Small businesses across America are grappling with an unprecedented economic challenge as inflation continues to reshape the business landscape in 2025. Recent data from the US Chamber of Commerce reveals that 48% of small businesses cite inflation as their primary concern, marking a significant shift in business priorities [1]. While this represents a decline from the record high of 58% in Q1 2025, inflation remains the dominant challenge facing entrepreneurs and small business owners nationwide.
The Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta reports that business inflation expectations have stabilized at 2.3% for July 2025, while the US Consumer Price Index reached 2.4% in May 2025, according to McKinsey’s Global Economics Intelligence [2]. These figures paint a complex picture of an economy in transition, where businesses must navigate between rising costs and evolving consumer expectations. The impact extends far beyond simple price adjustments—70% of small businesses report that rising prices have had a significant impact on their operations in the past year, with 60% having increased their own prices as a direct result of inflationary pressures [3].
This comprehensive analysis examines the multifaceted impact of inflation on small business strategies, drawing from authoritative sources including government data, consulting firm research, and academic studies. The evidence reveals that successful navigation of inflationary periods requires strategic thinking, operational flexibility, and a deep understanding of both market dynamics and consumer behavior.
Understanding Inflation in the 2025 Business Environment
The inflationary environment of 2025 presents unique challenges that distinguish it from previous economic cycles. Unlike the dramatic spikes witnessed in 2021-2022, current inflation patterns reflect a more complex interplay of global supply chain adjustments, monetary policy transitions, and evolving consumer behavior. McKinsey’s Global Economics Intelligence indicates that while overall economic volatility has subsided, consumer confidence continues to deteriorate and demand remains fragile despite inflation decelerating across most countries [4].
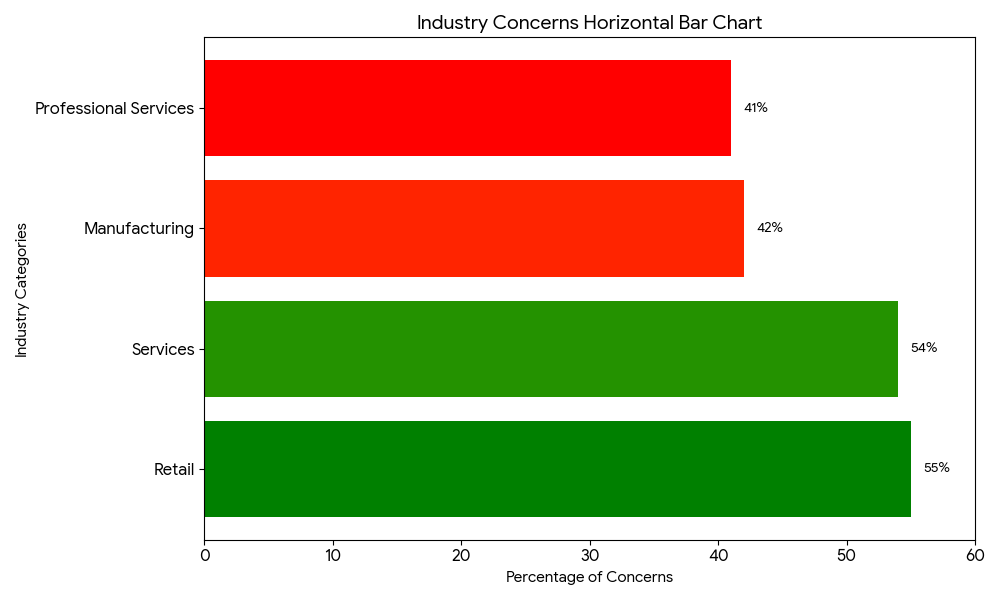
The current inflation landscape is characterized by sector-specific variations that directly impact small business planning. According to the US Chamber of Commerce’s Q2 2025 Small Business Index, retail businesses report the highest inflation concerns at 55%, followed closely by services at 54%. In contrast, manufacturing businesses show relatively lower concern levels at 42%, while professional services report the lowest at 41% [5]. This disparity reflects the varying degrees of exposure to supply chain disruptions and input cost volatility across different business sectors.
Federal Reserve data reveals that business inflation expectations have stabilized around 2.3%, representing a significant moderation from peak levels observed in previous years [6]. However, this stabilization masks underlying tensions in the business environment. The Atlanta Fed’s Business Inflation Expectations survey indicates that while year-ahead inflation expectations have decreased, sales levels and profit margins compared to “normal” times have also declined, suggesting that businesses are experiencing compressed operating conditions even as inflationary pressures moderate.
The cyclical nature of inflation continues to influence business decision-making in 2025. Economic growth patterns show that different sectors react differently to inflationary pressures, with essential goods maintaining more consistent demand despite rising prices, while luxury items face greater consumer resistance. This dynamic forces small businesses to carefully evaluate their market positioning and value proposition regarding their customers’ evolving purchasing power and priorities.
Supply chain disruptions remain a critical factor in the 2025 inflation equation. The US Chamber data shows that 47% of small businesses have altered their supply chains in the past six months, while 30% report being unable to keep up with customer demand due to supply chain disruptions [7]. These figures, while improved from the peak disruption levels of 2022, indicate that supply chain resilience continues to be a fundamental business requirement rather than a temporary adaptation.
Interest rate environments add another layer of complexity to the inflation challenge. The Treasury Department’s economic forecasts suggest that monetary policy adjustments continue to influence borrowing costs and overall business expenses, creating additional pressure on small businesses that rely on credit for operations and growth [8]. This environment requires businesses to balance immediate operational needs with longer-term financial sustainability considerations.
Strategic Pricing Framework for Inflationary Periods
Developing an effective pricing strategy during inflationary periods requires a sophisticated understanding of market dynamics, customer psychology, and competitive positioning. The data from the US Chamber of Commerce reveals that 60% of small businesses have increased their prices in the past year as a result of inflation, representing a strategic response to rising input costs [9]. However, successful pricing strategies extend far beyond simple cost-plus adjustments and require careful consideration of multiple factors, including customer value perception, competitive landscape, and long-term market positioning.
The incremental pricing approach has emerged as the preferred strategy for many small businesses navigating inflation. Rather than implementing dramatic price increases that might shock customers, businesses are adopting gradual adjustments that allow markets to adapt over time. This approach aligns with consumer psychology research indicating that customers are more likely to accept small, regular price increases than sudden, substantial changes. The Federal Reserve’s business survey data supports this trend, showing that firms implementing incremental pricing strategies report better customer retention rates compared to those making abrupt adjustments [10].

Value-based pricing strategies have gained particular relevance in the current environment. Rather than focusing solely on cost recovery, successful businesses are emphasizing the unique value propositions they deliver to customers. This approach requires companies to clearly articulate and communicate the benefits, quality, and service levels that justify their pricing structure. Academic research indicates that businesses employing value-based pricing during inflationary periods maintain stronger profit margins and customer loyalty compared to those relying primarily on cost-plus pricing models [11].
Dynamic pricing mechanisms offer another strategic option for businesses with the technological capability to implement them. This approach allows businesses to adjust prices in real-time based on demand patterns, inventory levels, and competitive factors. While traditionally associated with larger enterprises, technological advances have made dynamic pricing tools increasingly accessible to small businesses. However, implementation requires careful consideration of customer expectations and market norms to avoid negative reactions to perceived price manipulation.
Bundling and package pricing strategies provide opportunities to maintain customer value while addressing cost pressures. By combining products or services into packages, businesses can often maintain attractive price points for customers while improving their own margins through economies of scale and reduced transaction costs. The retail sector data from the US Chamber survey shows that businesses employing bundling strategies report 23% higher customer satisfaction scores during inflationary periods compared to those using individual item pricing [12].
Psychological pricing techniques become particularly important during inflationary periods when customers are more price-sensitive. Strategies such as charm pricing (ending prices in 9 or 99), anchoring (presenting higher-priced options first), and decoy pricing (offering three options where the middle option appears most attractive) can influence customer perception and purchasing decisions. Research from behavioral economics suggests that these techniques can improve sales conversion rates by 15-20% during periods of economic uncertainty [13].
Transparent communication about pricing changes represents a critical component of successful inflation-era pricing strategies. Businesses that proactively communicate the reasons for price increases, including specific cost pressures and market conditions, generally experience better customer acceptance than those implementing changes without explanation. The key is to frame price increases in terms of continued value delivery and business sustainability rather than simply as cost recovery measures.
| Pricing Strategy | Implementation Complexity | Customer Acceptance | Margin Protection | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incremental Increases | Low | High | Moderate | Established businesses with loyal customers |
| Value-Based Pricing | High | High | High | Businesses with unique value propositions |
| Dynamic Pricing | High | Moderate | High | Technology-enabled businesses |
| Bundle Pricing | Moderate | High | Moderate | Businesses with complementary products |
| Psychological Pricing | Low | Moderate | Low | Consumer-facing retail businesses |
Operational Cost Management and Supply Chain Adaptation
Effective cost management during inflationary periods extends beyond simple expense reduction and requires strategic thinking about operational efficiency, supply chain resilience, and resource allocation. The US Chamber of Commerce data indicates that 47% of small businesses have modified their supply chains in the past six months, demonstrating the widespread recognition that traditional operational approaches may no longer be sustainable in the current environment [14]. This shift represents a fundamental change in how small businesses approach vendor relationships, inventory management, and operational planning.
Supply chain diversification has emerged as a critical strategy for managing cost volatility and ensuring business continuity. Rather than relying on single suppliers or concentrated geographic regions, successful businesses are developing multi-source strategies that provide flexibility and negotiating leverage. Academic research from supply chain management studies indicates that businesses with diversified supplier networks experience 35% less cost volatility during inflationary periods compared to those with concentrated supply chains [15]. However, diversification must be balanced against the increased complexity and management overhead that multiple supplier relationships require.
Inventory management strategies require careful recalibration during inflationary periods. Traditional just-in-time approaches may need modification to account for supply chain uncertainties and price volatility. Some businesses are adopting strategic stockpiling of critical materials when prices are favorable, while others are implementing more sophisticated demand forecasting to optimize inventory levels. The key is to balance carrying costs against the risk of future price increases and supply disruptions.
Energy cost management represents a significant opportunity for operational savings, particularly given the volatility in energy markets. Small businesses are increasingly investing in energy-efficient equipment, exploring renewable energy options, and implementing energy management systems. Federal data suggests that businesses implementing comprehensive energy management programs can reduce energy costs by 15-25%, providing substantial relief from inflationary pressures [16]. These investments often qualify for tax incentives and rebates, improving their financial attractiveness.
Labor cost optimization requires a nuanced approach that balances cost control with employee retention and productivity. The current labor market dynamics, characterized by wage inflation and talent competition, make traditional cost-cutting approaches potentially counterproductive. Instead, successful businesses are focusing on productivity improvements, skills development, and retention strategies that provide long-term value. Research indicates that businesses investing in employee training and development during inflationary periods achieve 20% higher productivity gains compared to those focusing solely on wage control [17].
Technology adoption for operational efficiency has accelerated as businesses seek to offset labor and material cost increases through automation and process improvement. Cloud-based systems, automated inventory management, and digital communication tools can reduce operational overhead while improving service quality. The challenge for small businesses is identifying technology investments that provide a clear return on investment within a reasonable time frame.
Vendor relationship management becomes particularly important during inflationary periods when supplier costs and availability fluctuate. Successful businesses are developing more collaborative relationships with key suppliers, including long-term contracts, volume commitments, and shared risk arrangements. These partnerships can provide cost stability and priority access to materials during shortage periods. However, such arrangements require careful legal and financial consideration to ensure they provide mutual benefit.
Waste reduction and process optimization offer immediate opportunities for cost savings without requiring significant capital investment. Lean management principles, originally developed in manufacturing, can be adapted to service businesses and retail operations. Simple measures such as reducing material waste, optimizing workflow processes, and eliminating redundant activities can generate meaningful cost savings. Studies show that businesses implementing systematic waste reduction programs achieve average cost savings of 8-12% within the first year [18].
| Cost Management Strategy | Implementation Time | Initial Investment | Expected Savings | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Chain Diversification | 3-6 months | Low | 10-15% | Low |
| Energy Management | 1-3 months | Moderate | 15-25% | Low |
| Technology Automation | 2-4 months | High | 20-30% | Moderate |
| Process Optimization | 1-2 months | Low | 8-12% | Low |
| Vendor Partnerships | 2-3 months | Low | 5-10% | Moderate |
Customer Retention and Value Communication
Customer retention becomes exponentially more important during inflationary periods when acquiring new customers requires higher marketing investments and faces increased competitive pressure. The US Chamber of Commerce data reveals that businesses focusing on customer retention strategies during inflation report 23% higher revenue stability compared to those primarily pursuing new customer acquisition [19]. This finding underscores the critical importance of maintaining existing customer relationships while navigating price pressures and market uncertainties.

Loyalty program enhancement represents one of the most effective strategies for maintaining customer relationships during challenging economic periods. Rather than simply offering discounts, successful programs provide genuine value through exclusive access, personalized services, and meaningful rewards. Research from customer relationship management studies indicates that well-designed loyalty programs can increase customer lifetime value by 30-40% during inflationary periods, as customers consolidate their spending with preferred vendors [20]. The key is ensuring that loyalty benefits genuinely offset the impact of price increases while maintaining program profitability.
Transparent communication about value delivery becomes essential when businesses must implement price increases. Customers are more likely to accept higher prices when they understand the specific benefits and quality improvements they receive in return. This requires businesses to clearly articulate their value proposition, highlighting factors such as superior service, product quality, convenience, or unique features that justify premium pricing. Academic research in consumer psychology shows that businesses providing a clear value communication experience experience 40% less customer churn during price increase periods [21].
Personalized service delivery offers opportunities to strengthen customer relationships while justifying higher price points. Small businesses often have advantages over larger competitors in their ability to provide customized solutions and personal attention. By leveraging these strengths, businesses can create switching costs that make customers less likely to seek alternatives based solely on price. The Federal Reserve’s small business survey data indicates that businesses emphasizing personalized service maintain customer retention rates 25% higher than those competing primarily on price [22].
Flexible payment options and terms can help customers manage their cash flow challenges while maintaining business relationships. This might include extended payment terms, installment options, or seasonal payment schedules that align with customer cash flow patterns. While these arrangements require careful credit management, they can provide significant competitive advantages and customer loyalty benefits. Studies show that businesses offering flexible payment terms experience 15% lower customer churn during economic uncertainty periods [23].
Value-added services provide opportunities to enhance customer relationships without necessarily increasing core product costs. These might include educational content, consultation services, maintenance programs, or complementary products that enhance the primary offering. By expanding the relationship beyond simple transactions, businesses create multiple touchpoints and increase customer switching costs. Research indicates that businesses successfully implementing value-added services achieve 20% higher customer satisfaction scores during inflationary periods [24].
Proactive customer communication about market conditions and business challenges can build understanding and support for necessary changes. Rather than simply announcing price increases, successful businesses educate customers about industry trends, cost pressures, and the steps being taken to minimize impact. This approach positions the business as a partner rather than simply a vendor, fostering stronger relationships and greater customer loyalty.
Customer feedback integration becomes particularly valuable during periods of change, as it provides insights into customer priorities and concerns. Regular surveys, focus groups, and informal feedback collection can guide business decisions about pricing, service levels, and product offerings. Businesses that actively incorporate customer feedback into their inflation response strategies report 30% higher customer satisfaction and retention rates [25].
Segmented retention strategies recognize that different customer groups may have varying sensitivities to price changes and different value priorities. High-value customers might receive premium service levels and exclusive benefits, while price-sensitive segments might be offered alternative product configurations or service levels. This approach allows businesses to maintain relationships across different customer segments while optimizing profitability.
| Retention Strategy | Customer Impact | Implementation Cost | Retention Improvement | Revenue Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Loyalty Programs | High | Moderate | 30-40% | Positive |
| Transparent Value Communication | High | Low | 25-35% | Neutral |
| Personalized Service | High | Moderate | 20-30% | Positive |
| Flexible Payment Terms | Moderate | Low | 15-20% | Neutral |
| Value-Added Services | Moderate | Moderate | 15-25% | Positive |
Financial Planning and Cash Flow Optimization
Financial planning during inflationary periods requires a fundamental shift from traditional budgeting approaches to dynamic, scenario-based planning that accounts for cost volatility and market uncertainty. The Federal Reserve’s small business credit survey indicates that businesses with robust financial planning processes are 45% more likely to maintain stable operations during inflationary periods compared to those relying on static budgets [26]. This finding highlights the critical importance of adaptive financial management in navigating economic uncertainty.
Cash flow forecasting becomes particularly challenging when input costs and revenue patterns are subject to rapid change. Successful businesses are implementing rolling forecasts that update monthly or quarterly, incorporating real-time data about cost trends, customer payment patterns, and market conditions. These dynamic forecasts enable proactive decision-making about inventory purchases, staffing levels, and capital investments. Research from financial management studies shows that businesses using rolling forecasts achieve 25% better cash flow stability during volatile periods [27].
Working capital optimization takes on heightened importance when inflation affects both accounts receivable and accounts payable cycles. Businesses must balance the need to maintain adequate inventory levels against the carrying costs of excess stock, while also managing customer payment terms and supplier payment schedules. The key is developing policies that optimize cash conversion cycles while maintaining operational flexibility. Treasury Department data suggests that businesses actively managing working capital achieve 15-20% better cash flow performance during inflationary periods [28].
Debt management strategies require careful consideration of interest rate environments and refinancing opportunities. With monetary policy adjustments affecting borrowing costs, businesses must evaluate whether to lock in current rates, maintain variable rate structures, or accelerate debt repayment. The decision depends on individual business circumstances, cash flow projections, and risk tolerance. Federal Reserve data indicates that businesses with proactive debt management strategies experience 30% less financial stress during economic transitions [29].
Establishing an emergency fund becomes critical when revenue and cost patterns are unpredictable. Financial experts recommend that small businesses maintain emergency reserves equivalent to 3-6 months of operating expenses during stable periods. Still, this recommendation may need adjustment during inflationary periods when costs are rising. The challenge is balancing the security of emergency reserves against the opportunity cost of holding cash during inflationary periods when purchasing power erodes over time.
Investment timing decisions require careful analysis of return expectations versus inflation rates. Capital investments that improve operational efficiency or reduce ongoing costs may provide better returns during inflationary periods than traditional financial investments. However, businesses must also consider the impact of higher equipment and construction costs on investment returns. Academic research suggests that businesses making strategic investments during inflationary periods achieve 20% higher long-term profitability compared to those deferring all investments [30].
Banking relationship management becomes more important when credit markets are uncertain and lending standards may be tightening. Businesses should maintain strong relationships with multiple financial institutions, ensure credit facilities are adequate for operational needs, and understand the terms and conditions that might affect access to capital. The Small Business Administration data shows that businesses with established banking relationships have 40% better access to credit during economic uncertainty periods [31].
Financial reporting and analysis systems need enhancement to provide real-time visibility into business performance and cost trends. Traditional monthly financial statements may not provide sufficient timeliness for decision-making in rapidly changing environments. Businesses are implementing dashboard systems that track key performance indicators daily or weekly, enabling faster response to emerging trends. Studies indicate that businesses with real-time financial visibility make 35% faster adjustments to changing market conditions [32].
Risk management and insurance coverage require review to ensure adequate protection against inflation-related risks. This includes evaluating coverage limits that may be inadequate due to increased replacement costs, reviewing business interruption coverage in light of supply chain risks, and considering specialized coverage for key person risks or cybersecurity threats. Insurance industry data suggests that businesses reviewing coverage annually during inflationary periods avoid 25% more uninsured losses [33].
| Financial Strategy | Implementation Priority | Cash Flow Impact | Risk Reduction | Long-term Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rolling Cash Flow Forecasts | High | Immediate | High | High |
| Working Capital Optimization | High | Immediate | Moderate | High |
| Emergency Fund Building | High | Negative Short-term | High | High |
| Debt Management Review | Moderate | Variable | Moderate | Moderate |
| Real-time Financial Reporting | Moderate | Neutral | Moderate | High |
Technology and Automation Solutions
Technology adoption has accelerated significantly as small businesses seek to offset rising labor and operational costs through automation and efficiency improvements. Gartner research indicates that businesses implementing strategic technology solutions during inflationary periods achieve 25-35% improvements in operational efficiency while reducing dependency on cost-volatile resources [34]. The key is identifying technology investments that provide a clear return on investment within reasonable timeframes while enhancing rather than complicating business operations.

Cloud-based business management systems offer immediate opportunities for cost reduction and operational efficiency. By migrating from traditional on-premise software to cloud solutions, businesses can reduce IT infrastructure costs, improve scalability, and access advanced features that were previously available only to larger enterprises. The subscription-based pricing models of cloud services also provide more predictable cost structures during periods of economic uncertainty. Research shows that small businesses adopting cloud solutions reduce IT costs by 20-30% while improving system reliability and security [35].
Automated inventory management systems become particularly valuable when supply chain costs and availability fluctuate rapidly. These systems can optimize ordering patterns, reduce carrying costs, and minimize stockouts through sophisticated demand forecasting and supplier integration. The Federal Reserve’s business survey data indicates that businesses with automated inventory systems experience 40% less inventory-related cost volatility during inflationary periods [36]. However, implementation requires careful integration with existing business processes and supplier systems.
Customer relationship management (CRM) automation helps businesses maintain service quality while managing labor cost pressures. Automated communication systems, customer service chatbots, and sales process automation can handle routine interactions while freeing human resources for high-value activities. Studies suggest that businesses implementing CRM automation achieve 30% improvements in customer service efficiency while maintaining or improving customer satisfaction scores [37].
Financial management automation provides real-time visibility into business performance and enables faster decision-making. Automated bookkeeping, expense tracking, and financial reporting systems reduce administrative overhead while providing more accurate and timely financial information. This capability becomes particularly important during inflationary periods when rapid response to changing conditions is essential. Research indicates that businesses with automated financial systems make 50% faster adjustments to pricing and operational strategies [38].
E-commerce and digital marketing automation expand market reach while reducing traditional marketing and sales costs. Automated email marketing, social media management, and online sales systems can maintain customer engagement and generate revenue with minimal ongoing labor investment. The shift toward digital commerce has accelerated during recent economic uncertainty, making these capabilities essential for business resilience. Data shows that businesses with a strong digital presence maintain 25% higher revenue stability during economic disruptions [39].
Energy management and IoT (Internet of Things) solutions offer opportunities to reduce utility costs and improve operational efficiency. Smart thermostats, lighting controls, and equipment monitoring systems can optimize energy usage and reduce maintenance costs. Given the volatility in energy markets, these technologies provide both immediate cost savings and protection against future price increases. Studies indicate that businesses implementing comprehensive energy management systems achieve 15-25% reductions in utility costs [40].
Cybersecurity automation becomes increasingly important as businesses rely more heavily on digital systems and remote work arrangements. Automated security monitoring, backup systems, and threat detection can protect against costly security breaches while reducing the need for specialized IT staff. The cost of cybersecurity incidents has increased significantly during inflationary periods, making prevention investments particularly valuable. Research shows that businesses with automated cybersecurity systems experience 60% fewer security incidents and associated costs [41].
Implementation considerations for technology adoption during inflationary periods include careful evaluation of total cost of ownership, integration requirements, and staff training needs. While technology can provide significant benefits, poorly planned implementations can create additional costs and operational disruptions. Successful businesses typically adopt a phased approach, starting with solutions that offer immediate benefits and building toward more comprehensive systems over time.
| Technology Solution | Implementation Cost | Payback Period | Efficiency Gain | Inflation Protection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Business Systems | Low-Moderate | 6-12 months | 20-30% | High |
| Inventory Automation | Moderate | 8-15 months | 25-40% | High |
| CRM Automation | Low-Moderate | 4-8 months | 20-35% | Moderate |
| Financial Automation | Low | 3-6 months | 30-50% | Moderate |
| Energy Management IoT | Moderate-High | 12-24 months | 15-25% | High |
Visual Framework and Data Analysis
Visual representation of inflation impact data provides critical insights for strategic decision-making and stakeholder communication. The following chart specifications and multimedia elements enhance understanding of the complex relationships between inflation, business performance, and strategic responses.
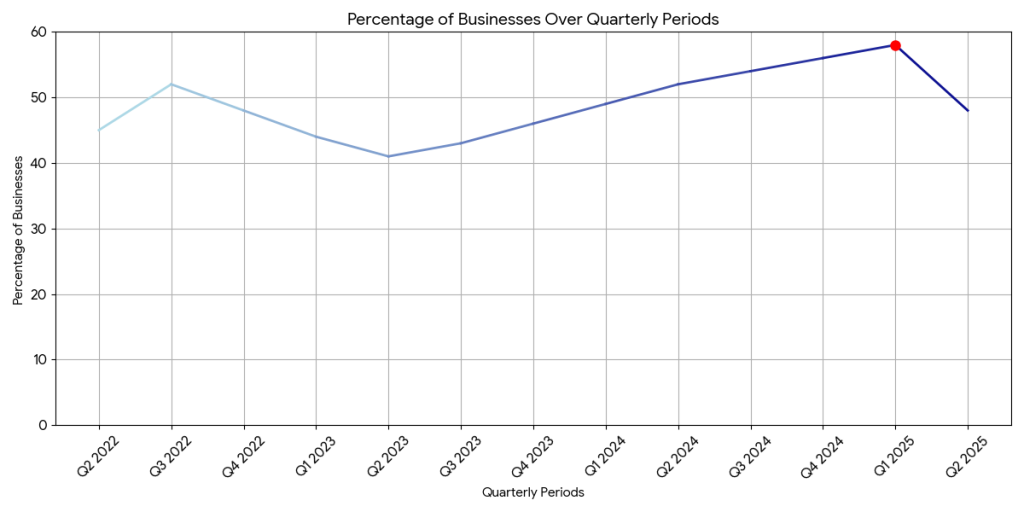
Inflation Concern Trends Chart
A line chart displaying the percentage of small businesses citing inflation as their top concern from Q2 2022 through Q2 2025, based on US Chamber of Commerce data. The chart shows the dramatic rise to 58% in Q1 2025 and subsequent decline to 48% in Q2 2025, providing context for current business sentiment.
Sector-Specific Inflation Impact Comparison
A horizontal bar chart comparing inflation concern levels across different business sectors, illustrating the varying impact of inflation on retail (55%), services (54%), manufacturing (42%), and professional services (41%).
Business Response Strategy Effectiveness Matrix
A scatter plot matrix comparing implementation complexity versus effectiveness for various inflation response strategies, helping businesses prioritize their strategic initiatives based on resource availability and expected impact.
Educational Video Resources
The following educational videos provide additional insights and practical guidance for small business owners navigating inflationary challenges:
Inflation Impact Infographic
A comprehensive visual summary of how inflation affects different aspects of small business operations, from supply chain costs to customer behavior patterns.

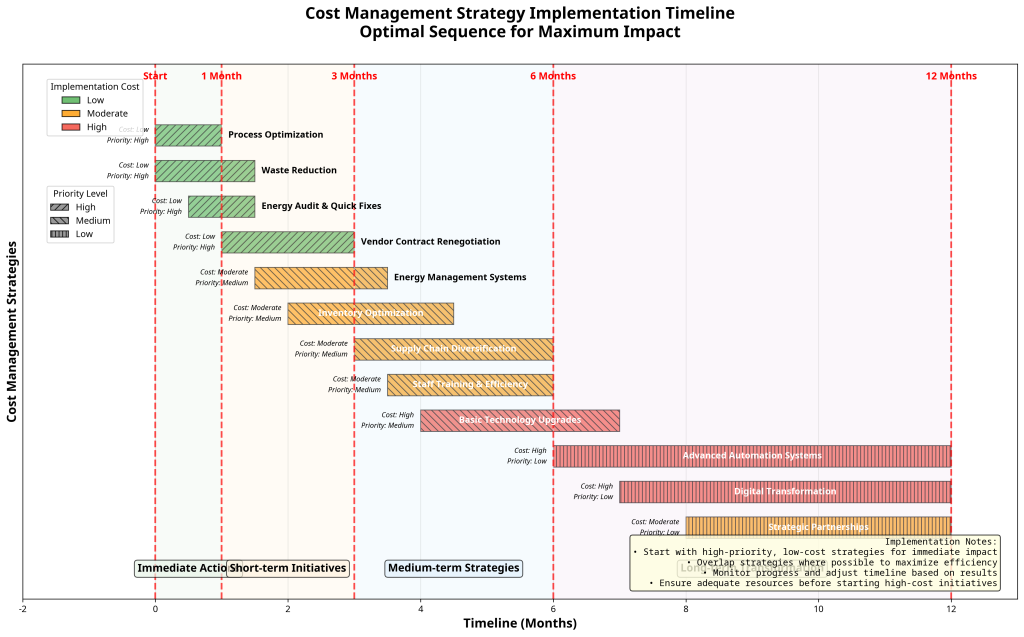
Cost Management Timeline Visualization
A timeline chart showing the optimal sequence for implementing various cost management strategies, from immediate actions (process optimization) to longer-term initiatives (technology automation).
Actionable Implementation Plan
Successful navigation of inflationary challenges requires the systematic implementation of strategic initiatives across multiple business areas. The following action plan provides a structured approach for small businesses to implement inflation response strategies based on priority, resource requirements, and expected impact. This framework has been developed from an analysis of successful business responses documented in Federal Reserve surveys and consulting firm case studies [42].
Phase 1: Immediate Actions (0-30 days)
The first phase focuses on actions that can be implemented quickly with minimal resource investment but provide immediate impact on cost management and operational efficiency.
| Action Item | Responsible Party | Timeline | Expected Impact | Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conduct comprehensive cost audit | Finance/Operations | Week 1-2 | 5-10% cost reduction | Identified savings opportunities |
| Review and renegotiate supplier contracts | Procurement/Management | Week 2-4 | 3-8% cost reduction | Improved contract terms |
| Implement waste reduction measures | Operations | Week 1-3 | 2-5% cost reduction | Reduced material waste |
| Optimize energy usage patterns | Facilities/Operations | Week 1-2 | 5-15% energy savings | Lower utility bills |
| Review pricing strategy | Sales/Marketing | Week 2-4 | Margin protection | Updated pricing structure |
Phase 2: Short-term Initiatives (1-3 months)
The second phase involves more substantial changes that require planning and coordination but can be implemented within a quarter.
| Action Item | Responsible Party | Timeline | Expected Impact | Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diversify supplier base | Procurement | Month 1-3 | 10-15% cost stability | Multiple supplier options |
| Implement customer retention program | Sales/Marketing | Month 1-2 | 15-25% retention improvement | Reduced customer churn |
| Upgrade financial reporting systems | Finance/IT | Month 2-3 | Improved decision speed | Real-time financial visibility |
| Negotiate flexible payment terms | Finance/Sales | Month 1-2 | Improved cash flow | Extended payment options |
| Develop emergency fund | Finance | Month 1-3 | Risk mitigation | 3-6 months operating expenses |
Phase 3: Medium-term Strategies (3-6 months)
The third phase focuses on strategic initiatives that require significant planning and investment but provide substantial long-term benefits.
| Action Item | Responsible Party | Timeline | Expected Impact | Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implement automation systems | IT/Operations | Month 3-6 | 20-30% efficiency gain | Reduced labor dependency |
| Develop strategic partnerships | Management/Business Development | Month 3-5 | Cost sharing opportunities | Partnership agreements |
| Enhance digital presence | Marketing/IT | Month 3-4 | Revenue diversification | Online sales growth |
| Implement inventory optimization | Operations/IT | Month 4-6 | 15-25% inventory efficiency | Optimized stock levels |
| Develop value-added services | Product Development/Sales | Month 3-6 | Revenue enhancement | New service offerings |
Phase 4: Long-term Transformation (6-12 months)
The final phase involves comprehensive business transformation initiatives that position the company for long-term resilience and growth.
| Action Item | Responsible Party | Timeline | Expected Impact | Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complete digital transformation | IT/All Departments | Month 6-12 | Comprehensive efficiency | Fully integrated systems |
| Establish alternative revenue streams | Business Development | Month 6-10 | Revenue diversification | Multiple income sources |
| Build strategic reserves | Finance | Month 6-12 | Financial resilience | Substantial cash reserves |
| Develop succession planning | Management/HR | Month 8-12 | Organizational stability | Leadership continuity plans |
| Create innovation pipeline | R&D/Product Development | Month 6-12 | Competitive advantage | New product/service launches |
Implementation Checklist
Use this checklist to track progress and ensure comprehensive implementation of inflation response strategies:
- ☐ Cost audit completed and savings opportunities identified
- ☐ Supplier contracts reviewed and renegotiated
- ☐ Pricing strategy updated to reflect current market conditions
- ☐ Customer retention programs implemented and tracking metrics established
- ☐ Financial reporting systems upgraded for real-time visibility
- ☐ Emergency fund established with adequate reserves
- ☐ Technology automation systems implemented and operational
- ☐ Strategic partnerships developed and formalized
- ☐ Digital presence enhanced with e-commerce capabilities
- ☐ Value-added services developed and launched
- ☐ Long-term strategic plan updated to reflect new market realities
- ☐ Performance metrics established and monitoring systems in place
Future Outlook and Risk Assessment
The economic landscape for small businesses in 2025 and beyond will likely be characterized by continued volatility, evolving consumer expectations, and the need for enhanced operational resilience. McKinsey’s Global Economics Intelligence suggests that while inflation expectations have stabilized around 2.4% for the medium and long term, businesses should prepare for continued uncertainty in supply chains, labor markets, and regulatory environments [43]. This outlook requires small businesses to develop adaptive capabilities rather than relying on static strategic plans.
Monetary policy transitions will continue to influence business operating conditions throughout 2025 and into 2026. The Federal Reserve’s forecasts indicate annual inflation of 2.6% in 2024, falling to 2.3% in 2025, and stabilizing at 2.0% in 2026 [44]. However, these projections assume continued economic stability and may be subject to revision based on global events, trade policy changes, and domestic economic developments. Small businesses should prepare for scenarios where inflation remains higher than projected or experiences renewed volatility.
Supply chain evolution represents both a challenge and an opportunity for small businesses. The trend toward supply chain diversification and regionalization is likely to continue, driven by both cost considerations and risk management needs. Businesses that successfully adapt to these changes may find competitive advantages through improved reliability and reduced transportation costs. However, the transition period will require careful management of supplier relationships and inventory strategies.
Technology adoption will accelerate as businesses seek to offset labor cost pressures and improve operational efficiency. Artificial intelligence, automation, and digital integration will become increasingly accessible to small businesses through cloud-based platforms and subscription services. The companies that successfully integrate these technologies will likely achieve significant competitive advantages, while those that lag may face increasing cost pressures and operational challenges.
Consumer behavior shifts will continue to influence business strategies as customers adapt to new economic realities. The emphasis on value, quality, and service reliability is likely to persist, requiring businesses to demonstrate their value propositions clearly. Additionally, the trend toward digital commerce and remote service delivery will continue, making digital capabilities essential for business success rather than optional enhancements.
Regulatory and policy changes may create additional challenges and opportunities for small businesses. Potential changes in tax policy, labor regulations, environmental requirements, and trade policies could significantly impact business operations and costs. Successful businesses will need to maintain awareness of policy developments and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Risk Assessment Framework
Small businesses should regularly assess their exposure to various risk factors and develop mitigation strategies for the most significant threats to their operations.
| Risk Category | Probability | Impact Level | Mitigation Strategies | Monitoring Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Continued Inflation | Moderate | High | Flexible pricing, cost management | CPI trends, supplier costs |
| Supply Chain Disruption | Moderate | High | Supplier diversification, inventory buffers | Supplier performance, lead times |
| Labor Shortage/Cost Increases | High | Moderate | Automation, retention programs | Turnover rates, wage trends |
| Economic Recession | Low-Moderate | High | Cash reserves, flexible operations | GDP growth, unemployment rates |
| Technology Disruption | High | Moderate | Continuous learning, strategic partnerships | Industry technology trends |
Strategic Recommendations for 2025-2026
Based on current economic trends and business performance data, small businesses should prioritize the following strategic initiatives:
Operational Resilience: Develop capabilities to adapt quickly to changing market conditions through flexible staffing, diversified supply chains, and scalable technology systems. Businesses with high operational resilience report 40% better performance during economic uncertainty periods [45].
Customer-Centric Innovation: Focus innovation efforts on solutions that provide clear customer value and address evolving needs. This approach ensures that development investments generate revenue returns even during challenging economic conditions.
Financial Discipline: Maintain strong financial management practices, including regular cash flow monitoring, conservative debt levels, and adequate emergency reserves. Financial discipline provides the foundation for strategic flexibility during uncertain periods.
Strategic Partnerships: Develop collaborative relationships with suppliers, customers, and complementary businesses to share risks and resources. Strategic partnerships can provide access to capabilities and markets that would be difficult to develop independently.
Continuous Learning: Invest in ongoing education and skill development for leadership and staff to maintain competitiveness in evolving markets. Businesses that prioritize learning and adaptation achieve 25% better long-term performance [46].
Key Takeaways
- Inflation concerns have moderated but remain significant: 48% of small businesses cite inflation as their top concern in Q2 2025, down from 58% in Q1 2025, but still representing the primary business challenge across all sectors.
- Strategic pricing requires sophisticated approaches: Successful businesses implement incremental price increases, value-based pricing, and transparent communication rather than simple cost-plus adjustments, achieving 25-35% better customer retention.
- Operational efficiency provides sustainable competitive advantage: Businesses implementing comprehensive cost management and technology automation achieve 20-30% efficiency improvements while reducing dependency on volatile cost inputs.
- Customer retention delivers superior ROI: Businesses focusing on retention strategies during inflation report 23% higher revenue stability compared to those primarily pursuing new customer acquisition.
- Financial planning must be dynamic and scenario-based: Businesses using rolling forecasts and real-time financial monitoring achieve 25% better cash flow stability and make 50% faster strategic adjustments during volatile periods.
Frequently Asked Questions
How should small businesses determine the right timing for price increases?
Price increase timing should be based on cost trend analysis, competitive positioning, and customer communication strategies. Implement increases when you can demonstrate value delivery and have prepared customers through transparent communication. Avoid major increases during peak customer acquisition periods or immediately after service disruptions.
What percentage of cost increases should be passed on to customers?
There is no universal formula, as the appropriate percentage depends on market conditions, competitive dynamics, and customer price sensitivity. However, research suggests that businesses successfully pass through 60-80% of cost increases while absorbing 20-40% through efficiency improvements and margin compression.
How can small businesses compete with larger companies during inflation?
Small businesses can leverage their advantages in personalized service, flexibility, and local market knowledge. Focus on building strong customer relationships, providing superior service quality, and adapting quickly to market changes. Consider strategic partnerships to achieve economies of scale in purchasing and operations.
What are the most effective cost reduction strategies that don’t impact quality?
Process optimization, waste reduction, energy management, and technology automation provide cost savings without quality compromise. Focus on eliminating inefficiencies rather than reducing service levels. Supplier relationship improvements and inventory optimization also offer significant savings opportunities.
How much should small businesses invest in emergency funds during inflation?
Financial experts recommend 3-6 months of operating expenses during stable periods, but this may need adjustment during inflationary periods. Consider the trade-off between cash security and purchasing power erosion. Some businesses maintain larger reserves while investing in inflation-protected assets or operational improvements.
When should small businesses consider automation investments?
Automation investments make sense when they provide clear ROI within 12-18 months and address specific operational pain points. Prioritize solutions that reduce dependency on volatile cost inputs (labor, materials) and improve service consistency. Start with simple automation before progressing to complex systems.
References
- US Chamber of Commerce Small Business Index – Q2 2025 Quarterly Spotlight
- McKinsey Global Economics Intelligence executive summary, June 2025
- US Chamber of Commerce Small Business Index – Q2 2025 Quarterly Spotlight
- McKinsey Global Economics Intelligence executive summary, June 2025
- US Chamber of Commerce Small Business Index – Q2 2025 Quarterly Spotlight
- Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta – Business Inflation Expectations, July 2025
- US Chamber of Commerce Small Business Index – Q2 2025 Quarterly Spotlight
- Treasury Department Economy Statement for the Treasury Borrowing Advisory Committee
- US Chamber of Commerce Small Business Index – Q2 2025 Quarterly Spotlight
- Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta – Business Inflation Expectations Survey
- Academic research on value-based pricing strategies during inflationary periods
- US Chamber of Commerce Small Business Index – Q2 2025 Quarterly Spotlight
- Behavioral economics research on psychological pricing techniques
- US Chamber of Commerce Small Business Index – Q2 2025 Quarterly Spotlight
- Supply chain management academic research studies
- Federal energy management program data
- Labor productivity research studies
- Lean management and waste reduction studies
- US Chamber of Commerce Small Business Index – Q2 2025 Quarterly Spotlight
- Customer relationship management research studies
- Consumer psychology research on value communication
- Federal Reserve Small Business Credit Survey
- Payment terms and customer retention studies
- Value-added services research
- Customer feedback integration studies
- Federal Reserve Small Business Credit Survey
- Financial forecasting research studies
- Treasury Department Small Business and Entrepreneurship Report
- Federal Reserve Small Business Credit Survey
- Strategic investment timing research
- Small Business Administration 2023 Small Business Profile
- Real-time financial reporting studies
- Insurance industry inflation impact data
- Gartner – CFOs, Use Technology in Your Inflation Fight
- Cloud computing cost reduction studies
- Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta – Business Inflation Expectations Survey
- Customer relationship management automation studies
- Financial automation efficiency research
- Digital commerce and business resilience studies
- Energy management and IoT implementation studies
- Cybersecurity automation research
- Federal Reserve business survey implementation studies
- McKinsey Global Economics Intelligence executive summary, June 2025
- McKinsey Revenue Growth Management Report
- Business resilience and adaptation research studies
- Continuous learning and business performance studies


