In an era where customer expectations continue to evolve at unprecedented speed, organizations that fail to embed customer-centricity into their cultural DNA risk becoming obsolete. Recent research from Forrester reveals that 100% of customer-obsessed companies prioritize teaching employees how to play their part in customer-centric transformation [1], while McKinsey data shows that companies successfully implementing customer-back business models achieve revenue growth rates 3.5 times higher than their competitors [2]. Yet despite these compelling statistics, many organizations struggle to move beyond superficial customer service improvements to achieve true cultural transformation.
The stakes have never been higher. Qualtrics research indicates that $3.7 trillion of global sales are at risk in 2024 due to poor customer experiences, with 50% of customers cutting spending after negative interactions [3]. This represents not just a customer service challenge, but a fundamental business survival issue that demands comprehensive organizational change.
The Strategic Context: Why Customer-Centric Culture Matters Now
Customer-centric culture represents far more than a customer service initiative—it constitutes a fundamental reimagining of how organizations create value, make decisions, and allocate resources. Forrester defines this as “a shared set of beliefs that drives business performance and impacts customers, organizations, employees and stakeholders” [1]. This definition underscores the comprehensive nature of cultural transformation required to achieve sustainable competitive advantage.
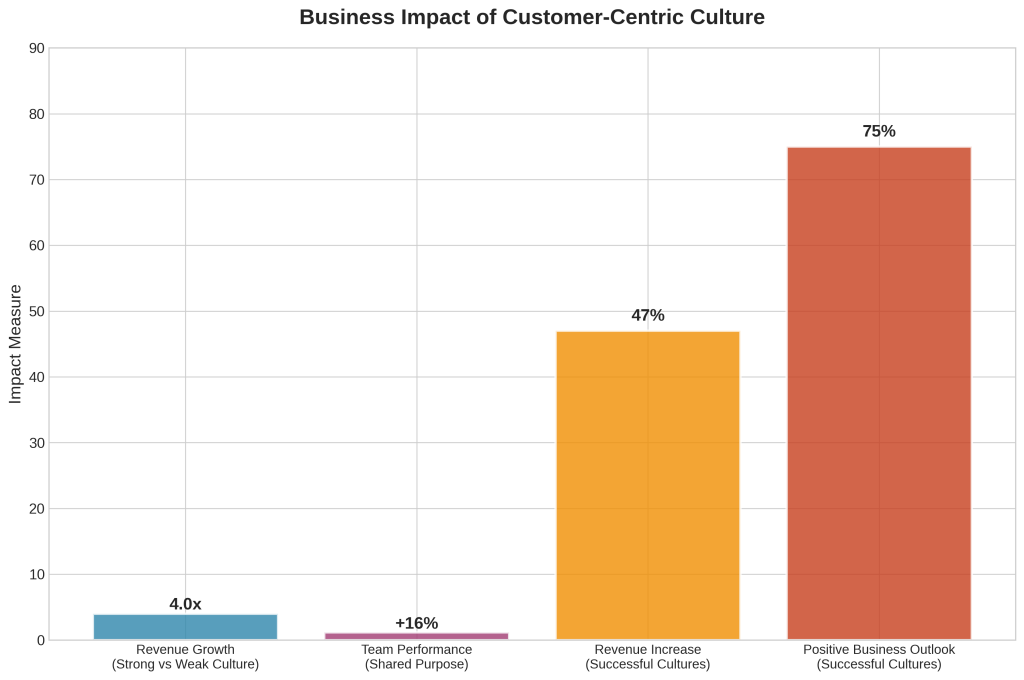
The business case for customer-centric culture has become increasingly compelling. Research from the Arbinger Institute demonstrates that companies with strong corporate cultures experience 4x revenue growth compared to organizations with weak cultures [4]. More specifically, 47% of organizations with very successful company cultures reported significant revenue increases in the past year, compared to just 9% of those with less successful cultures [4]. These statistics reflect not correlation but causation—customer-centric cultures drive measurable business outcomes through improved employee engagement, operational efficiency, and customer loyalty.
The urgency for cultural transformation has intensified due to several converging factors. Digital transformation has fundamentally altered customer expectations, with consumers now demanding seamless, personalized experiences across all touchpoints. Simultaneously, the rise of social media and online review platforms has amplified the impact of customer experiences, making reputation management a critical business function. Organizations that fail to adapt risk not only losing customers but also facing public criticism that can damage their brand for years.
However, the path to customer-centricity is fraught with challenges. McKinsey research reveals that organizations typically capture less than one-third of the value expected from digitalization efforts [2], often because they focus on technology implementation without addressing the underlying cultural foundations. This disconnect between technological capability and cultural readiness represents one of the most significant barriers to successful transformation.
The Four-Pillar Implementation Framework
Based on analysis of successful customer-centric transformations across multiple industries, four critical pillars emerge as essential for sustainable cultural change. This framework, synthesized from Forrester, McKinsey, and academic research, provides a structured approach to organizational transformation that addresses both strategic and operational dimensions.
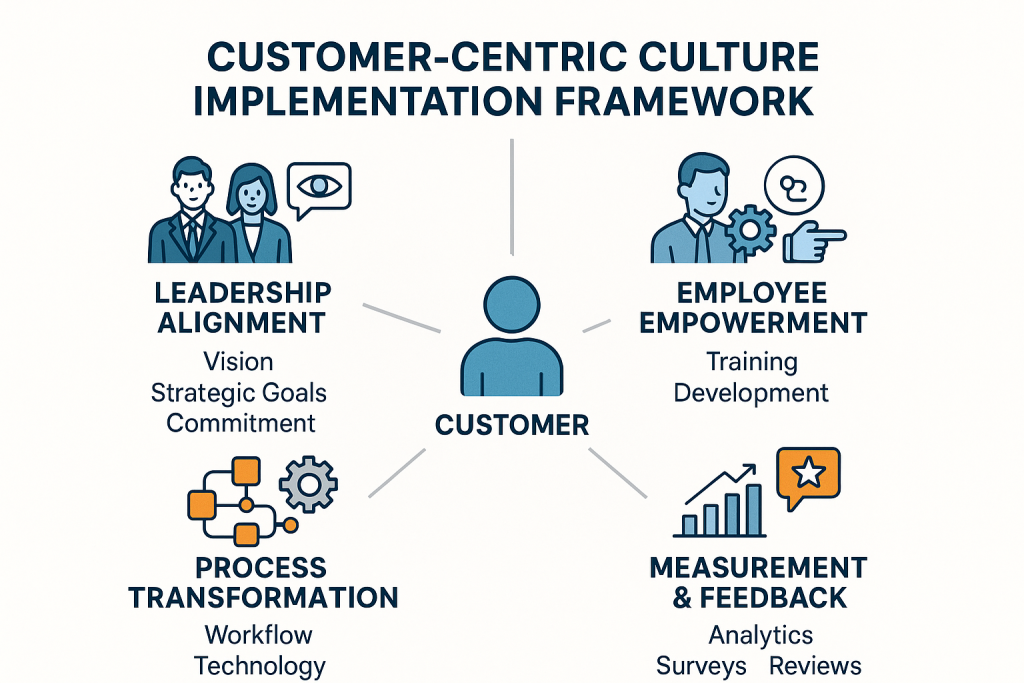
Pillar 1: Leadership Alignment and Vision
Leadership alignment represents the foundational pillar upon which all other transformation efforts depend. Forrester research emphasizes that customer-obsessed leadership is crucial to developing high-performing employees who embody a customer-first mindset [1]. This requires more than executive buy-in—it demands active modeling of customer-centric behaviors and decision-making processes at every leadership level.
The Center for Creative Leadership found that 60% of managers never received training when transitioning into their first leadership role [1], creating a significant gap in organizational capability. Organizations must address this deficit through comprehensive leadership development programs that align with customer-centric values. Successful companies invest in four key areas: defining customer-obsessed culture with clear behavioral expectations, implementing leadership development at all levels, leveraging technology to support growth, and recognizing exemplary customer-obsessed leadership [1].
Pillar 2: Employee Empowerment and Development
Employee empowerment extends beyond traditional training programs to encompass fundamental changes in how organizations hire, develop, and retain talent. Research indicates that organizations focusing on employee mindset are more likely to report that their workforce trusts each other and seeks to understand their impact on others [4]. This foundation of trust and empathy becomes critical for delivering authentic customer experiences.
The empowerment pillar requires systematic investment in capability building. Organizations must establish recognition and reward programs tied to customer obsession, create opportunities for employees to apply customer-centric knowledge, and provide personalized coaching aligned with individual goals [1]. This approach not only accelerates employee growth but also cultivates a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
Pillar 3: Process Transformation and Technology Integration
Process transformation involves reimagining business operations from the customer’s perspective, often requiring significant changes to established workflows and systems. McKinsey’s customer-back business model (CBM) approach emphasizes the importance of cross-cutting digital capabilities that generate new ways to create customer value [2]. This transformation must be business-focused rather than technology-driven, ensuring that digital tools enhance rather than complicate customer interactions.
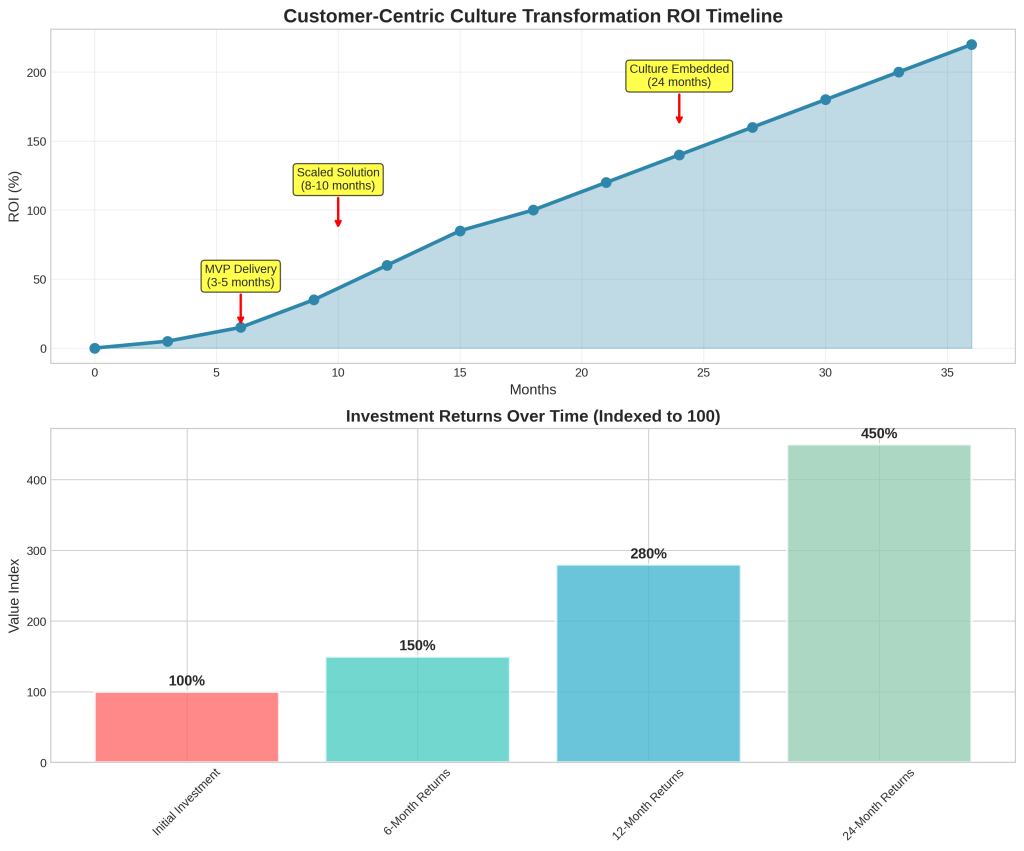
Successful process transformation follows a structured approach: setting ambitious business aspirations, prioritizing cross-functional initiatives that produce short-term impact, and applying digital technology to reimagined processes with rapid development and scaling [2]. Organizations should aim to deliver minimum viable products within 3-5 months and achieve industrialized solutions within 8-10 months [2].
Pillar 4: Measurement, Feedback, and Continuous Improvement
The measurement pillar ensures that customer-centric initiatives generate measurable value and provide data for continuous improvement. This requires sophisticated approaches to ROI measurement that go beyond traditional financial metrics to include customer lifetime value, retention rates, and employee engagement scores.
| Metric Category | Examples | Purpose | Measurement Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forensic Metrics | Customer Lifetime Value, Revenue Impact | Direction and magnitude of results | Quarterly |
| Performance Metrics | Churn Rate, Retention Rate | Direction of results | Monthly |
| Vanity Metrics | CSAT, NPS | General sentiment indicators | Continuous |
Leadership as the Cultural Catalyst
Leadership development emerges as the most critical success factor in customer-centric transformation. Arbinger Institute research reveals that 52% of respondents identify leadership development as having the greatest impact on improving organizational culture [4]. This finding underscores the pivotal role that managers and executives play in either enabling or hindering cultural change.

The leadership challenge is multifaceted. Gallup research demonstrates that 70% of variance in employee engagement directly relates to the manager [4], making front-line leadership development essential for cultural transformation. However, many organizations focus primarily on senior executive alignment while neglecting the middle management layer that directly influences employee behavior and customer interactions.
Effective leadership development for customer-centricity requires specific competencies. Leaders must develop skills in customer empathy, data-driven decision making, cross-functional collaboration, and change management. Organizations that focus on mindset in their leadership development programs are almost twice as likely to have employees who feel they are doing meaningful work [4]. This connection between leadership mindset and employee engagement creates a multiplier effect that amplifies customer-centric behaviors throughout the organization.
The most successful leadership development programs combine multiple learning modalities: expert-led classroom training, peer coaching, just-in-time e-learning, and ongoing coaching support [1]. This comprehensive approach ensures that leaders not only understand customer-centric principles but also develop the practical skills needed to implement them in their daily operations.
ROI Measurement and Performance Metrics
Measuring the return on investment for customer-centric culture initiatives presents unique challenges that require sophisticated analytical approaches. The basic ROI formula—(Benefit of initiative – Cost of initiative) / Cost of initiative—provides a starting point, but the complexity lies in accurately attributing benefits and accounting for long-term impacts [3].

Qualtrics research identifies three primary challenges in ROI measurement: attributing impact to specific initiatives, accounting for long-term benefits, and collecting comprehensive data on customer behavior [3]. These challenges require organizations to develop measurement frameworks that combine quantitative metrics with qualitative insights to provide a complete picture of transformation progress.
The measurement pyramid approach provides a structured framework for ROI assessment. Forensic metrics, such as customer lifetime value and revenue impact, offer the most actionable insights by showing both direction and magnitude of results. Performance metrics, including churn rates and retention rates, indicate directional trends but may not capture the full financial impact. Vanity metrics, while useful for general sentiment tracking, should not be relied upon as primary indicators of transformation success [3].
Organizations must also account for the significant costs associated with poor customer experience. Research indicates that quiet quitting alone leads to worldwide company losses of up to $1.5 trillion annually [4], while toxic culture is 10 times more likely to cause employee turnover than compensation issues [4]. These hidden costs often exceed the direct investments required for cultural transformation, making the business case for change even more compelling.
Implementation Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
Despite the clear business benefits, customer-centric culture transformation faces significant implementation challenges that organizations must anticipate and address proactively. Academic research identifies nine key shaping factors and three primary barriers to building customer-centric organizations, though the specific details require further investigation due to access limitations [5].
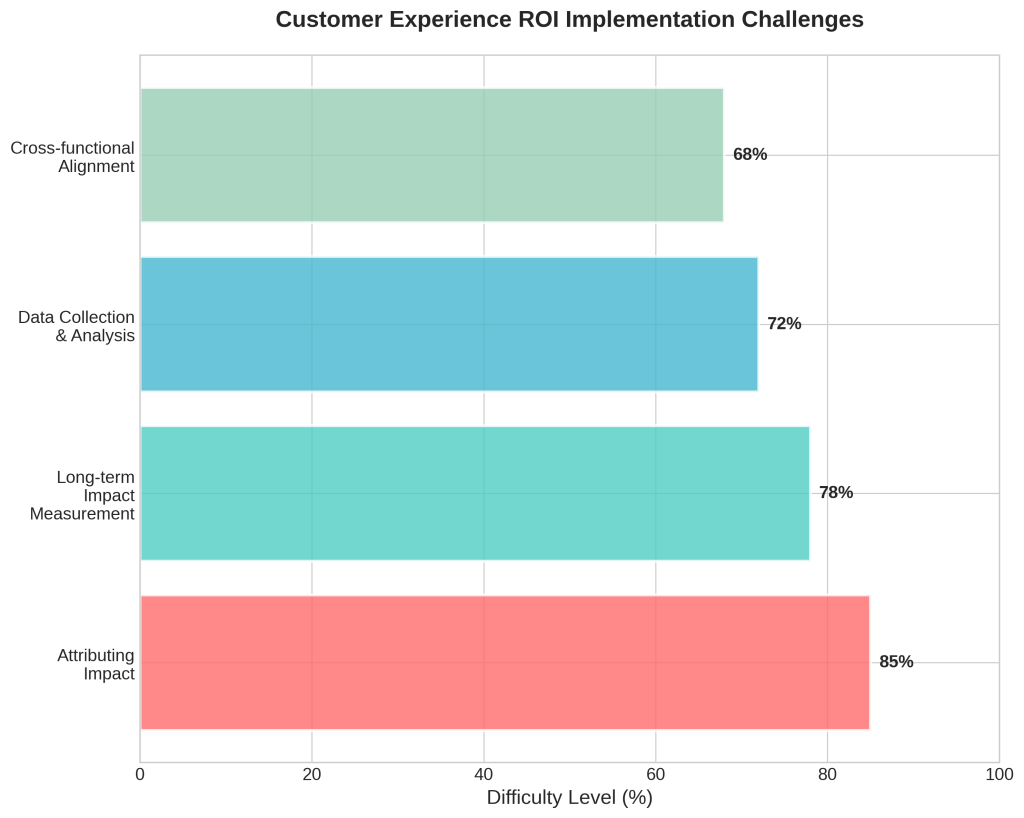
The most significant challenge involves attributing impact to specific customer-centric initiatives. Revenue growth and cost reduction result from multiple factors including marketing efforts, product enhancements, and economic conditions. Isolating the impact of cultural transformation requires sophisticated analytical capabilities and often specialized expertise that many organizations lack [3].
Long-term impact measurement presents another substantial challenge. Benefits such as improved brand reputation, enhanced customer lifetime value, and increased customer loyalty often take years to fully materialize. Organizations may undervalue transformation initiatives by focusing primarily on short-term financial metrics while overlooking these longer-term strategic advantages [3].
Data collection and analysis challenges compound these measurement difficulties. Gathering accurate, comprehensive data on customer behavior requires coordination across multiple departments and systems. Some data owners may be reluctant to share information, while organizations may not be collecting the necessary data in the first place. Customer feedback collection, while essential, requires significant time and effort to execute effectively [3].
Cultural resistance represents perhaps the most pervasive challenge. Long-standing habits and siloed thinking make it difficult for teams to embrace customer-first philosophies. This resistance often manifests as skepticism about new processes, reluctance to share information across departments, and preference for familiar metrics over customer-centric measures.
Mitigation Strategies
Successful organizations address these challenges through systematic mitigation strategies. For attribution challenges, they invest in advanced analytics capabilities and establish clear baseline measurements before implementing transformation initiatives. They also use control groups and A/B testing methodologies to isolate the impact of specific changes.
To address long-term measurement challenges, organizations develop balanced scorecards that include both short-term operational metrics and long-term strategic indicators. They also establish regular review cycles that track progress over extended periods and adjust strategies based on emerging data.
For data collection challenges, successful organizations invest in integrated customer data platforms and establish clear data governance protocols. They also create incentive structures that encourage data sharing and collaboration across departments.
Cultural resistance requires the most comprehensive mitigation approach. Organizations must invest heavily in change management, communication, and training programs. They also need to identify and address specific sources of resistance while celebrating early wins to build momentum for broader transformation.
The Transformation Journey: A Phased Approach
Customer-centric culture transformation requires a structured, phased approach that balances ambition with practical implementation realities. McKinsey research demonstrates that organizations can generate positive returns within six months through carefully sequenced initiatives, but achieving full cultural transformation typically requires 24-36 months of sustained effort [2].
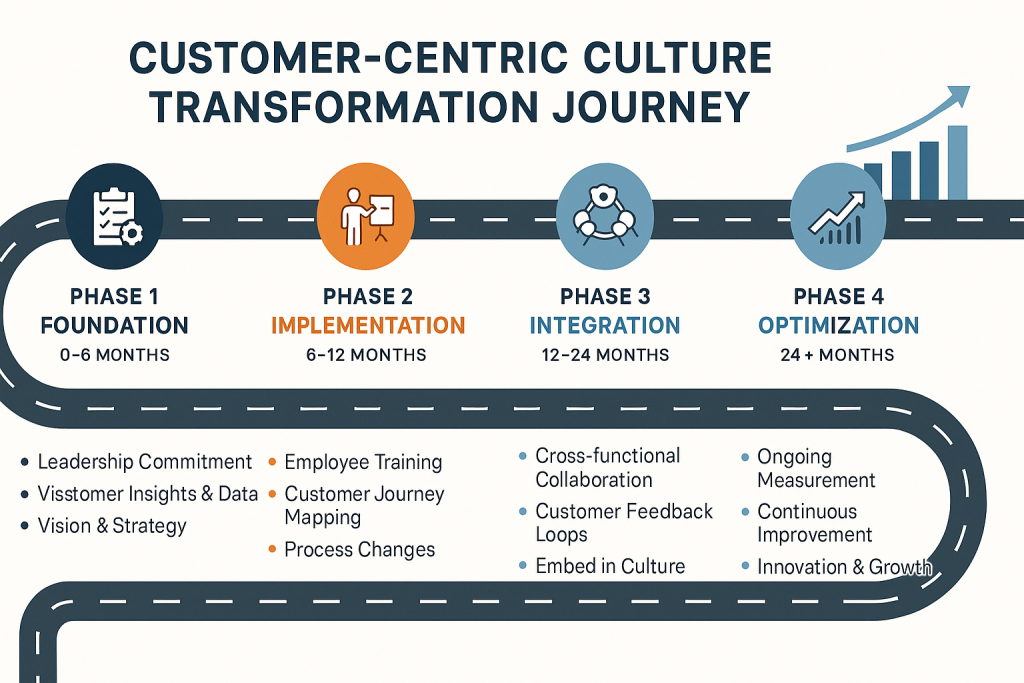
Phase 1: Foundation (0-6 months)
The foundation phase focuses on establishing the strategic and operational groundwork for transformation. Organizations must secure leadership commitment, develop customer insights and data capabilities, and create a clear vision and strategy for customer-centricity. This phase requires significant investment in planning and preparation but provides the foundation for all subsequent transformation efforts.
Key activities during the foundation phase include conducting comprehensive customer research, mapping current customer journeys, assessing organizational readiness for change, and developing detailed transformation roadmaps. Organizations should also establish baseline measurements and identify quick wins that can demonstrate early progress and build momentum for broader change.
Phase 2: Implementation (6-12 months)
The implementation phase involves executing initial customer-centric initiatives while building organizational capabilities for sustained transformation. This phase typically includes employee training programs, customer journey mapping exercises, and process changes designed to improve customer experiences. Organizations should focus on initiatives that can deliver measurable impact within 3-5 months while building capabilities for longer-term transformation [2].
During this phase, organizations often encounter their first significant resistance to change. Success requires strong change management capabilities, clear communication about transformation benefits, and visible leadership support for new customer-centric behaviors. Organizations should also establish feedback mechanisms to capture lessons learned and adjust their approach based on early results.
Phase 3: Integration (12-24 months)
The integration phase focuses on embedding customer-centric practices into organizational systems and processes. This involves cross-functional collaboration initiatives, customer feedback loops, and systematic integration of customer-centric metrics into performance management systems. Organizations must also address any remaining pockets of resistance while scaling successful initiatives across the entire organization.
Integration requires sophisticated coordination capabilities as organizations work to align previously siloed departments around common customer-centric goals. This phase often reveals additional opportunities for improvement while also highlighting the need for ongoing investment in capability building and system integration.
Phase 4: Optimization (24+ months)
The optimization phase involves ongoing measurement, continuous improvement, and innovation based on customer feedback and market changes. Organizations should establish systematic processes for monitoring customer-centric metrics, identifying improvement opportunities, and implementing innovative solutions that enhance customer experiences.
This phase represents the transition from transformation project to ongoing organizational capability. Successful organizations develop self-reinforcing systems that continuously improve customer experiences while adapting to changing market conditions and customer expectations.
Practical Action Plan for Implementation
Organizations seeking to build customer-centric cultures require detailed action plans that translate strategic concepts into specific, executable initiatives. Based on research from leading consulting firms and successful transformation case studies, the following action plan provides a practical framework for implementation.
Immediate Actions (First 30 Days)
Organizations should begin by conducting a comprehensive assessment of their current customer-centric maturity. This assessment should evaluate leadership alignment, employee engagement levels, customer satisfaction metrics, and organizational processes. The assessment provides baseline data for measuring transformation progress and identifies specific areas requiring immediate attention.
Leadership teams must also establish clear governance structures for transformation initiatives. This includes appointing transformation leaders, defining decision-making processes, and establishing communication protocols. Without strong governance, transformation efforts often lose momentum or become fragmented across different organizational units.
Organizations should also begin collecting customer feedback through multiple channels including surveys, interviews, and social media monitoring. This feedback provides essential insights into customer expectations and identifies specific pain points that transformation efforts should address.
Short-term Initiatives (30-90 Days)
The short-term phase focuses on building organizational capabilities and implementing quick wins that demonstrate transformation value. Organizations should establish customer journey mapping processes that identify key touchpoints and improvement opportunities. These maps provide visual representations of customer experiences and help teams understand how their actions impact customer satisfaction.
Leadership development programs should begin during this phase, starting with senior executives and cascading through middle management. These programs should focus on customer empathy, data-driven decision making, and change leadership skills. Organizations should also establish recognition and reward systems that reinforce customer-centric behaviors.
Technology infrastructure improvements often provide quick wins that enhance customer experiences while building organizational confidence in transformation efforts. These might include customer relationship management system upgrades, customer feedback platforms, or data analytics capabilities that provide better insights into customer behavior.
Medium-term Initiatives (90 Days – 12 Months)
Medium-term initiatives focus on systematic process improvements and organizational capability building. Organizations should implement cross-functional collaboration mechanisms that break down silos and improve coordination around customer needs. This often requires changes to organizational structure, performance metrics, and communication processes.
Employee training programs should expand during this phase to include all customer-facing roles and key support functions. Training should combine customer service skills with deeper understanding of customer psychology, data analysis, and problem-solving techniques. Organizations should also establish mentoring and coaching programs that reinforce learning and provide ongoing support for behavior change.
Process redesign initiatives should focus on eliminating customer pain points while improving operational efficiency. This often involves automating routine tasks, streamlining approval processes, and implementing self-service options that give customers more control over their experiences.
Long-term Initiatives (12+ Months)
Long-term initiatives focus on embedding customer-centricity into organizational DNA through systematic culture change. Organizations should establish ongoing measurement and improvement processes that continuously monitor customer satisfaction and identify new improvement opportunities. These processes should include regular customer research, employee engagement surveys, and competitive benchmarking.
Innovation programs should focus on developing new products, services, and experiences that exceed customer expectations. These programs should involve customers directly in the innovation process through co-creation workshops, beta testing programs, and feedback sessions.
Organizations should also develop strategic partnerships that enhance their ability to deliver exceptional customer experiences. These partnerships might include technology vendors, service providers, or other organizations that can provide complementary capabilities or access to new customer segments.
Future Outlook and Emerging Trends
The landscape of customer-centric culture continues to evolve rapidly, driven by technological advancement, changing customer expectations, and competitive pressures. Organizations must anticipate these trends and adapt their transformation strategies accordingly to maintain competitive advantage in an increasingly customer-driven marketplace.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are fundamentally changing how organizations understand and respond to customer needs. These technologies enable real-time personalization, predictive customer service, and automated problem resolution that can significantly enhance customer experiences. However, they also require new organizational capabilities and raise important questions about data privacy and human interaction preferences.
The rise of digital-native customer segments is creating new expectations for seamless, omnichannel experiences. These customers expect consistent service quality across all touchpoints and immediate resolution of issues regardless of communication channel. Organizations must develop integrated technology platforms and cross-functional coordination capabilities to meet these expectations.
Sustainability and social responsibility are becoming increasingly important factors in customer decision-making. Organizations must integrate these considerations into their customer-centric strategies while ensuring that sustainability initiatives enhance rather than compromise customer experiences. This requires sophisticated balancing of multiple stakeholder interests and long-term thinking about value creation.
Remote and hybrid work models are changing how organizations deliver customer service and build customer relationships. These models require new approaches to employee training, performance management, and customer interaction that maintain service quality while providing flexibility for both employees and customers.
Emerging Challenges and Opportunities
Data privacy regulations and customer concerns about data usage are creating new challenges for customer-centric organizations. Companies must balance the need for customer insights with respect for privacy preferences while maintaining transparency about data collection and usage practices. This requires sophisticated data governance capabilities and ongoing dialogue with customers about value exchange.
The increasing complexity of customer journeys across multiple channels and touchpoints is making it more difficult to deliver consistent experiences. Organizations must invest in integration technologies and cross-functional coordination capabilities while also simplifying customer interactions wherever possible.
Competitive pressures are intensifying as more organizations recognize the importance of customer-centricity. This creates opportunities for early movers while also raising the bar for customer experience quality across entire industries. Organizations must continuously innovate and improve to maintain competitive advantage.
Economic uncertainty and changing market conditions require organizations to balance customer-centric investments with financial performance pressures. This requires sophisticated ROI measurement capabilities and strategic thinking about which customer-centric initiatives provide the greatest value under different economic scenarios.
Key Takeaways
Building a customer-centric culture represents one of the most significant strategic imperatives facing organizations in 2026. The research evidence overwhelmingly demonstrates that companies with strong customer-centric cultures achieve superior financial performance, employee engagement, and customer loyalty compared to their competitors.
The business case is compelling: Organizations with strong corporate cultures experience 4x revenue growth, while customer-obsessed companies are 3.5 times more likely to achieve above-average revenue growth rates. The cost of inaction is equally significant, with $3.7 trillion in global sales at risk due to poor customer experiences.
Success requires systematic transformation: Customer-centric culture cannot be achieved through superficial changes or isolated initiatives. It requires comprehensive transformation across four critical pillars: leadership alignment, employee empowerment, process transformation, and measurement systems. Organizations must commit to multi-year transformation journeys with sustained investment and leadership support.
Leadership development is the critical success factor: With 70% of employee engagement variance directly related to managers, leadership development emerges as the most important lever for cultural transformation. Organizations must invest in comprehensive leadership development programs that build customer empathy, data-driven decision making, and change management capabilities.
Measurement complexity requires sophisticated approaches: ROI measurement for customer-centric initiatives presents unique challenges that require balanced approaches combining forensic, performance, and vanity metrics. Organizations must develop attribution capabilities while accounting for long-term benefits that may take years to fully materialize.
Implementation challenges are significant but manageable: Cultural resistance, data collection difficulties, and attribution challenges represent substantial barriers to transformation. However, organizations can overcome these challenges through systematic mitigation strategies, strong change management, and phased implementation approaches.
The future demands continuous adaptation: Emerging technologies, changing customer expectations, and competitive pressures require organizations to view customer-centricity as an ongoing capability rather than a one-time transformation project. Success requires continuous learning, innovation, and adaptation to changing market conditions.
References
[1] Forrester Research. “Support Growth By Creating A Customer-Centric Culture.” https://www.forrester.com/bold/customer-centric-culture/
[2] McKinsey & Company. “Growing through a customer-centric business model.” December 10, 2024. https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/industrials-and-electronics/our-insights/true-customer-centricity-an-operating-model-for-competitive-advantage
[3] Qualtrics. “Understanding Customer Experience ROI.” https://www.qualtrics.com/experience-management/customer/customer-experience-roi/
[4] Arbinger Institute. “The ultimate list of corporate culture statistics.” https://arbinger.com/blog/the-ultimate-list-of-corporate-culture-statistics/
[5] van den Hemel, Carmen, and Martijn F. Rademakers. “Building Customer-centric Organizations: Shaping Factors and Barriers.” Journal of Creating Value 2, no. 2 (2016): 211-230. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/2394964316647822

