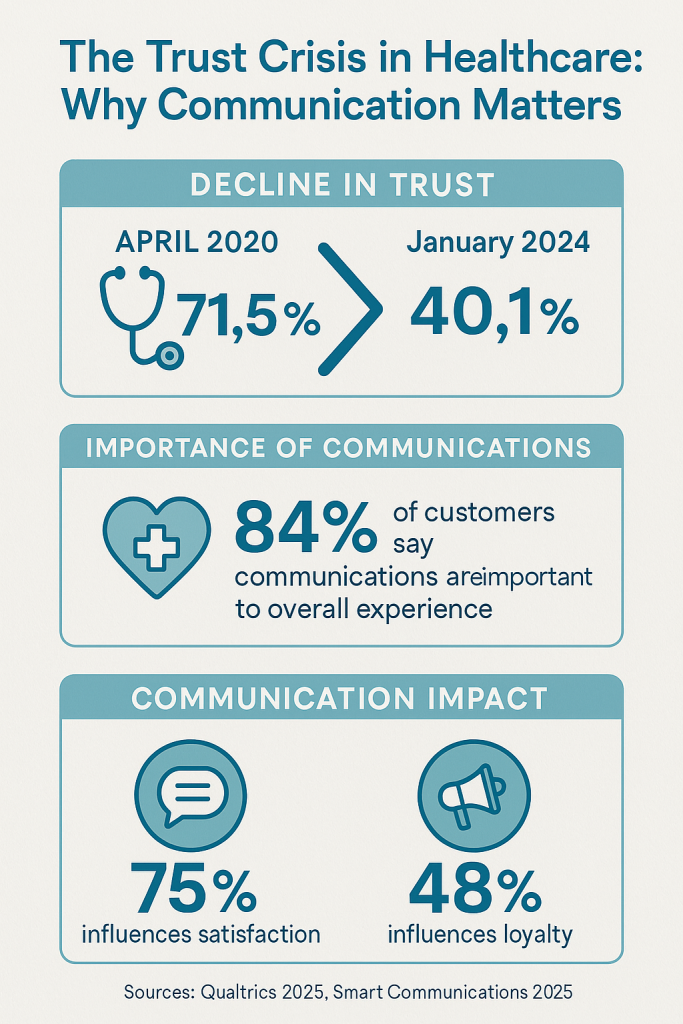
Healthcare organizations worldwide are experiencing a digital transformation crisis that demands immediate attention. With patient trust in healthcare providers plummeting from 71.5% in April 2020 to just 40.1% by January 2024 [1], the industry faces an unprecedented challenge in rebuilding relationships through enhanced digital customer experiences. This comprehensive analysis examines how healthcare organizations can leverage digital technologies to improve patient engagement, operational efficiency, and clinical outcomes while addressing the fundamental trust deficit that threatens the sector’s future.
The stakes have never been higher. As 90% of healthcare executives expect digital technology adoption to accelerate significantly in 2026 [2], organizations must navigate complex challenges including cybersecurity threats, workforce shortages, and evolving patient expectations. The evidence is clear: healthcare systems that successfully implement comprehensive digital customer experience strategies are seeing measurable improvements in patient satisfaction, appointment adherence, and operational efficiency.
The Current State of Healthcare Digital Transformation
Healthcare’s digital transformation journey reveals a sector in transition, with significant disparities between organizational intentions and actual implementation capabilities. According to Deloitte’s 2026 Global Healthcare Outlook, accelerated digital transformation was cited as the issue most likely to impact global health systems in 2026 [2]. This finding underscores a critical reality: healthcare remains years behind other industries such as retail and finance in adopting digital technologies.
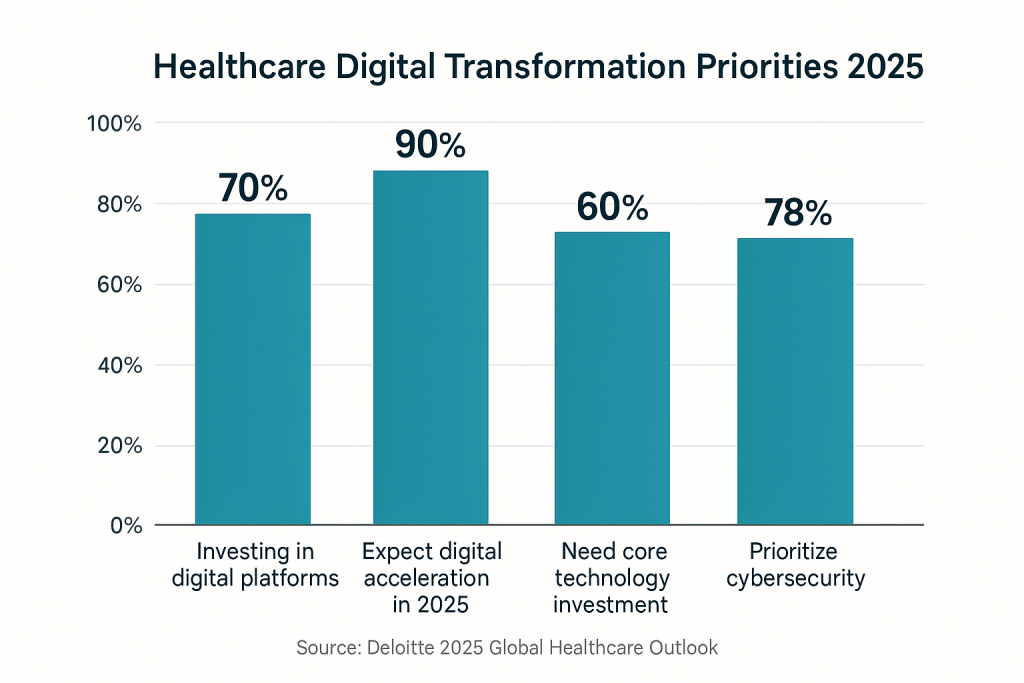
The data reveals both opportunity and urgency. While 70% of survey respondents indicated that investing in technology platforms for digital tools and services will be important for their organizations, 60% highlighted the critical need to invest in core technologies such as electronic medical records (EMRs) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) software [2]. This suggests that many healthcare systems are still addressing fundamental infrastructure gaps before they can implement more advanced digital customer experience initiatives.
The geographic disparities in digital transformation readiness are particularly striking. Among non-US respondents, 52% said digital transformation could have a significant impact on their organizational strategies, compared with just 30% of US respondents [2]. This difference may reflect varying levels of existing digital infrastructure, regulatory environments, and organizational readiness for change.
The persistence of outdated workflows presents both challenges and opportunities. Many health systems continue to rely on fax machines, manual processes, and paper-based workflows for critical functions such as patient referrals, appointment scheduling, and data entry [2]. These manual processes not only create inefficiencies but also represent significant barriers to delivering the seamless digital experiences that patients increasingly expect.
Infrastructure Investment Priorities
| Investment Area | Percentage of Organizations | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Digital platforms and tools | 70% | Enhanced patient engagement, streamlined workflows |
| Core technologies (EMR, ERP) | 60% | Data integration, operational efficiency |
| Cybersecurity enhancements | 78% | Risk mitigation, regulatory compliance |
| Cloud migration | Not specified | Scalability, computing power, security |
The cybersecurity imperative cannot be overstated. With 78% of surveyed executives indicating that enhancing cybersecurity is a priority for 2026 [2], organizations must balance the drive for digital transformation with the need to protect sensitive patient data. This dual challenge requires sophisticated approaches that enable innovation while maintaining robust security frameworks.
The Trust Crisis and Communication Imperative
The healthcare industry faces a profound trust crisis that directly impacts digital customer experience initiatives. The dramatic decline in patient trust—from 71.5% in April 2020 to 40.1% by January 2024—represents more than a statistical concern; it reflects a fundamental breakdown in the patient-provider relationship that digital technologies must help address [1].
Qualtrics’ 2026 Healthcare Trends Report provides crucial insights into the factors that drive patient trust. The research indicates that emotion—specifically, how patients perceive the staff’s concern for them as individuals—has the most profound effect on trust, significantly surpassing the ease of accessing care and even the success in receiving it [1]. This finding has profound implications for digital customer experience design, suggesting that technology implementations must prioritize emotional connection and personalized care delivery.
The role of care team collaboration emerges as a critical factor in shaping patient emotional experiences. Patients identified teamwork—collaboration among members of the care team—as the most significant element affecting their emotional experience of care across all three care settings: inpatient, outpatient, and emergency room [1]. This insight challenges healthcare organizations to ensure that their digital tools enhance rather than fragment care coordination.
The Communication-Experience Connection
Smart Communications’ 2026 Healthcare Benchmark Report reveals the critical importance of communication quality in healthcare customer experience. An overwhelming 84% of customers globally say communications are important when it comes to their overall experience with a company [3]. In healthcare specifically, this translates to measurable impacts on both satisfaction and loyalty: 75% of healthcare consumers report that communications influence their overall satisfaction, while 48% say communications directly influence their loyalty to healthcare providers [3].
The quality assessment data provides both encouraging and concerning insights. While 63% of healthcare customers view communications as very good or excellent—an improvement from 51% in 2024—a significant 37% of healthcare customers disagree with positive communication assessments, putting their loyalty at risk [3]. This polarization suggests that while some organizations are succeeding in their communication strategies, others are falling significantly short of patient expectations.
The research identifies several key areas where healthcare communications are failing to meet customer expectations. Forms and digital interfaces are falling short of customer expectations, with patients demanding more guided digital conversations and intuitive user experiences [3]. Additionally, patients are increasingly seeking channel choice—the ability to communicate with their healthcare providers through their preferred methods, whether that’s phone, email, text messaging, or patient portal interactions.
Digital Tools Driving Patient Engagement
The evidence for digital tools’ impact on patient engagement and healthcare outcomes is compelling and measurable. Epic Research’s comprehensive 2024 study, analyzing more than 1.6 billion face-to-face outpatient visits, provides definitive proof of patient portals’ effectiveness in improving appointment adherence and overall patient engagement [4].
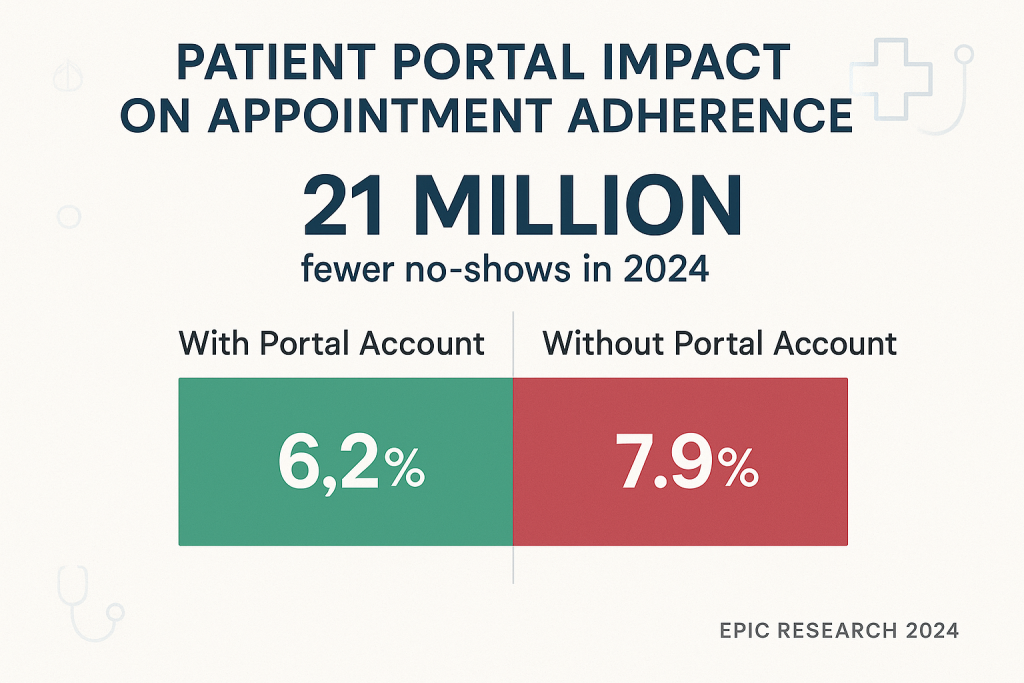
The study’s findings are remarkable in their scope and consistency. Patients with an active patient portal account at the time of scheduling their appointment were 21.5% less likely to no-show than those without an account, with a no-show rate of 6.2% for those with a patient portal account compared to 7.9% for those without [4]. When extrapolated across the healthcare system, this translates to more than 21 million fewer no-shows in 2024 across the 1.26 billion scheduled visits among patient portal users.
The age-based analysis reveals important insights about digital tool adoption and effectiveness across different patient populations. The greatest difference in no-show rates was observed among patients aged 50-64, with portal users having a 6.2% no-show rate compared to 8.7% of non-users [4]. This finding challenges common assumptions about older patients’ comfort with digital technologies and suggests that well-designed patient portals can be particularly effective for middle-aged and older adult populations.
Patient Portal Usage Trends and Outcomes
The broader landscape of patient portal adoption shows significant growth and evolving usage patterns. According to the National Center for Health Statistics, 34% of individuals became frequent portal users in 2024, accessing their records six or more times in the past year—a substantial increase from just 15% in 2019 [5]. This growth trajectory indicates increasing patient comfort with digital health tools and growing expectations for digital access to health information.
The most common uses of patient portals in 2024 were viewing laboratory test results and clinical notes, accounting for 90% and 80% of portal use, respectively [6]. This usage pattern suggests that patients are primarily using portals for information access rather than interactive features, indicating potential opportunities for healthcare organizations to expand portal functionality and engagement.
However, the data also reveals important limitations and disparities in portal adoption. While 61.3% of respondents accessed patient portals within the past year, only 33.4% of those users could be classified as frequent users [7]. Additionally, more than half of individuals nationally (59%) had multiple online medical records or patient portals in 2024, but only 7% reported using a portal organizing tool to manage these multiple accounts [8]. This fragmentation presents significant challenges for patients trying to manage their healthcare information across multiple providers and systems.
Mobile Health Applications and Patient Satisfaction
The mobile health application landscape presents additional opportunities and challenges for healthcare customer experience. Recent research indicates that 55% of patients prefer using mobile apps for healthcare interactions, with 53% of U.S. consumers believing that adding more technology to healthcare settings would improve patient experience [9]. This preference for mobile-first interactions aligns with broader consumer technology trends and suggests that healthcare organizations must prioritize mobile-optimized experiences.
The relationship between mobile health applications and patient outcomes shows promising results, though with important caveats. Studies examining mobile applications’ effect on patient satisfaction and compliance have found that 75% of research concluded that mobile applications improved patient satisfaction, while 25% reported no differences when compared with routine care [10]. These mixed results highlight the importance of thoughtful application design and implementation rather than simply deploying technology for its own sake.
AI and Automation in Healthcare Experience
Artificial intelligence and automation represent both the greatest opportunity and the most significant challenge in healthcare digital customer experience. The current state of AI adoption in healthcare reveals a cautious but optimistic approach from both providers and patients, with clear preferences for supportive rather than replacement roles for AI technologies.
Healthcare providers’ comfort with AI varies significantly based on the specific application. Among various AI applications, comfort levels for doctors and nurses are highest (53%) when it comes to AI managing administrative tasks [1]. This preference for AI in administrative roles rather than direct patient care reflects providers’ protective instincts regarding patient safety and their desire to maintain meaningful human connections in clinical interactions.
The generative AI landscape in healthcare shows rapid evolution and measured optimism. More than 40% of healthcare organizations report that they have already experienced significant-to-moderate return on their investments in generative AI, while 37% indicate it is too early to determine ROI [2]. This split suggests that while early adopters are seeing benefits, the technology is still in its early stages of healthcare implementation.
AI Implementation Priorities and Challenges
The potential applications for AI in healthcare customer experience are extensive, particularly in addressing the manual processes that currently plague healthcare operations. Administrative processes that are still performed manually in health systems around the world could be automated using generative AI and other digital technologies [2]. Examples include patient referrals typically made via fax, phone, or email, followed by manual data entry into patient records, as well as appointment scheduling, confirmation calls, and data entry for visits, diagnoses, treatment plans, and post-discharge care.
Autonomous generative AI agents, also known as “agentic AI,” represent the next frontier in healthcare automation. These software solutions are capable of completing complex tasks and meeting objectives with minimal or no human supervision [2]. Unlike chatbots and co-pilots, agentic AI has the potential to increase the productivity of knowledge workers and automate multi-step processes across business functions, potentially transforming healthcare administrative efficiency.
However, significant challenges and limitations accompany AI implementation in healthcare. The technology has been shown to “hallucinate” and produce false information if it hasn’t been trained on appropriate data sets or quality-checked by humans [2]. Additionally, if the data used to train AI models is biased or unbalanced, the information produced could be unreliable, potentially exacerbating existing healthcare disparities.
Regulatory Landscape and AI Governance
The regulatory environment for AI in healthcare is rapidly evolving, with more than 80% of surveyed health system executives expecting the proliferation of generative AI to have either significant (26%) or moderate (55%) impact on their organizations in 2026 [2]. Respondents also agreed that regulatory oversight of this technology is necessary, indicating industry recognition of the need for appropriate governance frameworks.
In the United States, the FDA is updating regulations to manage the growing use of AI in healthcare, with a focus on patient safety and the lifecycle of AI tools [2]. Similarly, the European Union has introduced a comprehensive framework to address AI use in healthcare through the EU AI Act, which defines AI systems and classifies them into four risk categories: unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal risk, with unacceptable systems being prohibited and requiring phase-out [2].
Implementation Challenges and Limitations
While the potential benefits of healthcare digital customer experience initiatives are substantial, organizations face significant implementation challenges that must be acknowledged and addressed. These challenges span technical, organizational, cultural, and financial dimensions, each requiring specific strategies and resources to overcome.
Workforce and Organizational Challenges
The healthcare workforce crisis presents a fundamental challenge to digital transformation initiatives. Despite improvements in provider engagement—with doctor/physician burnout rates falling below 50% for the first time in four years in 2024—retention challenges persist [1]. Specifically, 30% of doctors and 42% of nurses are contemplating leaving their organizations within the next five years, representing a 12-point gap that has increased from nine points in 2023 [1].
These workforce challenges directly impact digital customer experience initiatives in several ways. First, staff shortages can limit the human resources available to support digital transformation projects. Second, high turnover rates can disrupt the continuity needed for successful technology implementations. Third, the stress and burnout that contribute to turnover can create resistance to new technologies and processes, particularly if they are perceived as adding to workload rather than reducing it.
The transformation of care teams presents additional complexity. Recent years have seen notable changes with the rise of traveling nurses, higher turnover rates, reduced staffing ratios, and increasing reliance on advanced practice providers [1]. These shifts affect both local teams and overall organizational culture, potentially impacting the collaborative teamwork that patients identify as crucial to their emotional experience of care.
Technical and Infrastructure Limitations
Many healthcare organizations continue to operate with legacy systems and outdated infrastructure that create barriers to digital customer experience improvements. The persistence of fax machines, manual processes, and paper-based workflows reflects deeper infrastructure challenges that cannot be resolved through surface-level digital initiatives [2].
Cloud migration represents a critical infrastructure challenge for many organizations. Those that have not yet transitioned to cloud environments may find it challenging to implement transformative technologies [2]. The cloud provides substantial computing power, data storage, and security capabilities that are essential for supporting advanced digital customer experience tools, including AI and machine learning applications.
Data integration and interoperability remain persistent challenges. High-quality, unbiased data is crucial for digital technologies to reach their full potential in improving efficiencies [2]. Health systems often need to integrate data from multiple platforms across their organizations, requiring careful attention to governance, automation, privacy, and security considerations.
Patient Adoption and Digital Divide Concerns
While patient portal adoption has grown significantly, important disparities and limitations persist. The fragmentation of patient portal experiences—with 59% of individuals having multiple online medical records or patient portals but only 7% using organizing tools to manage them—creates confusion and reduces the effectiveness of digital tools [8].
Age-related adoption patterns reveal both opportunities and challenges. While the Epic Research study showed that patients aged 50-64 had the greatest improvement in no-show rates when using patient portals, younger patients (18-34) showed smaller gaps between portal users and non-users [4]. This suggests that digital native populations may have different expectations and usage patterns that require distinct approaches.
The digital divide remains a significant concern, particularly for vulnerable populations who may face barriers to accessing or effectively using digital health tools. These barriers can include limited internet access, lack of digital literacy, language barriers, and economic constraints that prevent access to necessary devices or reliable internet connections.
Strategic Action Framework for 2026
Based on the comprehensive research and analysis presented, healthcare organizations require a structured approach to implementing digital customer experience improvements. The following framework provides actionable strategies that address both immediate needs and long-term transformation goals, while acknowledging the constraints and challenges identified in the research.
Phase 1: Foundation Building (Months 1-6)
The foundation phase focuses on establishing the infrastructure and organizational readiness necessary for successful digital customer experience initiatives. Organizations must begin by conducting comprehensive assessments of their current digital maturity, identifying gaps in core technologies, and establishing governance frameworks for digital transformation.
Infrastructure modernization should prioritize the three key areas identified in the Deloitte research: modernizing data and core technology infrastructure, migrating to cloud environments, and reinforcing cybersecurity measures [2]. Organizations should develop detailed migration plans that minimize disruption to patient care while establishing the technical foundation for advanced digital tools.
Workforce preparation is equally critical during this phase. Given that 53% of healthcare providers are most comfortable with AI managing administrative tasks [1], organizations should focus initial automation efforts on back-office processes that can demonstrate clear value without impacting direct patient care. This approach can help build staff confidence and support for broader digital initiatives.
Phase 2: Core Digital Experience Implementation (Months 7-18)
The implementation phase should prioritize high-impact, evidence-based digital tools that have demonstrated measurable benefits. Patient portal optimization should be a primary focus, given the Epic Research findings showing 21.5% reduction in no-show rates and 21 million fewer missed appointments annually [4].
Communication enhancement initiatives should address the critical finding that 84% of customers consider communications important to their overall experience [3]. Organizations should implement multi-channel communication strategies that provide patients with choice while ensuring consistency and quality across all touchpoints. This includes optimizing appointment reminders, test result notifications, and care plan communications.
Mobile-first design principles should guide all digital customer experience initiatives, reflecting the finding that 55% of patients prefer using mobile apps for healthcare interactions [9]. Organizations should ensure that all patient-facing digital tools are optimized for mobile devices and provide intuitive, user-friendly experiences that reduce rather than increase patient burden.
Phase 3: Advanced Integration and Optimization (Months 19-36)
The optimization phase focuses on integrating advanced technologies and refining digital customer experience based on usage data and patient feedback. AI implementation should follow the cautious but strategic approach indicated by the research, beginning with administrative tasks where providers show highest comfort levels [1].
Care team collaboration tools should be prioritized, given the research finding that teamwork among care teams is the most significant element affecting patients’ emotional experience of care [1]. Digital tools should enhance rather than fragment care coordination, ensuring that all team members have access to relevant patient information and can communicate effectively.
Personalization and predictive analytics capabilities should be developed to address individual patient needs and preferences. This includes implementing systems that can identify patients at risk for no-shows, those who may benefit from additional support, and opportunities to improve care coordination and communication.
Success Metrics and Continuous Improvement
Organizations should establish comprehensive measurement frameworks that track both operational and experiential outcomes. Key performance indicators should include appointment adherence rates, patient satisfaction scores, communication effectiveness metrics, and staff engagement measures. The Epic Research methodology provides a valuable model for measuring digital tool impact through large-scale data analysis [4].
Regular assessment of patient trust levels should be incorporated into measurement frameworks, given the critical importance of rebuilding trust identified in the Qualtrics research [1]. Organizations should track trust metrics alongside operational metrics to ensure that efficiency improvements do not come at the expense of patient relationships.
Future Outlook and Emerging Trends
The healthcare digital customer experience landscape will continue evolving rapidly through 2026 and beyond, driven by technological advancement, changing patient expectations, and regulatory developments. Several key trends will shape the future of healthcare digital customer experience, each presenting both opportunities and challenges for healthcare organizations.
Artificial Intelligence and Automation Evolution
The evolution of AI in healthcare will likely accelerate beyond the current focus on administrative tasks. As providers become more comfortable with AI applications and regulatory frameworks mature, we can expect to see expanded use of AI in clinical decision support, personalized patient communications, and predictive analytics for patient engagement.
Autonomous AI agents will likely become more sophisticated and capable of handling complex, multi-step processes that currently require human intervention. However, the healthcare industry’s cautious approach to AI adoption will likely continue, with emphasis on human oversight and validation of AI-generated recommendations and actions.
The regulatory landscape will continue evolving, with both the FDA in the United States and the European Union’s AI Act providing frameworks for safe and effective AI implementation in healthcare [2]. Organizations will need to stay current with regulatory requirements while balancing innovation with patient safety and privacy concerns.
Integration and Interoperability Advances
The fragmentation challenges identified in current patient portal usage—with patients managing multiple accounts across different providers—will likely drive increased focus on interoperability and integration solutions. Industry initiatives and regulatory pressure will push toward more seamless data sharing and unified patient experiences across healthcare systems.
Cloud-based platforms will become increasingly central to healthcare digital infrastructure, enabling more sophisticated data analytics, AI applications, and integrated patient experiences. Organizations that have not yet migrated to cloud environments will face increasing competitive disadvantages as cloud-native solutions become the standard.
Patient Expectations and Engagement Models
Patient expectations for digital healthcare experiences will continue rising, influenced by their experiences with digital services in other industries. The preference for mobile-first interactions will intensify, requiring healthcare organizations to prioritize mobile optimization and native mobile applications.
The demand for personalized, proactive healthcare communications will grow, moving beyond reactive appointment reminders to predictive engagement that anticipates patient needs and preferences. This will require sophisticated data analytics capabilities and AI-driven personalization engines.
Generational differences in digital tool adoption and preferences will require healthcare organizations to develop multi-generational strategies that serve both digital natives and patients who prefer traditional communication methods.
Workforce and Organizational Transformation
The healthcare workforce challenges identified in the research—including high turnover intentions among both doctors (30%) and nurses (42%)—will continue driving organizational transformation [1]. Digital tools will need to address workforce satisfaction and efficiency, not just patient experience, to be successful.
The integration of digital tools into clinical workflows will require ongoing training and support for healthcare providers. Organizations will need to invest in change management and digital literacy programs to ensure successful adoption and utilization of new technologies.
Care team collaboration models will continue evolving, with digital tools playing increasingly important roles in coordinating care across different providers, locations, and specialties. The emphasis on teamwork as a driver of patient emotional experience will require digital solutions that enhance rather than complicate care coordination [1].
Key Takeaways
The comprehensive analysis of healthcare digital customer experience reveals several critical insights that should guide organizational strategy and implementation decisions:
Trust rebuilding is paramount. The dramatic decline in patient trust from 71.5% to 40.1% between 2020 and 2024 represents the most significant challenge facing healthcare organizations [1]. Digital customer experience initiatives must prioritize emotional connection and care team collaboration, as these factors have the greatest impact on patient trust and satisfaction.
Digital tools deliver measurable outcomes when properly implemented. The Epic Research study provides compelling evidence that patient portals can reduce no-show rates by 21.5%, resulting in 21 million fewer missed appointments annually [4]. However, success requires thoughtful implementation that addresses patient needs and preferences rather than simply deploying technology.
Communication quality directly impacts loyalty and satisfaction. With 84% of patients considering communications important to their overall experience, and 75% reporting that communications influence satisfaction, healthcare organizations must prioritize communication strategy as a core component of digital customer experience [3].
AI adoption requires a cautious, strategic approach. While 40% of healthcare organizations report positive ROI from generative AI investments, providers are most comfortable with AI in administrative roles (53% comfort level) rather than direct patient care [1, 2]. Successful AI implementation should begin with back-office processes and gradually expand based on demonstrated value and provider comfort.
Infrastructure modernization is essential for advanced capabilities. Organizations must address fundamental infrastructure gaps—including cloud migration, data integration, and cybersecurity enhancement—before implementing advanced digital customer experience tools. The 78% of executives prioritizing cybersecurity reflects the critical importance of security in digital transformation [2].
Workforce challenges must be addressed alongside technology implementation. With 30% of doctors and 42% of nurses considering leaving their organizations within five years, digital initiatives must support rather than burden healthcare providers [1]. Technology should enhance care team collaboration and reduce administrative burden to be successful.
References
- Qualtrics. (2025). 2025 Healthcare Trends Report: Four trends shaping the healthcare industry in 2025. Retrieved from https://www.qualtrics.com/blog/healthcare-experience-trends/
- Deloitte US Center for Health Solutions. (2025). 2025 global health care outlook. Deloitte Insights. Retrieved from https://www.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/health-care/life-sciences-and-health-care-industry-outlooks/2025-global-health-care-executive-outlook.html
- Smart Communications. (2025). 2025 Healthcare Benchmark Report: Customer Experience and Communications in Healthcare. Retrieved from https://www.smartcommunications.com/resource-center/white-papers-ebooks/2025-healthcare-benchmark-report-customer-experience-communications
- Epic Research. (2025). Patient Portal Use Associated with 21 Million Fewer Visit No-Shows in 2024. Retrieved from https://epicresearch.org/articles/patient-portal-use-associated-with-21-million-fewer-visit-no-shows-in-2024
- This Week Health. (2025). Patient Portal Usage Surged in 2024, Trend Expected to Continue. Retrieved from https://thisweekhealth.com/news_story/patient-portal-usage-surges-in-2024-empowering-self-managed-health/
- HealthIT.gov. (2025). How Digitization of Patient Access Empowered Patients. Retrieved from https://www.healthit.gov/buzz-blog/digital-dividends-2/how-digitization-of-patient-access-empowered-patients
- Journal of Medical Internet Research. (2025). Patient Factors Associated With the Use of Online Portal Health Records. Retrieved from https://www.jmir.org/2025/1/e60472
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2024). Individuals’ Access and Use of Patient Portals and Smartphone Health Apps. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK616185/
- RXNT. (2025). Why 55% of Patients Prefer Using Mobile Apps for Healthcare. Retrieved from https://www.rxnt.com/why-55-of-patients-prefer-using-mobile-apps-for-healthcare/
- Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Global Research & Reviews. (2023). Mobile Application’s Effect on Patient Satisfaction and Compliance After Total Joint Arthroplasty. Retrieved from https://journals.lww.com/jaaosglobal/fulltext/2023/09000/mobile_application_s_effect_on_patient.5.aspx

