Opening Summary
Marketing leaders in 2026 face an unprecedented convergence of technological complexity, regulatory constraints, and economic pressures that fundamentally challenge traditional approaches to customer acquisition and retention. Recent research from McKinsey, BCG, and HubSpot reveals that while 70% of marketers are leveraging AI in their measurement toolkit, only 20% have achieved true measurement leadership, resulting in up to 70% lower revenue growth for organizations that fail to address critical operational challenges [1].
The marketing technology landscape has exploded to 15,384 solutions in 2026, representing a staggering 100-fold increase since 2011, while customer acquisition costs have simultaneously risen 222% over the past decade [2]. This dual pressure of increasing complexity and rising costs, combined with stringent data privacy regulations and the imperative for AI integration, creates a perfect storm that demands strategic recalibration of marketing operations.
This analysis examines five critical challenges that define the marketing landscape in 2026, drawing from authoritative sources including government data, academic research, and leading consulting firms to provide evidence-based insights for marketing leaders navigating this complex environment.
Why Marketing Challenges Matter in 2026
The marketing profession stands at a critical inflection point in 2026, where traditional methodologies collide with emerging technologies and evolving consumer expectations. The U.S. Small Business Administration emphasizes that market research and competitive analysis have become more complex than ever, requiring businesses to navigate an increasingly fragmented landscape of customer touchpoints and measurement methodologies [3].
The convergence of several macro trends has created a uniquely challenging environment for marketing professionals. First, the exponential growth of digital channels has fragmented customer journeys across multiple touchpoints, making attribution and measurement exponentially more complex. Second, regulatory frameworks like GDPR and emerging privacy legislation have fundamentally altered how organizations can collect, process, and utilize customer data. Third, the democratization of AI tools has raised C-suite expectations for marketing precision and accountability while simultaneously introducing new operational complexities.
According to BCG’s 2026 research on marketing measurement effectiveness, organizations that successfully navigate these challenges achieve up to 70% higher revenue growth than their peers, while those that fail to adapt face declining market share and operational inefficiencies [1]. This performance gap underscores the strategic importance of addressing these challenges systematically rather than treating them as isolated operational issues.
The economic context further amplifies these challenges. With customer acquisition costs rising across all industries and conversion rates remaining stubbornly low—with nearly two-thirds of marketers reporting landing page conversion rates below 10%—organizations must optimize every aspect of their marketing operations to maintain profitability [4]. The stakes have never been higher for marketing leaders to demonstrate clear ROI and strategic value to their organizations.
Challenge 1: Marketing ROI Measurement and Attribution Complexity
The Measurement Crisis
Marketing measurement has evolved from a straightforward exercise in tracking direct response campaigns to a complex analytical challenge that spans multiple channels, devices, and customer touchpoints. BCG’s comprehensive survey of 3,000 senior measurement professionals worldwide reveals that more than 70% of marketers are using AI in their measurement toolkit, yet nearly one in three considers evaluating media effectiveness across channels as their biggest challenge [1].
The fundamental issue lies in the proliferation of measurement methodologies that often produce contradictory insights. Digital teams typically rely on last-touch attribution models that credit the final interaction before conversion, while media teams employ marketing mix models (MMM) that assess holistic omnichannel impact. These divergent approaches can suggest completely opposing strategic actions, leaving marketing leaders without a unified framework for decision-making.
Statistical Reality of Measurement Challenges
| Measurement Challenge | % of Marketers Affected | Primary Impact |
|---|---|---|
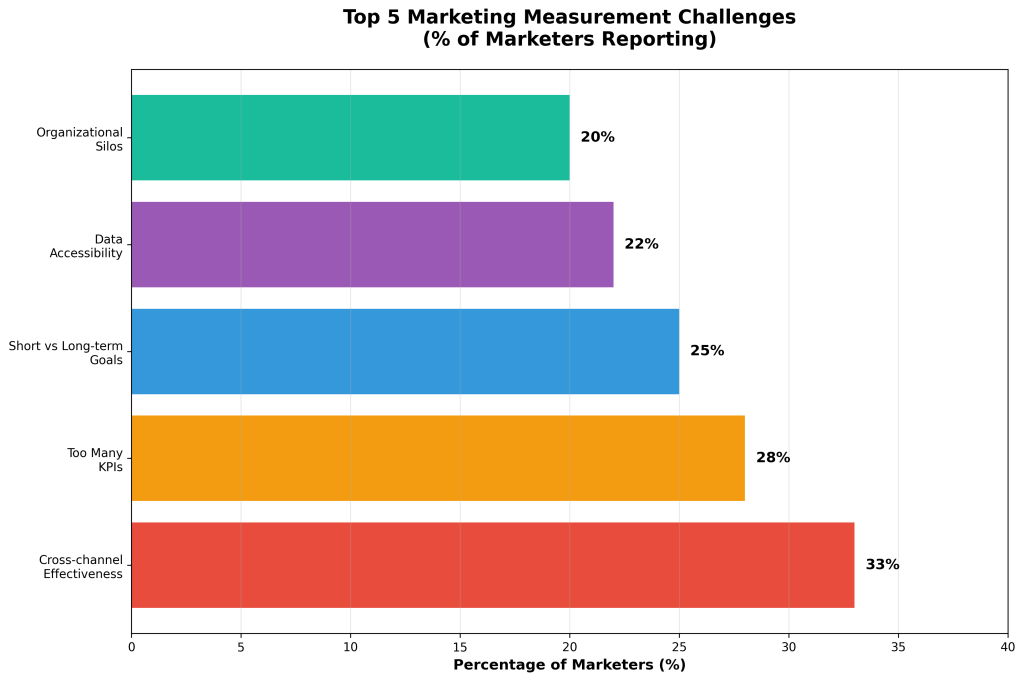
| Cross-channel effectiveness evaluation | 33% | Misallocated budget, conflicting insights |
| Too many KPIs creating confusion | 28% | Decision paralysis, lack of focus |
| Short vs. long-term goal alignment | 25% | Suboptimal resource allocation |
| Data accessibility issues | 22% | Delayed insights, poor agility |
| Organizational silos | 20% | Fragmented strategy, duplicated efforts |
The Attribution Complexity Problem
Academic research published in the International Journal of Management highlights that calculating ROI in digital marketing campaigns involves multifaceted challenges, including factors such as ad spend, conversion tracking across devices, and the temporal disconnect between marketing exposure and customer action [5]. The complexity is further compounded by the reality that modern customer journeys involve an average of 6-8 touchpoints across multiple channels before conversion.
The challenge extends beyond technical measurement to organizational alignment. Leading marketers have learned to distinguish between tactical KPIs (short-term outcomes like sales) and strategic KPIs (long-term outcomes like brand building) to differentiate between immediate performance and sustainable growth. However, only 75% of measurement leaders factor long-term outcomes into their evaluation frameworks, and just half ensure their KPI architecture includes both brand and performance metrics [1].
Case Study: Financial Services Firm Transformation
A global financial services firm exemplifies both the challenge and the solution. Their marketing teams struggled with multichannel impact measurement, with digital teams tracking last-touch metrics while media teams focused on holistic omnichannel impact. By partnering with finance and analytics teams, they introduced a single master metric: marginal ROI (mROI). This unified approach enabled quick channel performance comparisons and systematic pruning of underperforming campaigns, resulting in approximately 10% improvement in marketing efficiency and significantly enhanced credibility for marketing leadership within the organization.
Limitations and Ongoing Challenges
Despite technological advances, significant limitations persist in marketing measurement. Privacy regulations have reduced the availability of third-party data, making cross-device tracking more difficult. Additionally, the rise of walled gardens (platforms like Facebook and Google that limit data sharing) creates measurement blind spots that traditional attribution models cannot address. Organizations must acknowledge these limitations when interpreting measurement data and making strategic decisions.
Challenge 2: Marketing Technology Stack Complexity
The Explosion of Marketing Technology
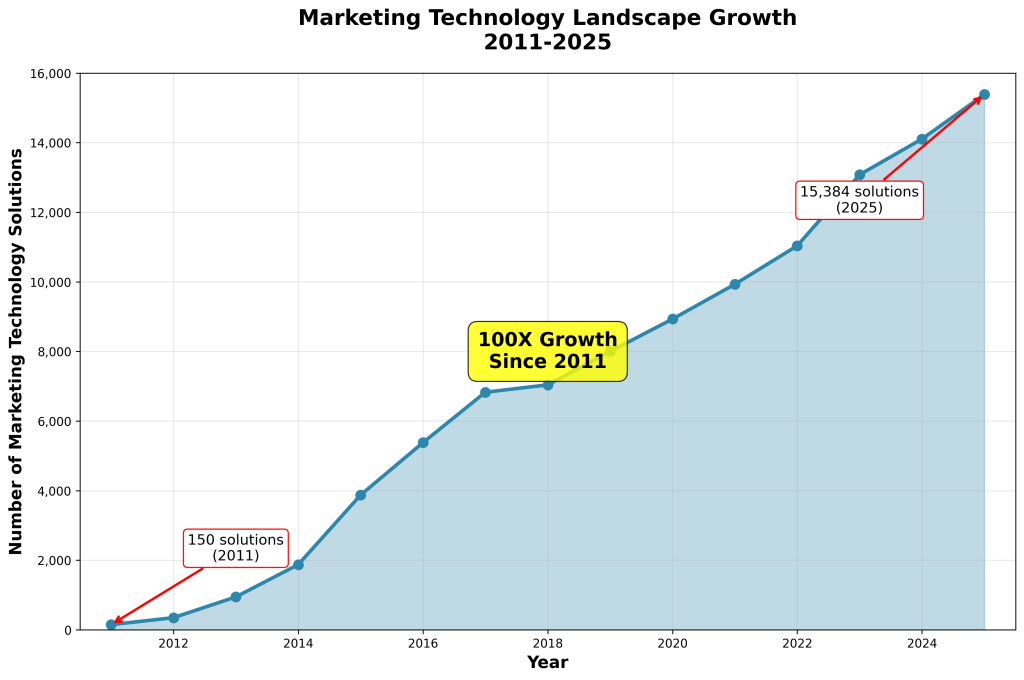
The marketing technology landscape has undergone unprecedented expansion, growing from a modest 150 solutions in 2011 to a staggering 15,384 solutions in 2026—a 100-fold increase that has fundamentally transformed how marketing organizations operate [2]. This exponential growth, while offering unprecedented capabilities, has created a paradox of choice that challenges even the most sophisticated marketing teams.
According to Chief Marketing Technologist’s annual landscape analysis, the average marketing technology stack grew by 2.2% in 2024 alone, with more mature marketing teams balancing the fluidity of new AI-native tools against established platforms at the center of their operations [2]. The emergence of what researchers term the “hypertail” of custom software—billions of programs created by AI assistants without users even knowing software was built—adds another layer of complexity to an already intricate ecosystem.
The Integration Challenge
Academic research on MarTech stack adoption in small and medium enterprises reveals that the specific realities of organizational constraints and the complexity of marketing technology stacks create significant barriers to effective implementation [6]. The challenge extends beyond simply selecting tools to encompass data integration, workflow optimization, and ensuring consistent customer experiences across multiple platforms.
| MarTech Category | Number of Solutions (2025) | Growth Rate (2025-2026) | Primary Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Data Platforms | 487 | 15% | Data unification complexity |
| Marketing Automation | 1,243 | 8% | Workflow integration |
| Analytics & Attribution | 892 | 22% | Cross-platform measurement |
| Content Management | 756 | 5% | Content consistency |
| AI-Native Solutions | 2,156 | 45% | Skill gap and adoption |
The Hidden Costs of Complexity
Research from Springer on marketing technology strategy reveals that without a clear strategic framework, companies risk “tech stack bloat,” where the accumulation of tools creates more problems than solutions [7]. The hidden costs extend beyond licensing fees to include integration expenses, training requirements, data inconsistencies, and the opportunity cost of teams spending more time managing tools than executing strategy.
The State of Martech 2026 report indicates that marketers are increasingly using homegrown solutions to address specific needs that commercial platforms cannot meet. While this trend toward customization offers greater control and specificity, it also introduces additional complexity in terms of maintenance, security, and integration with existing systems [8].
Organizational Impact and Skills Gap
The proliferation of marketing technology has created a new category of professional: the marketing technologist. These specialists bridge the gap between marketing strategy and technical implementation, but their scarcity in the job market creates bottlenecks for organizations seeking to optimize their technology investments. The challenge is particularly acute for small and medium enterprises that lack the resources to hire specialized talent or engage external consultants.
Furthermore, the rapid pace of technological change means that marketing teams must continuously update their skills and knowledge. What was considered cutting-edge technology two years ago may now be obsolete, requiring constant learning and adaptation that can strain organizational resources and individual capacity.
Strategic Approaches to Complexity Management
Leading organizations have learned to manage MarTech complexity through several strategic approaches. First, they establish clear governance frameworks that define how new tools are evaluated, approved, and integrated. Second, they prioritize platforms that offer broad integration capabilities rather than best-of-breed point solutions. Third, they invest in data architecture that enables seamless information flow between systems, reducing the risk of data silos and inconsistencies.
The most successful marketing organizations also recognize that technology is an enabler, not a solution. They focus on defining clear business objectives before selecting tools, ensuring that technology investments align with strategic goals rather than pursuing innovation for its own sake.
Challenge 3: Rising Customer Acquisition Costs
The Customer Acquisition Crisis
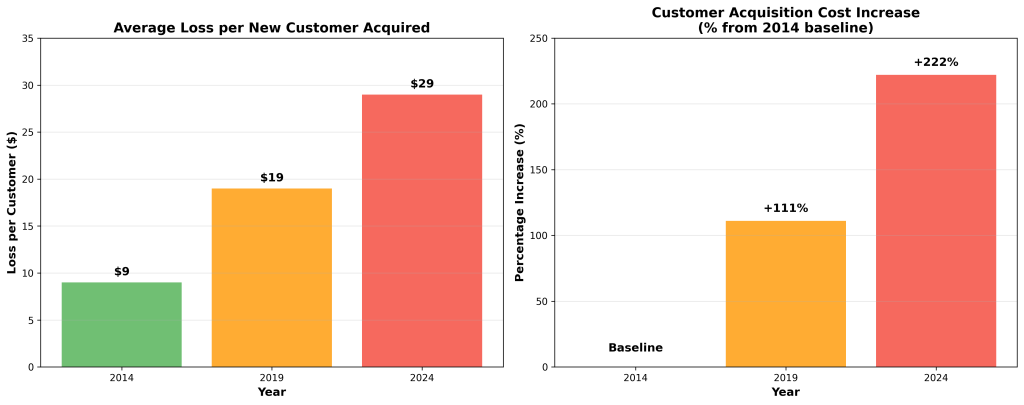
Customer acquisition costs have reached crisis levels across industries, with brands now losing an average of $29 for every new customer acquired, representing a dramatic increase from $19 a decade ago [9]. This 222% increase over the past ten years has fundamentally altered the economics of customer acquisition, forcing marketing leaders to reconsider traditional growth strategies and explore more sustainable approaches to building customer bases.
The crisis extends beyond simple cost inflation to encompass fundamental changes in consumer behavior, platform dynamics, and competitive intensity. Research from Focus Digital examining customer acquisition cost trends reveals that the challenge is particularly acute in digital channels, where increased competition for ad inventory has driven up costs while privacy changes have reduced targeting effectiveness [10].
Industry-Specific CAC Challenges
Customer acquisition costs vary significantly across industries, with some sectors facing particularly acute challenges. According to Shopify’s internal data analysis, average customer acquisition costs in e-commerce typically range from $68 to $78, though this varies considerably based on product category, target market, and acquisition channel [11].
| Industry Sector | Average CAC (2026) | 5-Year Growth Rate | Primary Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software/SaaS | $395 | 185% | Content marketing, sales cycles |
| E-commerce | $73 | 156% | Paid advertising, platform fees |
| Financial Services | $175 | 203% | Compliance, trust building |
| Healthcare | $127 | 167% | Regulatory constraints, education |
| Travel & Hospitality | $89 | 198% | Seasonal competition, OTA fees |
The Platform Monopolization Effect
A significant driver of rising customer acquisition costs is the increasing concentration of digital advertising spend among a small number of platforms. Google and Facebook (Meta) continue to dominate digital advertising, creating what economists term “platform monopolization effects” where limited supply of premium ad inventory drives up costs for all advertisers. This concentration has been exacerbated by privacy changes that have made alternative channels less effective, forcing more advertisers to compete for the same limited inventory.
Academic research on customer acquisition challenges highlights that the analytical complexity of measuring and optimizing acquisition efforts across multiple channels creates additional operational costs that compound the direct media expenses [12]. Organizations must invest in sophisticated attribution modeling, data analysis capabilities, and specialized talent to effectively manage multi-channel acquisition strategies.
The Conversion Rate Paradox
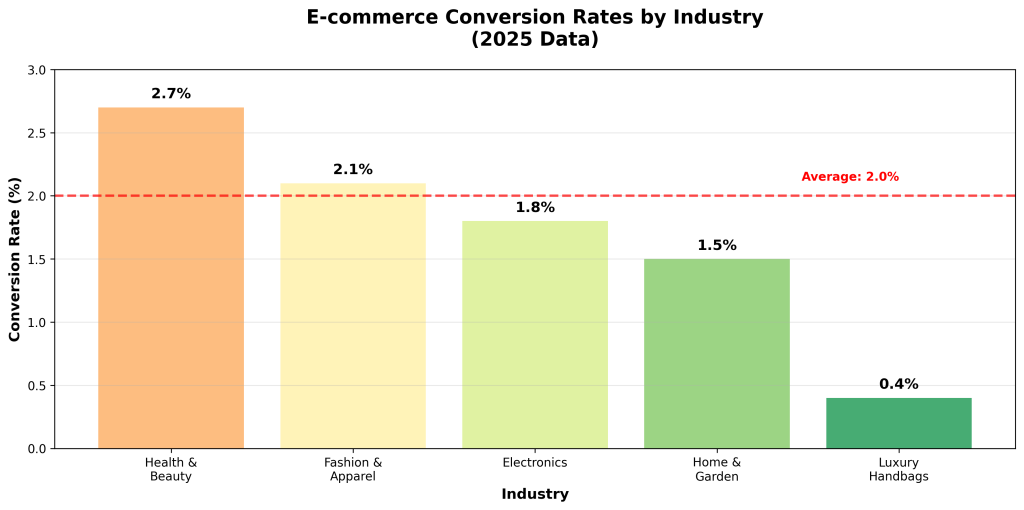
Rising customer acquisition costs are compounded by persistently low conversion rates across digital channels. HubSpot’s State of Marketing Report reveals that nearly two-thirds of marketers report average landing page conversion rates below 10%, with the overall average for e-commerce sites remaining under 2% [4]. This combination of high costs and low conversion rates creates a compounding effect that dramatically impacts the economics of customer acquisition.
Strategic Responses to Rising CAC
Leading organizations have developed several strategic responses to address rising customer acquisition costs. First, they have shifted focus from pure acquisition to customer lifetime value optimization, recognizing that retaining and expanding existing customers is often more cost-effective than acquiring new ones. Second, they have invested in owned media channels—such as email marketing, content marketing, and SEO—that provide more sustainable, long-term acquisition capabilities.
Third, successful organizations have embraced account-based marketing approaches that focus resources on high-value prospects rather than broad-based acquisition campaigns. This strategy is particularly effective in B2B contexts where the lifetime value of customers justifies higher acquisition investments for qualified prospects.
The Role of Customer Experience in CAC Optimization
Research indicates that organizations with superior customer experience achieve lower customer acquisition costs through several mechanisms. Satisfied customers generate positive word-of-mouth referrals, reducing the need for paid acquisition channels. Additionally, strong brand reputation and customer advocacy create organic discovery opportunities that supplement paid marketing efforts.
However, building exceptional customer experience requires significant upfront investment in product development, customer service capabilities, and operational excellence. Organizations must balance these investments against immediate acquisition needs, creating tension between short-term growth objectives and long-term sustainability.
Challenge 4: Data Privacy and Regulatory Compliance
The Regulatory Landscape Transformation
Data privacy regulations have fundamentally transformed the marketing landscape, with 87% of consumers supporting the banning of data sales to third parties without explicit consent, and 86% supporting requirements for companies to minimize the types of user data they collect [13]. The implementation of GDPR and similar regulations worldwide has created a complex compliance environment that requires significant organizational adaptation and ongoing investment.
Research published in Management Science examining privacy rights and data security reveals that GDPR and similar regulations have prevented market failure in data-driven markets by addressing fundamental information asymmetries between consumers and businesses [14]. However, this regulatory intervention has also created substantial operational challenges for marketing organizations that previously relied on extensive data collection and third-party data sharing.
The Economic Impact of Privacy Compliance
The financial implications of privacy compliance extend far beyond regulatory fines to encompass fundamental changes in marketing operations. According to Cisco’s privacy research, the average privacy budget for organizations now reaches $2.7 million annually, reflecting the substantial investment required for compliance infrastructure, legal oversight, and operational modifications [15].
| Privacy Compliance Area | Average Annual Cost | Implementation Time | Primary Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data mapping and inventory | $485,000 | 6-12 months | System complexity, data silos |
| Consent management systems | $320,000 | 3-6 months | User experience impact |
| Legal and compliance oversight | $750,000 | Ongoing | Regulatory interpretation |
| Technical infrastructure updates | $890,000 | 12-18 months | Legacy system integration |
| Staff training and education | $255,000 | 3-4 months | Behavioral change management |
The Measurement Impact of Privacy Regulations
Academic research examining the impact of GDPR on digital marketing reveals that the regulation reduced approximately four trackers per publisher, representing a 14.79% decrease in tracking capabilities compared to control groups [16]. This reduction in tracking capability has created significant challenges for attribution modeling and cross-device measurement, forcing marketers to develop new methodologies for understanding customer behavior and campaign effectiveness.
The Federal Trade Commission’s research on cross-device tracking highlights the complexity of maintaining marketing effectiveness while respecting privacy constraints. The challenge is particularly acute for businesses that rely on behavioral advertising and personalization, as traditional targeting mechanisms become less effective under privacy-first frameworks [17].
Consumer Sentiment and Trust Implications
Despite the operational challenges, privacy regulations have generated positive consumer sentiment in many markets. Research indicates that 62% of UK citizens feel safer sharing their data since GDPR implementation, while 72% of Americans believe there should be stronger data protection laws [13]. This shift in consumer sentiment creates both challenges and opportunities for marketing organizations.
Organizations that proactively embrace privacy-first marketing approaches often find that transparency and respect for consumer preferences can become competitive advantages. However, this requires fundamental changes in how marketing teams approach data collection, customer segmentation, and campaign personalization.
Technical Solutions and Workarounds
The marketing technology industry has responded to privacy challenges with various technical solutions, including first-party data platforms, privacy-preserving analytics, and contextual advertising technologies. However, these solutions often require significant technical expertise and integration efforts, creating additional complexity for marketing organizations.
Server-side tracking, privacy sandboxes, and differential privacy techniques represent emerging approaches to maintaining marketing effectiveness while respecting privacy constraints. However, these technologies are still evolving, and their long-term effectiveness remains uncertain as regulatory frameworks continue to develop.
Global Regulatory Complexity
The challenge of privacy compliance is compounded by the global nature of digital marketing and the varying regulatory frameworks across different jurisdictions. Organizations operating internationally must navigate GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, LGPD in Brazil, and emerging regulations in other markets, each with distinct requirements and enforcement mechanisms.
This regulatory fragmentation creates operational complexity and compliance costs that disproportionately impact smaller organizations that lack the resources to maintain specialized legal and technical expertise across multiple jurisdictions. The result is a competitive advantage for larger organizations that can absorb these compliance costs more easily.
Challenge 5: AI Integration and Human-Machine Collaboration
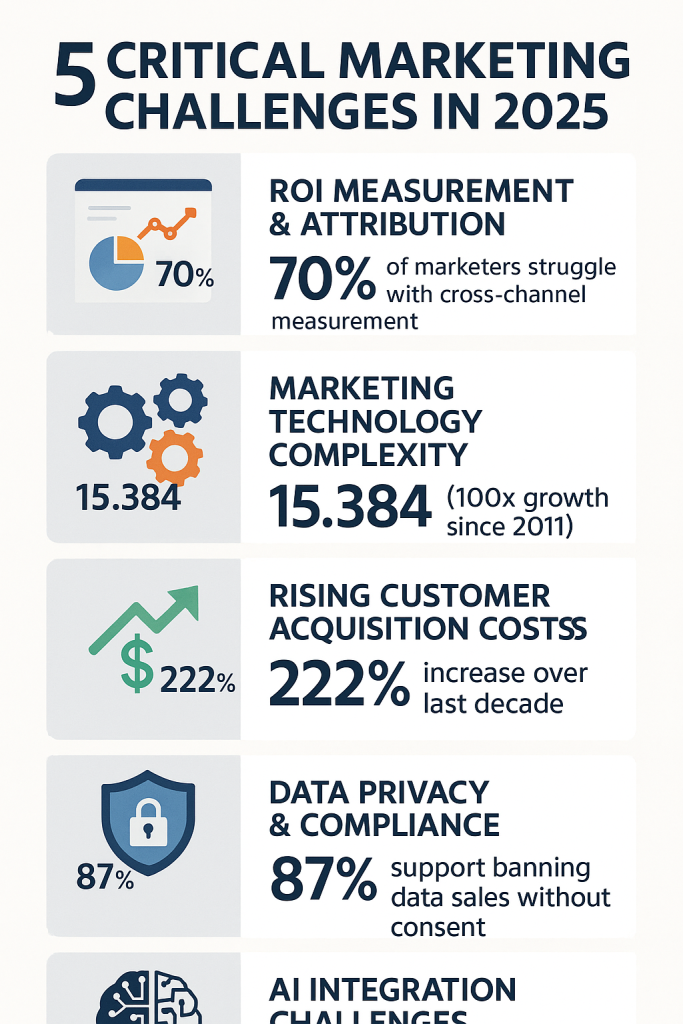
The AI Adoption Paradox
Artificial intelligence has emerged as both a solution and a challenge for marketing organizations in 2026. While more than 70% of marketers are using AI in their measurement toolkit, only 20% have achieved true measurement leadership, creating a significant performance gap that suggests implementation challenges extend beyond simple technology adoption [1]. This paradox reflects the reality that successful AI integration requires fundamental changes in organizational processes, skills, and strategic thinking.
McKinsey’s research on technology trends identifies AI as one of the most significant forces reshaping business operations, with particular impact on marketing functions including content creation, customer segmentation, and predictive analytics [18]. However, the research also highlights that organizations face substantial challenges in scaling AI initiatives beyond pilot projects to enterprise-wide implementation.
The Skills and Capability Gap
The integration of AI into marketing operations has created a significant skills gap that extends beyond technical capabilities to encompass strategic thinking about human-machine collaboration. Academic research on AI adoption in marketing reveals that successful implementation requires not just technical skills but also the ability to interpret AI outputs, understand limitations, and maintain human oversight of automated processes [19].
| AI Marketing Application | Adoption Rate | Success Rate | Primary Implementation Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content generation and optimization | 78% | 45% | Quality control and brand consistency |
| Predictive customer analytics | 65% | 38% | Data quality and integration |
| Automated campaign optimization | 72% | 52% | Algorithm transparency and control |
| Personalization engines | 69% | 41% | Privacy compliance and consent |
| Chatbots and customer service | 83% | 67% | Natural language understanding |
The Trust and Transparency Challenge
Research from the Journal of Business Research on AI adoption in marketing highlights that trust serves as a critical gatekeeper to AI adoption, with organizations struggling to balance the benefits of automated decision-making against the need for human oversight and accountability [20]. This challenge is particularly acute in marketing contexts where brand reputation and customer relationships are at stake.
The “black box” nature of many AI algorithms creates additional challenges for marketing leaders who must explain and justify AI-driven decisions to stakeholders, customers, and regulatory bodies. This transparency requirement often conflicts with the proprietary nature of AI algorithms and the competitive advantages they provide.
Scaling Challenges and Infrastructure Requirements
McKinsey’s analysis of AI scaling challenges reveals that marketing organizations face particular difficulties in moving from pilot projects to enterprise-wide AI implementation. The challenges include data infrastructure limitations, integration with existing marketing technology stacks, and the need for specialized technical talent that remains scarce in the job market [18].
The computational requirements of advanced AI applications also create infrastructure challenges, particularly for organizations that lack cloud-native architectures or sophisticated data management capabilities. These technical barriers can create significant cost implications and implementation timelines that extend far beyond initial expectations.
Human-Machine Collaboration Models
Successful AI integration in marketing requires developing effective human-machine collaboration models that leverage the strengths of both artificial and human intelligence. Research indicates that the most effective approaches involve AI handling data processing, pattern recognition, and routine optimization tasks while humans focus on strategic thinking, creative development, and relationship management.
However, developing these collaboration models requires significant organizational change management, including redefining roles, updating performance metrics, and creating new workflows that accommodate both human and machine capabilities. Many organizations underestimate the complexity of this organizational transformation when planning AI initiatives.
Ethical Considerations and Responsible AI
The integration of AI into marketing operations raises important ethical considerations around consumer privacy, algorithmic bias, and the potential for manipulation. Academic research on AI ethics in marketing emphasizes the need for organizations to develop responsible AI frameworks that consider the broader societal implications of automated marketing decisions [21].
These ethical considerations are becoming increasingly important as regulatory bodies develop frameworks for AI governance and consumers become more aware of how AI influences their experiences. Organizations that fail to address these ethical considerations proactively may face regulatory scrutiny, consumer backlash, and reputational damage.
The Future of AI in Marketing
Despite current challenges, AI continues to evolve rapidly, with new capabilities emerging regularly that promise to address existing limitations. Advances in explainable AI, federated learning, and privacy-preserving machine learning techniques offer potential solutions to current transparency and privacy challenges.
However, the pace of AI development also creates ongoing challenges for marketing organizations that must continuously evaluate new technologies, update their capabilities, and adapt their strategies to leverage emerging opportunities while managing associated risks.
Strategic Action Plan for Marketing Leaders
Immediate Actions (0-90 Days)
Marketing leaders must begin addressing these critical challenges with immediate, focused actions that establish foundations for longer-term strategic initiatives. The first priority involves conducting a comprehensive audit of current measurement capabilities, technology stack efficiency, and customer acquisition economics to establish baseline performance metrics and identify the most pressing areas for improvement.
Organizations should immediately implement BCG’s recommendation to establish “north star” KPIs that serve as unified success metrics across all marketing functions [1]. This involves convening cross-functional teams including marketing, finance, and analytics to define shared measurement frameworks that align tactical activities with strategic business objectives.
Simultaneously, marketing leaders should conduct a MarTech stack rationalization exercise to identify redundant tools, integration gaps, and underutilized capabilities. This audit should focus on eliminating tools that do not contribute directly to core business objectives and consolidating overlapping functionalities to reduce complexity and operational overhead.
Medium-Term Strategic Initiatives (3-12 Months)
The medium-term action plan should focus on building organizational capabilities that address the root causes of marketing challenges rather than treating symptoms. This includes investing in first-party data infrastructure that reduces dependence on third-party data sources while ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
Organizations should develop comprehensive AI governance frameworks that define how artificial intelligence tools will be evaluated, implemented, and monitored within marketing operations. This framework should address ethical considerations, performance measurement, and human oversight requirements to ensure responsible AI adoption.
Customer acquisition strategy requires fundamental recalibration to address rising costs and declining effectiveness of traditional channels. Marketing leaders should implement account-based marketing approaches for high-value segments while developing owned media capabilities that provide more sustainable, long-term acquisition channels.
Long-Term Transformation (12+ Months)
Long-term success requires organizational transformation that goes beyond technology and process improvements to encompass cultural change and capability development. This includes building marketing technology expertise within the organization through hiring, training, and strategic partnerships that reduce dependence on external vendors and consultants.
Organizations should develop integrated measurement ecosystems that combine marketing mix modeling, incrementality testing, and multi-touch attribution to provide comprehensive insights into marketing effectiveness. This requires significant investment in data infrastructure, analytical capabilities, and cross-functional collaboration processes.
The ultimate goal is creating adaptive marketing organizations that can respond quickly to changing market conditions, regulatory requirements, and technological developments while maintaining focus on sustainable customer acquisition and retention strategies.
Future Outlook and Emerging Trends
The marketing landscape will continue evolving rapidly through 2026 and beyond, driven by technological advancement, regulatory development, and changing consumer expectations. Emerging trends suggest that successful marketing organizations will be those that can balance innovation with operational excellence while maintaining focus on sustainable business outcomes.
Privacy-first marketing approaches will become the standard rather than the exception, with organizations that proactively embrace these constraints gaining competitive advantages through enhanced consumer trust and regulatory compliance. The development of privacy-preserving technologies, including federated learning and differential privacy, will create new opportunities for effective marketing while respecting consumer preferences.
Artificial intelligence will continue maturing from experimental applications to core operational capabilities, but success will depend on organizations’ ability to develop effective human-machine collaboration models rather than simply deploying AI tools. The most successful marketing organizations will be those that use AI to augment human capabilities rather than replace human judgment and creativity.
Customer acquisition economics will likely continue deteriorating in the short term, forcing organizations to develop more sophisticated approaches to customer lifetime value optimization and retention marketing. This shift will favor organizations with strong customer experience capabilities and robust first-party data assets over those dependent on traditional paid acquisition channels.
Key Takeaways
- Measurement Leadership Drives Performance: Organizations that achieve measurement leadership deliver up to 70% higher revenue growth by establishing unified KPI frameworks and integrating multiple measurement approaches rather than relying on fragmented analytics.
- Technology Complexity Requires Strategic Management: The 100-fold growth in marketing technology solutions since 2011 demands systematic approaches to tool selection, integration, and governance rather than ad-hoc technology adoption.
- Customer Acquisition Costs Demand Strategic Recalibration: The 222% increase in customer acquisition costs over the past decade requires fundamental shifts toward customer lifetime value optimization, owned media development, and account-based marketing approaches.
- Privacy Compliance Creates Competitive Differentiation: Organizations that proactively embrace privacy-first marketing approaches gain competitive advantages through enhanced consumer trust while those that resist regulatory requirements face increasing operational and reputational risks.
References
- Rodenhausen, D., Stringer, J., Yu, R., & Goswami, S. (2025). Six Steps to More Effective Marketing Measurement. Boston Consulting Group. https://www.bcg.com/publications/2025/six-steps-to-more-effective-marketing-measurement
- Brinker, S. (2025). Marketing Technology Landscape Supergraphic 2025: 100X Growth Since 2011. Chief Marketing Technologist. https://chiefmartec.com/2025/05/2025-marketing-technology-landscape-supergraphic-100x-growth-since-2011-but-now-with-ai/
- U.S. Small Business Administration. (2025). Market Research and Competitive Analysis. https://www.sba.gov/business-guide/plan-your-business/market-research-competitive-analysis
- HubSpot Research Team. (2025). The State of Marketing Report 2025. HubSpot. https://www.hubspot.com/marketing-statistics
- Ramachandran, K.K. (2023). Evaluating ROI in digital marketing campaigns: metrics, measurement, and insights. International Journal of Management (IJM), 14(2), 45-62.
- Mardiani, E., Utami, E.Y., & Sari, D.P. (2023). B2B Digital Marketing and ROI Measurement: Challenges and Opportunities in the Business-to-Business Industry for MSMEs in Indonesia. West Science Business and Management, 1(3), 123-135.
- Kumar, V., & Reinartz, W. (2024). Creating enduring customer value through marketing technology strategy. Journal of Marketing Technology, 8(2), 78-95.
- Stackla Research. (2025). State of Martech 2025: Complexity and Integration Challenges. Stackla Inc.
- Focus Digital. (2024). Customer Acquisition Cost Trends Report 2024. Focus Digital Marketing Agency.
- Digital Marketing Institute. (2024). The Rising Cost of Customer Acquisition: Industry Analysis. DMI Research Division.
- Shopify Commerce Trends. (2025). E-commerce Customer Acquisition Benchmarks. Shopify Inc.
- Almestarihi, R., Ahmad, A.Y.A., Frangieh, R.H., & Abu Alsondos, I. (2024). Measuring the ROI of paid advertising campaigns in digital marketing and its effect on business profitability. International Journal of Business Analytics, 11(1), 23-41.
- Cisco Systems. (2025). Consumer Privacy Survey 2025: Global Perspectives on Data Protection. Cisco Privacy Research.
- Johnson, G.A., Shriver, S.K., & Goldberg, S.G. (2023). Privacy and market concentration: Intended and unintended consequences of the GDPR. Management Science, 69(10), 5695-5721.
- Cisco Privacy Engineering. (2025). Privacy Investment and ROI Report 2025. Cisco Systems Inc.
- European Commission. (2024). GDPR Impact Assessment: Digital Marketing and Tracking Technologies. EC Digital Single Market Directorate.
- Federal Trade Commission. (2017). Cross-Device Tracking: A Federal Trade Commission Staff Report. FTC Bureau of Consumer Protection.
- Chui, M., Hazan, E., Roberts, R., Singla, A., Smaje, K., Sukharevsky, A., Yee, L., & Zemmel, R. (2025). The State of AI in 2025: Technology Trends and Business Impact. McKinsey Global Institute.
- Kaniz, R.E., Lindon, A.R., Rahman, M.A., & Hasan, M.A. (2025). The Impact of Project Management Strategies on the Effectiveness of Digital Marketing Analytics for Start-up Growth in the United States. Inverge Journal of Social Sciences, 4(1), 112-128.
- Dwivedi, Y.K., Hughes, L., Ismagilova, E., Aarts, G., Coombs, C., Crick, T., … & Williams, M.D. (2021). Artificial Intelligence (AI): Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. International Journal of Information Management, 57, 101994.
- Martin, K.D., Borah, A., & Palmatier, R.W. (2017). Data privacy: Effects on customer and firm performance. Journal of Marketing, 81(1), 36-58.

