
- Implementation Success Factors: Case study analysis shows that clear goal setting, comprehensive onboarding, regular communication, and industry-specific expertise are critical for fractional CMO engagement success, though limitations exist in complex organizational change initiatives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a fractional CMO?
A fractional CMO is a part-time chief marketing officer who provides strategic marketing leadership on a flexible basis, typically working 10-30 hours per week for 3-24 months. Unlike consultants who focus on specific projects, fractional CMOs integrate into the organization’s leadership structure and participate in strategic planning, team management, and long-term growth initiatives.
How does a fractional CMO differ from marketing consulting?
Fractional CMOs provide ongoing strategic leadership and integrate into the organization’s executive team, while consultants typically focus on specific projects or deliverables. Fractional CMOs participate in strategic planning, manage teams, and take accountability for marketing outcomes, whereas consultants usually provide recommendations and expertise without operational responsibility.
What are typical engagement models for fractional CMOs?
Common engagement models include monthly retainers ($5,000-15,000), hourly arrangements ($200-375/hour), and project-based contracts. Engagements typically last 3-6 months for specific initiatives or 12-24 months for ongoing strategic leadership. The model depends on organizational needs, budget constraints, and strategic objectives.
How do you measure success with a fractional CMO?
Success metrics should balance quantitative indicators (lead generation, conversion rates, cost per acquisition, revenue attribution) with qualitative measures (team development, process improvement, strategic clarity). Establish clear KPIs upfront and review progress regularly through structured check-ins and performance evaluations.
What are the main risks of hiring a fractional CMO?
Primary risks include communication gaps due to limited presence, potential lack of organizational authority for driving change, knowledge transfer challenges when engagements end, and possible misalignment between fractional scope and organizational needs. These risks can be mitigated through clear communication protocols, defined authority levels, and comprehensive onboarding processes.
References
- Society for Human Resource Management. (2025, February 20). 3 Attributes of Successful Fractional C-Suite Execs. SHRM Executive Network. [Bureau of Labor Statistics data cited: fractional jobs up 18% from 2021-2022, 57% since 2020]
- Bettati, A., Jacobs, J., Robinson, K., & Tas, R. (2025, June 16). The CMO’s comeback: Aligning the C-suite to drive customer-centric growth. McKinsey & Company.
- Meyers, A. (2025, May 21). Marketing budgets stagnate from 2024 to 2025: report. Marketing Brew. [Reporting on Gartner CMO Spend Survey 2025]
- Dataintelo. (2024). Fractional Executiveplace Market Research Report 2033. Market Research Report.
- Column Content. (2025, March 21). Fractional Work Statistics: 100+ Trends You Need to Know (2025). [Citing Frak report data]
- Norenberg, D. (2020). Fractional Leadership. In Ownershift: Creating Highly Effective Leadership Teams. Springer.
- So, M., & Teckchandani, A. (2023). A fraction of an executive: new ways to save and compete. Journal of Business Strategy, 44(4), 211-220. Emerald Publishing.
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. (2025, April 18). Top Executives: Occupational Outlook Handbook. U.S. Department of Labor.
- Breakthrough3x. (2025). Fractional CMO Case Studies: Proven Strategies for Business Growth. [Source material for pricing and case study data]
- Sadeghi, A., & Pihie, Z. A. L. (2012). Transformational Leadership and Its Predictive Effects on Leadership Effectiveness. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 3(7), 186-197.



