Marketing channel integration has evolved from a competitive advantage to an operational necessity, with companies implementing omnichannel strategies reporting 287% higher purchase rates and 89% customer retention compared to single-channel approaches. As consumer behavior increasingly spans multiple touchpoints—with 73% of customers using multiple channels throughout their purchasing journey—organizations face mounting pressure to deliver seamless, unified experiences across all marketing channels.
This comprehensive analysis examines the strategic imperatives, implementation challenges, and measurable outcomes of marketing channel integration, drawing from authoritative research by McKinsey & Company, Forbes Agency Council, and leading industry studies. The evidence reveals that while omnichannel marketing can increase annual revenue growth by 9.5% compared to 3.4% for non-integrated approaches, successful implementation requires addressing fundamental organizational, technological, and strategic barriers that continue to challenge even sophisticated marketing organizations.
Understanding Marketing Channel Integration
Marketing channel integration represents a fundamental shift from traditional siloed marketing approaches to a unified, customer-centric strategy that coordinates all touchpoints across the customer journey. According to McKinsey & Company’s comprehensive research, omnichannel marketing is defined as “a customer-centric approach in which all channels are integrated so the customer has a unified and consistent experience whether shopping online, by phone, or in a brick-and-mortar store” [1].
The distinction between multichannel and omnichannel approaches has become increasingly critical for marketing effectiveness. While multichannel marketing simply utilizes multiple channels, true channel integration requires seamless data sharing, consistent messaging, and coordinated campaign execution across all touchpoints. Forbes Agency Council research demonstrates that this integration approach yields substantially higher performance metrics, with marketers using three or more integrated channels achieving a 287% higher purchase rate than single-channel campaigns [2].
The evolution of channel integration reflects changing consumer behavior patterns that have accelerated since the COVID-19 pandemic. McKinsey’s research indicates that more than half of B2C customers now engage with three to five channels each time they make a purchase or resolve a request, while the average customer making a single hotel reservation online switches nearly six times between websites and mobile channels [1]. This behavior pattern has created what researchers term “channel fluidity,” where customers expect seamless transitions between digital and physical touchpoints without encountering inconsistent information or fragmented experiences.
Contemporary channel integration encompasses several key components that distinguish it from traditional marketing approaches. First, unified messaging ensures that brand communications maintain consistency across all channels while adapting to the unique characteristics of each platform. Second, seamless data integration enables real-time customer insights and personalized experiences based on cross-channel behavior patterns. Third, coordinated campaign execution synchronizes marketing activities to create cohesive customer journeys rather than isolated channel-specific interactions.
The Strategic Importance in 2026
The strategic imperative for marketing channel integration has intensified dramatically as consumer expectations and competitive pressures converge to create new operational requirements for sustainable business growth. Contemporary market research reveals that 60 to 70 percent of consumers now research and shop both in stores and online, while over one-third of Americans have made omnichannel features—such as buying online and picking up in store or curbside delivery—part of their regular shopping routines since the COVID-19 pandemic [1].
The financial implications of channel integration strategies extend far beyond customer satisfaction metrics to fundamental business performance indicators. Companies implementing comprehensive omnichannel transformations report revenue growth of 5 to 15 percent alongside improvements in cost-to-serve efficiencies, according to McKinsey’s analysis of retail transformation initiatives [1]. More significantly, Aberdeen Group’s longitudinal study demonstrates that companies with strong omnichannel strategies retain an average of 89% of their customers compared to just 33% retention rates for companies with weak omnichannel customer engagement [3].
The customer lifetime value implications of integrated channel strategies represent perhaps the most compelling business case for implementation. Research conducted by ITC reveals that omnichannel shoppers demonstrate 30% higher lifetime value compared to single-channel customers, while also exhibiting 1.7 times higher shopping frequency [3]. This behavioral pattern reflects the compound effect of channel integration on customer engagement, where seamless experiences across touchpoints increase both purchase frequency and average transaction values.
Post-pandemic consumer behavior changes have created what McKinsey researchers describe as “sticky” adoption patterns that are likely to persist long-term. Approximately 70% of consumers who first tried self-checkout during the pandemic indicate they will continue using these services, while similar retention rates apply to curbside pickup and “buy online, pay in store” models [1]. These behavioral shifts have fundamentally altered customer expectations regarding channel flexibility and integration capabilities.
The competitive landscape has evolved to make channel integration a defensive necessity rather than merely an offensive opportunity. Industry analysis reveals that 87% of store owners now consider using multiple customer reach methods essential for business viability, while 74% of shoppers rely on social networks for purchasing decisions [3]. Organizations that fail to provide integrated experiences risk customer defection to competitors who can deliver the seamless, personalized interactions that have become standard expectations.
B2B markets have experienced parallel transformation pressures, with McKinsey identifying five critical requirements for B2B omnichannel success: offering performance guarantees (crucial for nearly 80% of B2B customers), showing product availability online, enabling purchases across any channel, providing real-time customer service, and ensuring consistent customer experiences as buyers toggle between channels [1]. These requirements reflect the professionalization of B2B buying processes and the increasing influence of consumer-grade experience expectations in business contexts.
| Integration Level | Customer Retention Rate | Revenue Growth (YoY) | Purchase Rate Index | Customer Lifetime Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Channel | 33% | 3.4% | 100 | Baseline |
| Multi-Channel | 55% | 5.2% | 187 | +15% |
| Cross-Channel | 75% | 7.8% | 250 | +22% |
| Omnichannel | 89% | 9.5% | 287 | +30% |
Table 1: Comparative Performance Metrics by Channel Integration Level (Sources: McKinsey & Company, Aberdeen Group, Forbes Agency Council)
Performance Analysis and Benchmarks
Comprehensive performance analysis of marketing channel integration initiatives reveals significant variations in outcomes based on implementation approach, organizational readiness, and strategic focus. The most authoritative benchmarking data, compiled from McKinsey & Company, Forbes Agency Council, and industry research organizations, demonstrates clear performance differentials across integration maturity levels.
Purchase rate effectiveness represents the most immediately measurable impact of channel integration strategies. Forbes Agency Council’s analysis of campaign performance data shows that marketers utilizing three or more channels in integrated campaigns achieve 287% higher purchase rates compared to single-channel approaches [2]. This performance differential reflects the compound effect of multiple touchpoints reinforcing consistent messaging and providing customers with flexible engagement options that accommodate diverse preferences and shopping behaviors.
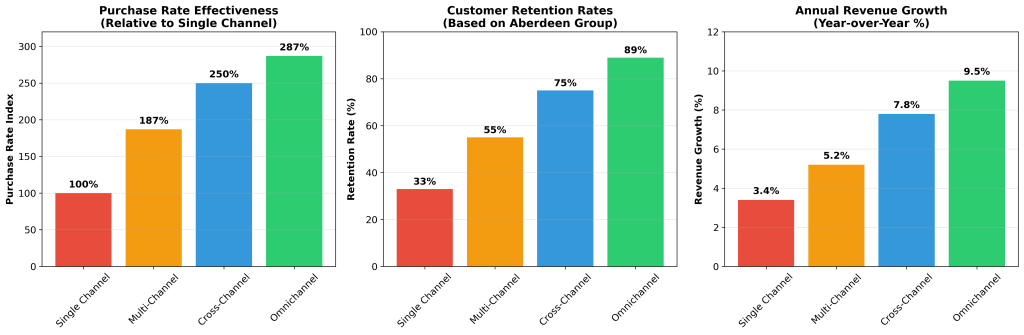
Customer retention metrics provide insight into the long-term value creation potential of integrated channel strategies. Aberdeen Group’s longitudinal study of retail organizations reveals that companies with strong omnichannel customer engagement strategies retain 89% of their customers annually, compared to 33% retention rates for organizations with weak omnichannel implementation [3]. This 56 percentage point differential represents substantial lifetime value implications, particularly when combined with the 30% higher lifetime value demonstrated by omnichannel customers compared to single-channel shoppers.
Revenue growth analysis demonstrates the scalable impact of channel integration on organizational performance. Companies implementing comprehensive omnichannel strategies report average annual revenue growth of 9.5% compared to 3.4% for non-integrated approaches [3]. This 6.1 percentage point advantage compounds over time, creating significant competitive advantages for organizations that successfully implement integrated channel strategies.
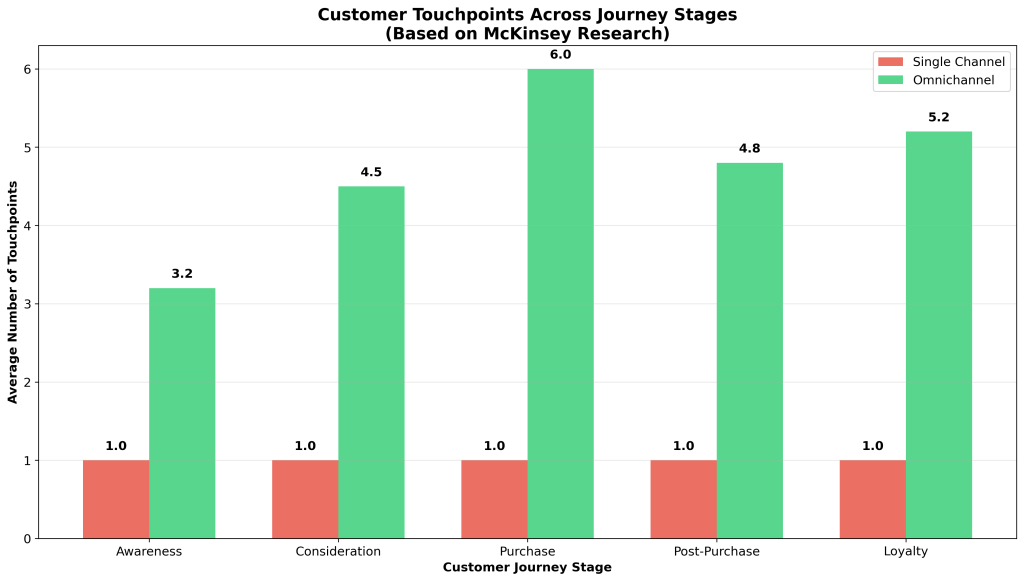
The touchpoint analysis reveals important insights into customer journey complexity and channel utilization patterns. McKinsey’s research indicates that omnichannel customers engage with an average of 3 to 5 channels during each purchase or service interaction, with some customer segments utilizing up to 6 different touchpoints before completing transactions [1]. This behavior pattern has created what researchers term “channel orchestration” requirements, where organizations must coordinate experiences across multiple simultaneous touchpoints rather than managing sequential channel interactions.
Social media integration has emerged as a critical component of channel performance, with 74% of shoppers relying on social networks for purchasing decisions and 87% of online shoppers believing social media highly influences their purchases [3]. The conversion impact of social media integration demonstrates measurable results, with 76% of consumers purchasing products they discovered through brand social media posts, distributed across immediate purchases (11%), later online purchases (44%), and subsequent in-store purchases (21%) [3].
Personalization effectiveness within integrated channel strategies shows substantial performance improvements when implemented systematically. McKinsey’s analysis indicates that organizations achieving omnichannel personalization excellence can increase revenue by 5 to 15 percent across their full customer base [1]. However, this performance level requires sophisticated data integration capabilities and coordinated content management systems that many organizations struggle to implement effectively.
The measurement challenges associated with channel integration performance create important limitations for benchmarking analysis. Traditional attribution models often fail to capture the full impact of integrated strategies, leading to undervaluation of channel integration investments. Organizations implementing advanced attribution methodologies report 24% higher conversion rates for multi-channel campaigns compared to single-channel approaches, suggesting that measurement sophistication significantly influences perceived performance outcomes [4].
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Despite compelling performance benefits, marketing channel integration initiatives face substantial implementation barriers that have prevented many organizations from realizing their full potential. McKinsey & Company’s analysis of omnichannel transformation efforts identifies three primary challenges that consistently emerge across industries and organizational contexts: unclear prioritization of integration components, excessive focus on technology rather than customer value, and failure to sequence investments strategically [5].
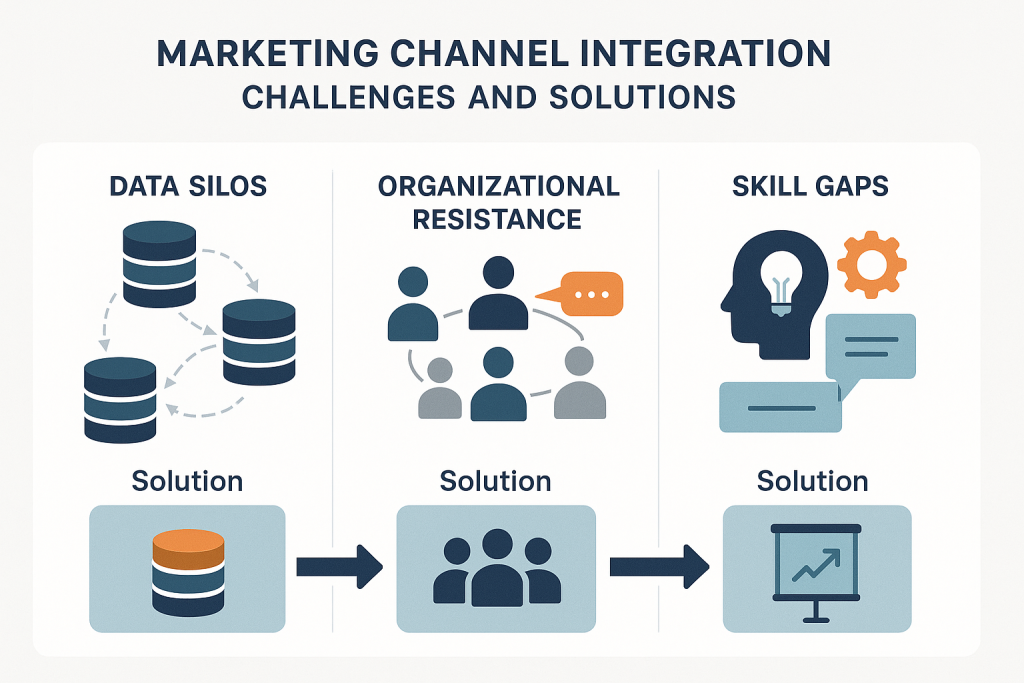
Data Silos and Integration Complexity
The most fundamental challenge facing channel integration initiatives involves the technical and organizational complexity of unifying disparate data sources across marketing channels. Forbes Agency Council research indicates that data silos result from various departments—including marketing, sales, and research and development teams—storing data independently, making it virtually impossible for organizations to access unified views of customer behavior and preferences [2]. This fragmentation creates what researchers describe as “data archipelagos,” where valuable customer insights remain isolated within departmental systems.
The technical implications of data fragmentation extend beyond simple integration challenges to fundamental questions of data quality, consistency, and real-time accessibility. Organizations attempting channel integration often discover that customer data collected through different channels utilizes incompatible formats, measurement methodologies, and attribution models. This incompatibility creates substantial barriers to the seamless data sharing that McKinsey identifies as essential for effective omnichannel marketing [1].
Resolution of data integration challenges requires comprehensive investment in integrated data management platforms that support real-time synchronization across multiple departments and systems. Successful organizations implement what Forbes describes as “companywide integrated data management software that supports data sharing and synchronization across multiple teams and departments” [2]. However, these technical solutions must be accompanied by organizational changes that promote data sharing and collaborative analytics approaches.
Organizational Resistance and Cultural Barriers
Organizational resistance represents perhaps the most persistent barrier to successful channel integration, reflecting deep-seated cultural patterns and performance measurement systems that reward channel-specific optimization rather than integrated performance. McKinsey’s research reveals that too few retailers have established alignment across their organizations on omnichannel agendas, including long-term vision and current status assessment [5]. Without strategic alignment, organizations often invest in what McKinsey describes as “scattershot fashion, funding divergent priorities in e-commerce, store operations, supply chain, marketing, and technology.”
The cultural dimensions of organizational resistance often manifest through departmental competition for resources and recognition, where channel-specific teams resist integration initiatives that might diminish their perceived importance or budget allocations. Forbes Agency Council identifies this pattern as teams becoming “accustomed to working in silos and resisting the collaborative approach” required for effective integration [2]. This resistance can undermine even technically sound integration initiatives by creating implementation gaps and inconsistent execution across channels.
Successful resolution of organizational resistance requires what Forbes describes as “fostering a culture of collaboration through effective communication, training programs, and showcasing the benefits of marketing technology integration to key stakeholders” [2]. This cultural transformation often requires executive leadership commitment and performance measurement systems that reward integrated outcomes rather than channel-specific metrics.
Skill Gaps and Capability Development
The technical and strategic complexity of channel integration has created substantial skill gaps within marketing organizations, where traditional channel-specific expertise proves insufficient for managing integrated customer experiences. Forbes Agency Council research indicates that marketing teams often lack the skill sets necessary to “navigate and effectively leverage integrated systems” [2]. These capability gaps extend beyond technical proficiency to include strategic thinking about customer journey orchestration and cross-channel attribution analysis.
The scope of required capabilities for effective channel integration encompasses data analytics, customer experience design, technology platform management, and strategic coordination across multiple organizational functions. Many organizations discover that their existing talent base lacks the interdisciplinary knowledge required for successful integration, while external talent with appropriate experience commands premium compensation that strains marketing budgets.
Addressing skill gaps requires comprehensive training and upskilling programs that Forbes describes as essential for “equipping various teams with the skills to manage, use, and capitalize on integrated marketing technologies” [2]. However, successful capability development often requires longer timeframes than organizations anticipate, creating tension between integration ambitions and practical implementation timelines.
Technology Focus vs. Customer Value Orientation
McKinsey’s analysis reveals a persistent tendency for organizations to prioritize technology implementation over customer value creation, leading to what researchers describe as “shiny objects that drain capital expenditures” without delivering meaningful customer experience improvements [5]. Many retailers have embraced “tech-enabled, flashy innovations like smart mirrors, Bluetooth beacons, and in-store kiosks to create differentiation” without establishing proper grounding in customer needs or determining how these investments create and sustain value at scale.
This technology-first approach often results from organizational pressure to demonstrate innovation and competitive differentiation, combined with vendor marketing that emphasizes technical capabilities rather than customer outcomes. The result is fragmented technology investments that fail to create cohesive customer experiences and may actually increase complexity rather than reducing it.
Successful channel integration requires what McKinsey describes as “laser-like focus on value creation” where organizations “take a hard look at their strategic and customer priorities and decide who they want to be from an omnichannel perspective” [5]. This customer-centric approach prioritizes experience design over technology implementation and ensures that technical investments support clearly defined customer value propositions.
Framework for Successful Integration
Successful marketing channel integration requires a systematic framework that addresses the strategic, operational, and technological dimensions of omnichannel implementation. Based on analysis of successful transformation initiatives and authoritative research from McKinsey & Company and Forbes Agency Council, effective frameworks incorporate five critical components: strategic alignment, customer journey mapping, technology infrastructure, organizational capabilities, and performance measurement systems.
Strategic Alignment and Vision Development
The foundation of successful channel integration lies in establishing clear strategic alignment across organizational functions and leadership levels. McKinsey’s research emphasizes that organizations must “step back and consider the underlying drivers of value for their specific business” before implementing technical solutions [5]. This strategic foundation requires explicit definition of customer value propositions, competitive positioning, and integration objectives that extend beyond technology implementation to encompass customer experience transformation.
Strategic alignment must address what McKinsey describes as the “crawl, walk, run” approach to integration, where organizations sequence investments based on capability development and customer impact rather than technology availability [5]. This sequencing prevents the fragmented investments that often characterize failed integration initiatives and ensures that each implementation phase builds systematically toward comprehensive omnichannel capabilities.
Customer Journey Orchestration
Effective channel integration requires sophisticated understanding of customer journey complexity and touchpoint interactions across multiple channels. Research indicates that contemporary customers utilize an average of 3 to 5 channels during each purchase interaction, with some segments engaging up to 6 different touchpoints before completing transactions [1]. This complexity requires what researchers term “journey orchestration” capabilities that coordinate experiences across simultaneous touchpoints rather than managing sequential channel interactions.
Customer journey mapping must account for the behavioral patterns that McKinsey identifies as characteristic of omnichannel customers, including higher shopping frequency (1.7 times more than single-channel customers) and increased spending patterns [1]. These behavioral differences require tailored engagement strategies that recognize omnichannel customers as distinct segments with unique value creation potential.
Technology Infrastructure and Data Integration
The technical foundation for channel integration requires comprehensive data integration capabilities that support real-time customer insights and coordinated campaign execution. Forbes Agency Council research emphasizes that successful integration depends on “seamless data sharing across all channels” that enables “uninterrupted insights from multiple platforms, whether they’re social media networks, owned assets like websites, or even email marketing” [2].
Technology infrastructure must support what Forbes describes as “personalized campaigns with real-time consumer behavior” insights that enable dynamic content adaptation across channels [2]. This capability requires sophisticated data management platforms, customer data platforms (CDPs), and marketing automation systems that can process and act upon customer behavior data in real-time across multiple touchpoints.
| Framework Component | Key Requirements | Success Metrics | Implementation Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic Alignment | Cross-functional leadership commitment, clear value proposition definition | Executive engagement, resource allocation consistency | 3-6 months |
| Customer Journey Mapping | Touchpoint analysis, behavioral segmentation, experience design | Journey completion rates, satisfaction scores | 6-9 months |
| Technology Infrastructure | Data integration platforms, real-time analytics, automation systems | Data quality, integration speed, system reliability | 12-18 months |
| Organizational Capabilities | Skill development, process redesign, performance systems | Capability assessments, training completion, collaboration metrics | 9-15 months |
| Performance Measurement | Integrated attribution, customer lifetime value tracking, ROI analysis | Attribution accuracy, measurement consistency, ROI improvement | 6-12 months |
Table 2: Channel Integration Framework Components and Implementation Requirements
Strategic Action Plan
Implementation of effective marketing channel integration requires a systematic action plan that addresses the strategic, operational, and technological requirements identified through authoritative research and successful case study analysis. This action plan provides specific steps for organizations seeking to develop comprehensive omnichannel capabilities while avoiding the common pitfalls that McKinsey and Forbes research have identified in failed integration initiatives.
Phase 1: Foundation Development (Months 1-6)
The initial phase focuses on establishing the strategic and organizational foundations necessary for successful integration. Organizations must begin by conducting comprehensive assessments of current channel performance, customer journey complexity, and organizational readiness for integration initiatives. This assessment should utilize the performance benchmarks identified in authoritative research, including the 287% purchase rate differential between integrated and single-channel approaches [2].
Strategic alignment development requires executive leadership commitment to integration objectives that extend beyond technology implementation to encompass customer experience transformation. Organizations should establish cross-functional integration teams that include representatives from marketing, sales, customer service, and technology functions, ensuring that integration planning addresses the organizational resistance patterns that Forbes identifies as critical barriers to success [2].
Customer research and journey mapping activities should focus on understanding the multi-channel behavior patterns that McKinsey research identifies as characteristic of contemporary customers, including the utilization of 3 to 5 channels per purchase interaction [1]. This research should identify specific touchpoint interactions, channel switching patterns, and experience gaps that integration initiatives should address.
Phase 2: Pilot Implementation (Months 7-12)
The pilot phase implements integration capabilities for specific customer segments or product categories, allowing organizations to develop operational expertise while managing implementation complexity. Pilot selection should focus on customer segments that demonstrate high omnichannel engagement potential, based on the behavioral patterns that research associates with 30% higher lifetime value [3].
Technology implementation during the pilot phase should prioritize data integration capabilities that support the “seamless data sharing across all channels” that Forbes identifies as essential for personalized campaign development [2]. Organizations should implement customer data platforms and marketing automation systems that can process real-time behavioral data and coordinate campaign execution across multiple touchpoints.
Performance measurement systems established during the pilot phase should incorporate the integrated attribution methodologies necessary for accurately assessing channel integration impact. Traditional attribution models often undervalue integration benefits, leading to suboptimal investment decisions and reduced organizational support for integration initiatives.
Phase 3: Scaled Implementation (Months 13-24)
The scaled implementation phase extends integration capabilities across additional customer segments, product categories, and geographic markets based on pilot phase learnings and performance validation. Scaling decisions should be guided by the performance differentials that research demonstrates for comprehensive integration, including the 9.5% annual revenue growth achieved by organizations with strong omnichannel strategies [3].
Organizational capability development becomes critical during the scaling phase, requiring the comprehensive training and upskilling programs that Forbes identifies as necessary for “equipping various teams with the skills to manage, use, and capitalize on integrated marketing technologies” [2]. These capability development initiatives should address both technical proficiency and strategic thinking about customer journey orchestration.
Advanced personalization capabilities should be implemented during the scaling phase, targeting the 5 to 15 percent revenue increase potential that McKinsey associates with omnichannel personalization excellence [1]. However, organizations must ensure that personalization initiatives are grounded in customer value creation rather than technology demonstration, avoiding the “shiny objects” trap that McKinsey identifies as a common failure pattern [5].
Future Outlook and Trends
The trajectory of marketing channel integration continues to evolve rapidly, driven by technological advancement, changing consumer expectations, and competitive pressures that are reshaping industry standards for customer experience delivery. Analysis of emerging trends and authoritative research projections indicates several critical developments that will influence channel integration strategies through 2026 and beyond.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are creating new possibilities for real-time channel orchestration and predictive customer experience optimization. These technological capabilities address some of the complexity challenges that McKinsey identifies in current integration initiatives, potentially enabling more sophisticated coordination of customer touchpoints and more accurate prediction of customer channel preferences [5]. However, successful AI implementation will require the data integration foundations and organizational capabilities that continue to challenge many organizations.
Consumer behavior evolution suggests continued acceleration of omnichannel expectations, particularly among younger demographic segments. McKinsey’s research indicates that Gen Z consumers “don’t even think in terms of traditional channel boundaries” and “increasingly evaluate brands and retailers on the seamlessness of their experience” [5]. This behavioral trend suggests that channel integration will become increasingly essential for customer acquisition and retention rather than merely competitive differentiation.
The integration of physical and digital experiences is expected to deepen significantly, with technologies such as augmented reality, virtual reality, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices creating new touchpoint possibilities that require coordination within integrated channel strategies. These technological developments will likely increase the complexity of channel orchestration while creating new opportunities for personalized customer experiences.
Regulatory and privacy considerations are creating new constraints and requirements for channel integration initiatives, particularly regarding data collection, storage, and utilization across multiple touchpoints. Organizations implementing integration strategies must navigate evolving privacy regulations while maintaining the data integration capabilities that research demonstrates as essential for omnichannel effectiveness.
The competitive landscape suggests that channel integration capabilities will become increasingly commoditized, requiring organizations to develop more sophisticated differentiation strategies based on customer experience quality rather than channel availability. This evolution will likely increase the importance of the customer value focus that McKinsey emphasizes as critical for successful integration [5].
Key Takeaways
Marketing channel integration has evolved from competitive advantage to operational necessity, with authoritative research demonstrating substantial performance benefits for organizations that successfully implement comprehensive omnichannel strategies. The evidence reveals four critical insights that should guide organizational decision-making regarding channel integration investments:
Performance Impact is Substantial and Measurable: Organizations implementing integrated channel strategies achieve 287% higher purchase rates, 89% customer retention compared to 33% for weak integration, and 9.5% annual revenue growth compared to 3.4% for non-integrated approaches. These performance differentials represent significant competitive advantages that compound over time.
Implementation Challenges are Systematic and Addressable: The three primary barriers to successful integration—data silos, organizational resistance, and skill gaps—require systematic solutions that address technical, cultural, and capability dimensions simultaneously. Organizations that approach these challenges comprehensively achieve significantly higher success rates than those focusing primarily on technology implementation.
Customer-Centric Approach is Essential: Successful integration requires focus on customer value creation rather than technology demonstration. Organizations that prioritize customer experience design and journey orchestration over technical capabilities achieve better performance outcomes and more sustainable competitive advantages.
Strategic Sequencing Determines Success: The “crawl, walk, run” approach to integration implementation, with careful attention to organizational readiness and capability development, produces better outcomes than aggressive technology-first strategies. Systematic sequencing prevents the fragmented investments that characterize many failed integration initiatives.
References
[1] McKinsey & Company. (2022, August 17). What is omnichannel marketing? https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/mckinsey-explainers/what-is-omnichannel-marketing
[2] Schwartz, J. (2024, March 26). How Marketing Integration Boosts Cross-Channel Success. Forbes Agency Council. https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbesagencycouncil/2024/03/26/how-marketing-integration-boosts-cross-channel-success/
[3] WiserNotify. (2025). 45 Omnichannel Statistics & Trends (New 2025 Data). https://wisernotify.com/blog/omnichannel-stats/
[4] ROI Amplified. (2024, December 19). Integrating Multiple Marketing Channels Effectively. https://roiamplified.com/insights/integrating-multiple-marketing-channels-effectively/
[5] McKinsey & Company. (2021, April 30). Omnichannel: The path to value. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/growth-marketing-and-sales/our-insights/the-survival-guide-to-omnichannel-and-the-path-to-value

