Despite unprecedented investment in sales technology, 45% of B2B enablement tech deployments remain dramatically underutilized, resembling “buying a Maserati only to drive it on Sunday mornings,” according to recent Forrester research. [1] This stark reality underscores a critical disconnect between the explosive growth of the sales technology market—projected to surge from $47.3 billion in 2024 to $229.3 billion by 2034—and organizations’ ability to extract meaningful value from their investments. [2] As sales teams grapple with increasingly complex buyer journeys and heightened performance expectations, the strategic assembly and optimization of a sales enablement technology stack has emerged as a defining competitive advantage, yet one that remains elusive for most organizations.
The Strategic Imperative: Why Sales Enablement Technology Matters in 2026
The convergence of digital transformation acceleration, evolving buyer behaviors, and intensified competitive pressures has fundamentally reshaped the sales landscape. Organizations that previously relied on relationship-driven sales approaches now find themselves competing in an environment where data-driven insights, automated workflows, and personalized customer experiences have become table stakes rather than differentiators.
The COVID-19 pandemic served as an unexpected catalyst, compressing what might have been a decade of digital transformation into mere months. Remote selling became the norm, forcing sales organizations to rapidly adopt technologies that could replicate and enhance traditional face-to-face interactions. This shift revealed both the immense potential and the significant challenges inherent in sales technology adoption. While some organizations thrived by leveraging sophisticated tech stacks to maintain and even improve sales performance, others struggled with fragmented systems, poor user adoption, and diminishing returns on their technology investments.
Today’s buyers conduct extensive research independently before engaging with sales representatives, often completing 70% of their purchase journey without direct vendor interaction. This behavioral shift demands that sales teams be equipped with comprehensive intelligence about prospects’ digital footprints, content consumption patterns, and engagement preferences. Traditional CRM systems, while foundational, prove insufficient for capturing and acting upon these complex buyer signals. The modern sales enablement technology stack must therefore encompass a broader ecosystem of tools designed to surface actionable insights, automate routine tasks, and deliver personalized experiences at scale.
The financial stakes are substantial. Organizations with mature sales enablement programs report 35% higher productivity rates and 50% reduction in administrative time, translating to millions of dollars in improved efficiency and revenue generation. [3] However, achieving these outcomes requires more than simply purchasing and deploying technology solutions. It demands a strategic approach to technology selection, integration, and optimization that many organizations have yet to master.
The Explosive Growth of Sales Enablement Technology
The sales technology market is experiencing unprecedented expansion, driven by organizations’ recognition that traditional sales approaches are insufficient for today’s complex B2B environment. Market research indicates that the global sales technology sector has evolved from a niche category to a critical business infrastructure, with compound annual growth rates that significantly outpace broader technology spending trends.
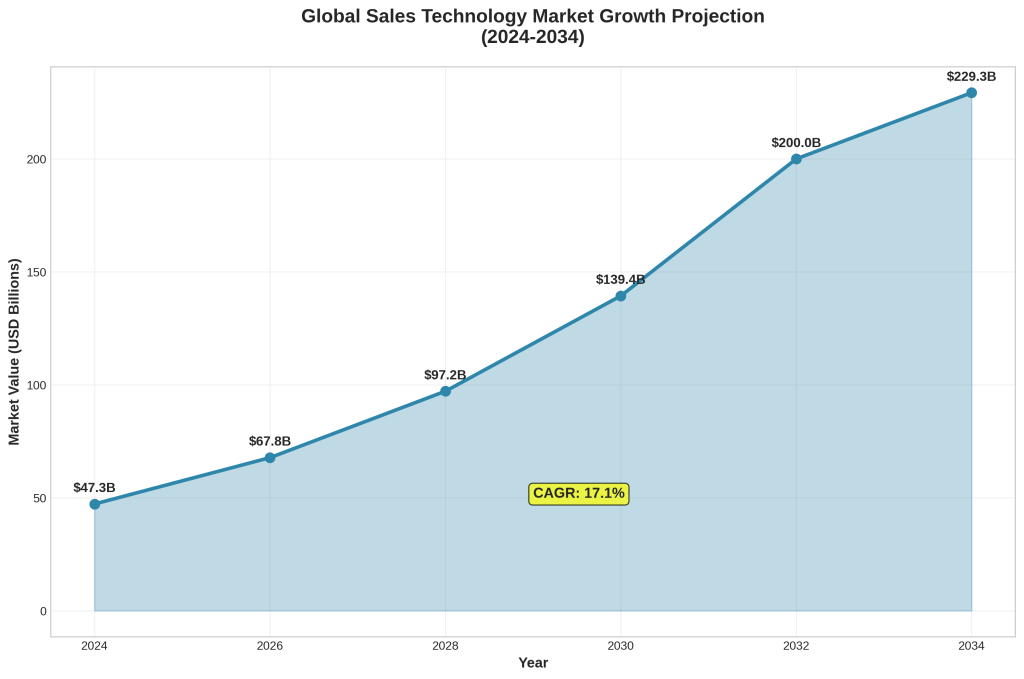
The trajectory from $47.3 billion in 2024 to a projected $229.3 billion by 2034 represents a compound annual growth rate of 17.1%, reflecting both the urgency with which organizations are investing in sales technology and the expanding scope of what constitutes essential sales infrastructure. [2] This growth significantly exceeds the broader technology sector’s projected 9.3% growth rate for 2026, indicating that sales technology has become a priority investment category for businesses across industries. [4]
However, market size alone does not tell the complete story. The adoption patterns reveal significant disparities based on organizational characteristics, geographic regions, and industry sectors. European organizations lead in CRM adoption with an 85.7% adoption rate, compared to lower rates in other regions, suggesting that regulatory environments, business cultures, and competitive pressures influence technology adoption decisions. [5] This geographic variation highlights the importance of understanding local market dynamics when developing global sales technology strategies.
| Company Size | Dedicated Enablement | CRM Adoption | Full-Scale Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500+ employees | 77.1% | 85.7% (Europe) | <40% globally |
| <500 employees | 39.3% | ~65% (estimated) | <25% (estimated) |
| Enterprise (1000+) | 90% | ~90% (estimated) | ~45% (estimated) |
The data reveals a pronounced correlation between organizational size and sales technology sophistication. While 90% of sales organizations maintain some form of dedicated sales enablement program, person, or function, the quality and comprehensiveness of these initiatives vary dramatically. [6] Large organizations with sales forces exceeding 500 people demonstrate significantly higher adoption rates for dedicated enablement programs (77.1%) compared to smaller organizations (39.3%), reflecting both resource availability and the complexity of sales operations that necessitate formal enablement structures.
Perhaps most concerning is the persistent gap between technology acquisition and effective implementation. Despite widespread CRM adoption, less than 40% of organizations achieve full-scale implementation, indicating that purchasing technology represents only the initial step in a complex transformation process. [7] This implementation gap explains why many organizations fail to realize the promised benefits of their technology investments, leading to the underutilization patterns identified in Forrester’s research.
The sales enablement tool usage has increased by 48% in 2024 alone, suggesting that organizations are not only investing in new technologies but also expanding their existing technology portfolios. [6] However, this rapid expansion raises questions about integration capabilities, user training requirements, and the potential for technology sprawl to actually hinder rather than enhance sales performance. The challenge for sales leaders is not simply acquiring more tools, but rather creating cohesive technology ecosystems that amplify human capabilities rather than overwhelming sales teams with complexity.
Essential Components of a Modern Sales Tech Stack
The modern sales enablement technology stack has evolved far beyond simple contact management systems to encompass a sophisticated ecosystem of interconnected tools designed to support every aspect of the sales process. Understanding the architectural layers of this ecosystem is crucial for organizations seeking to build coherent, high-performing sales technology environments.

The foundational layer consists of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, which serve as the central nervous system for all sales activities. Despite their ubiquity—with adoption rates reaching 85.7% in leading markets—CRM systems continue to present implementation challenges that prevent organizations from realizing their full potential. [5] The core issue is not technological capability but rather the complexity of data management, user adoption, and process integration required to transform a CRM from a simple database into a strategic sales asset.
Modern CRM systems must manage hundreds or thousands of buyer-facing and seller-supporting assets, requiring sophisticated data architecture and governance frameworks. [1] The challenge extends beyond storage to encompass data quality, accessibility, and actionability. Organizations frequently discover that their CRM systems become data graveyards rather than intelligence engines, filled with incomplete records, outdated information, and disconnected data points that provide little strategic value.
The enablement layer builds upon the CRM foundation by providing tools for content management, training delivery, and sales process standardization. Revenue Enablement Platforms (REPs) represent the most sophisticated evolution of this layer, designed to surface contextually relevant content and training materials based on specific deal characteristics and buyer journey stages. However, Forrester research indicates that only 50% of REP owners effectively implement this contextual delivery capability, primarily due to the resource-intensive nature of content tagging and taxonomy management. [1]
The automation layer introduces workflow optimization and process standardization capabilities that can dramatically reduce administrative burden while improving consistency and compliance. Email sequencing, lead scoring, and workflow automation tools in this layer have demonstrated the ability to reduce administrative time by up to 50% when properly implemented. [3] However, the effectiveness of automation depends heavily on the quality of underlying data and the sophistication of rule-based logic governing automated actions.
The intelligence layer represents the most rapidly evolving component of the modern sales tech stack, incorporating analytics dashboards, artificial intelligence insights, and predictive analytics capabilities. The adoption of generative AI tools in sales and marketing doubled in 2024, indicating that organizations are increasingly recognizing the potential for AI to enhance human decision-making and automate complex analytical tasks. [8] However, the implementation of AI-powered tools requires significant data quality improvements and change management initiatives to ensure that insights translate into actionable sales behaviors.
| Component | Primary Function | Adoption Rate | ROI Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| CRM Systems | Customer Data Management | 85.7% (Europe) | 6-12 months |
| Revenue Enablement Platforms | Content & Training | 50% effective use | 12-18 months |
| Sales Automation | Process Optimization | ~70% (estimated) | 3-6 months |
| Analytics & AI | Performance Insights | 48% growth in 2024 | 18-24 months |
The integration layer represents perhaps the most critical yet underappreciated component of the modern sales tech stack. API connections, data synchronization, and third-party tool integration capabilities determine whether individual tools function as isolated point solutions or as components of a cohesive sales ecosystem. The complexity of integration challenges increases exponentially with each additional tool, creating potential points of failure that can undermine the entire technology investment.
Organizations frequently underestimate the ongoing maintenance requirements associated with integration management. As vendors update their platforms, modify APIs, or change data structures, integration connections require continuous monitoring and adjustment. This technical debt can accumulate rapidly, leading to data inconsistencies, workflow disruptions, and user frustration that ultimately drives down adoption rates and ROI realization.
The most successful sales technology implementations recognize that each layer must be optimized not only for individual performance but also for seamless interaction with other layers. This systems thinking approach requires significant upfront planning, ongoing governance, and dedicated technical resources that many organizations fail to adequately provision. The result is technology sprawl rather than technology synergy, explaining why so many organizations struggle to translate their technology investments into measurable business outcomes.
Bridging the Gap Between Investment and Results
The persistent disconnect between sales technology investment and realized value represents one of the most significant challenges facing modern sales organizations. Forrester’s characterization of 45% of B2B enablement tech deployments as resembling “buying a Maserati only to drive it on Sunday mornings” captures the frustration experienced by sales leaders who have made substantial technology investments without achieving proportional performance improvements. [1]
The root causes of this underutilization extend far beyond technology selection to encompass fundamental challenges in implementation strategy, change management, and organizational readiness. Many organizations approach sales technology adoption with a “plug-and-play” mentality, assuming that purchasing sophisticated tools will automatically translate into improved sales performance. This assumption fails to account for the complex interplay between technology capabilities, user behavior, organizational processes, and data quality requirements.
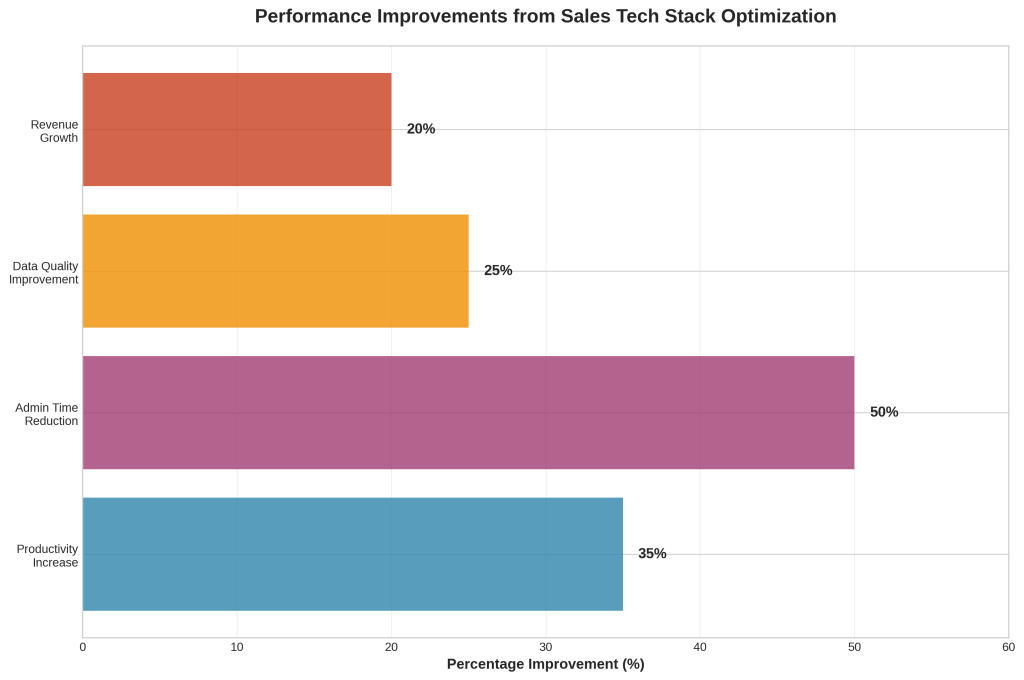
Organizations that successfully optimize their sales technology stacks demonstrate measurable improvements across multiple performance dimensions. Research indicates that properly implemented sales technology can deliver a 35% increase in productivity, 50% reduction in administrative time, and 25% improvement in data quality. [3] However, achieving these outcomes requires addressing several critical implementation challenges that many organizations underestimate or ignore entirely.
The taxonomy and content tagging challenge represents perhaps the most significant barrier to effective sales enablement technology utilization. Revenue Enablement Platforms require extensive content categorization based on buyer persona, industry, journey stage, and product offering to deliver contextually relevant materials to sales representatives. [1] This manual tagging process is resource-intensive and requires ongoing maintenance as content libraries expand and business requirements evolve.
Most B2B sales organizations manage hundreds or thousands of buyer-facing and seller-supporting assets, making comprehensive taxonomy management a substantial undertaking that often exceeds available resources. [1] The temptation to shortcut this process by implementing basic categorization schemes ultimately undermines the platform’s ability to deliver intelligent content recommendations, reducing the system to a glorified file repository rather than a strategic sales asset.
Integration complexity presents another significant implementation challenge that organizations frequently underestimate. Modern sales teams utilize multiple specialized tools for different aspects of the sales process, from prospecting and lead generation to proposal creation and contract management. Ensuring seamless data flow between these systems requires sophisticated integration architecture and ongoing technical maintenance that many organizations lack the resources to properly support.
The challenge is compounded by the rapid pace of technology evolution, which requires continuous adaptation of integration connections as vendors update their platforms and modify their APIs. Organizations that fail to adequately provision for ongoing integration maintenance often experience data inconsistencies, workflow disruptions, and system reliability issues that drive down user adoption and undermine ROI realization.
User adoption represents the ultimate determinant of sales technology success, yet it remains one of the most difficult aspects of implementation to manage effectively. Sales representatives are typically results-oriented individuals who prioritize activities that directly contribute to revenue generation. Technology tools that require significant learning curves, disrupt established workflows, or fail to demonstrate clear value propositions will encounter resistance regardless of their theoretical capabilities.
The most successful implementations recognize that technology adoption is fundamentally a change management challenge rather than a technical implementation project. This requires comprehensive training programs, ongoing support structures, and incentive alignment that encourages technology utilization. Organizations that treat technology deployment as a one-time event rather than an ongoing transformation process consistently struggle to achieve full adoption and value realization.
Data quality issues further complicate the implementation challenge, as sales technology tools are only as effective as the data they process. CRM systems filled with incomplete records, outdated contact information, and inconsistent data entry practices cannot support sophisticated analytics or automation capabilities. Improving data quality requires not only technical solutions but also process standardization and cultural changes that emphasize data hygiene as a critical sales discipline.
The ROI timeline for sales technology investments varies significantly based on the complexity of the tools and the sophistication of the implementation approach. Simple automation tools may deliver measurable benefits within 3-6 months, while comprehensive revenue enablement platforms typically require 12-18 months to achieve full value realization. [3] Organizations that fail to set appropriate expectations for ROI timelines often abandon promising initiatives before they have sufficient time to mature and deliver results.
Case studies of successful implementations consistently emphasize the importance of executive sponsorship, dedicated project management, and phased rollout strategies that allow for iterative learning and adjustment. Organizations that attempt to implement comprehensive sales technology stacks simultaneously across large sales teams often encounter overwhelming complexity that leads to implementation failure and user resistance.
However, even successful implementations face ongoing challenges related to technology evolution, changing business requirements, and competitive pressures. The sales technology landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with new tools and capabilities emerging regularly. Organizations must balance the desire to leverage cutting-edge technologies with the need to maintain stable, reliable systems that support consistent sales performance.
The AI Revolution in Sales Enablement
Artificial intelligence represents the most transformative force currently reshaping the sales enablement technology landscape. The adoption of generative AI tools in sales and marketing doubled in 2024, indicating that organizations are moving beyond experimental implementations to production deployments that directly impact sales performance. [8] However, the integration of AI capabilities into sales technology stacks presents both unprecedented opportunities and significant implementation challenges that organizations must carefully navigate.
The most promising AI application in sales enablement involves automated content discovery and taxonomy management. Current revenue enablement platforms require extensive manual tagging of content assets based on buyer persona, industry, journey stage, and product offering—a process that Forrester identifies as the primary barrier to effective platform utilization. [1] Generative AI offers the potential to automate this taxonomy work by analyzing content characteristics and automatically assigning appropriate tags based on sophisticated pattern recognition and natural language processing capabilities.
Imagine directing a large language model across an entire enablement ecosystem—buyer-facing assets, seller-supporting learning and development pathways, courseware, win/loss analytics, and rep performance metrics—and instructing it to discover and tag thousands of items based on multiple variables simultaneously. [1] This capability could transform revenue enablement platforms from resource-intensive manual systems into self-optimizing intelligence engines that continuously improve their content recommendations based on usage patterns and outcome data.
However, current AI implementations in sales enablement remain limited in scope and sophistication. Forrester research indicates that no major revenue enablement platform today provides true self-discovering AI taxonomy capability, though this functionality is likely to emerge in the near future. [1] The development of such capabilities requires significant advances in AI model training, data integration, and human oversight mechanisms to ensure accuracy and relevance of automated categorization decisions.
Predictive analytics represents another area where AI is beginning to demonstrate significant value in sales enablement applications. By analyzing historical sales data, customer interaction patterns, and market trends, AI-powered tools can identify prospects most likely to convert, recommend optimal engagement strategies, and predict deal closure probabilities with increasing accuracy. These insights enable sales representatives to prioritize their efforts more effectively and customize their approaches based on data-driven recommendations rather than intuition alone.
The integration of AI capabilities also extends to real-time coaching and performance optimization. Advanced sales enablement platforms are beginning to incorporate AI-powered analysis of sales conversations, email communications, and presentation effectiveness to provide immediate feedback and improvement recommendations. This capability has the potential to accelerate sales skill development and ensure consistent application of best practices across large sales teams.
However, the implementation of AI-powered sales enablement tools requires addressing several critical challenges. Data quality remains paramount, as AI systems are only as effective as the data they process. Organizations with incomplete, inconsistent, or biased historical data will struggle to achieve reliable AI-powered insights, potentially leading to misguided recommendations that undermine rather than enhance sales performance.
Privacy and compliance considerations also complicate AI implementation in sales environments. Sales data often includes sensitive customer information, competitive intelligence, and proprietary business strategies that require careful protection. AI systems must be designed with robust security measures and compliance frameworks that meet regulatory requirements while enabling sophisticated analytical capabilities.
The human element remains crucial even as AI capabilities advance. Sales is fundamentally a relationship-driven discipline that requires emotional intelligence, creative problem-solving, and adaptive communication skills that current AI systems cannot replicate. The most effective AI implementations augment rather than replace human capabilities, providing sales representatives with enhanced intelligence and automation support while preserving the human connections that drive successful sales outcomes.
Building Your Sales Enablement Technology Strategy
Developing an effective sales enablement technology strategy requires a systematic approach that balances ambitious performance goals with realistic implementation constraints. Organizations must resist the temptation to pursue comprehensive technology transformation simultaneously, instead adopting phased implementation strategies that allow for iterative learning and continuous optimization.
The assessment phase should begin with a comprehensive audit of current technology capabilities, user adoption rates, and performance gaps. This analysis must extend beyond simple tool inventories to examine data quality, integration effectiveness, and user satisfaction levels. Organizations frequently discover that their technology challenges stem not from inadequate tools but from poor implementation, insufficient training, or misaligned processes that prevent existing tools from delivering their full potential.
Technology selection should prioritize integration capabilities and vendor stability over feature richness. The most sophisticated individual tools provide little value if they cannot effectively share data with other systems or if their vendors lack the resources to provide ongoing support and development. Organizations should evaluate potential vendors based on their integration APIs, data export capabilities, and long-term viability rather than focusing exclusively on current feature sets.
Implementation planning must account for the resource requirements associated with data migration, user training, and ongoing system maintenance. Organizations consistently underestimate these requirements, leading to rushed implementations that compromise user adoption and system effectiveness. Successful implementations typically require dedicated project management resources, comprehensive training programs, and ongoing support structures that extend well beyond the initial deployment period.
Change management represents perhaps the most critical success factor in sales technology implementations. Sales representatives must understand not only how to use new tools but also why these tools will improve their performance and career prospects. This requires clear communication of value propositions, demonstration of early wins, and alignment of incentive structures that reward technology adoption and effective utilization.
What’s Next for Sales Technology
The sales technology landscape will continue evolving rapidly through 2030, driven by advances in artificial intelligence, changing buyer behaviors, and increasing competitive pressures. Organizations that anticipate these trends and prepare their technology infrastructures accordingly will gain significant competitive advantages over those that react to changes after they occur.
AI-powered automation will expand beyond simple task automation to encompass sophisticated decision support and strategic recommendation capabilities. Revenue enablement platforms will evolve into intelligent sales assistants that provide real-time guidance based on comprehensive analysis of customer data, market conditions, and historical performance patterns. However, this evolution will require significant improvements in data quality and integration capabilities that many organizations currently lack.
Market consolidation is likely to accelerate as larger technology vendors acquire specialized point solutions to create comprehensive platform offerings. This consolidation may simplify technology selection and integration challenges but could also reduce innovation and increase vendor lock-in risks. Organizations should monitor these market dynamics carefully and maintain flexibility in their technology architectures to adapt to changing vendor landscapes.
Privacy regulations and data security requirements will continue to evolve, potentially constraining certain AI applications while creating new compliance obligations for sales technology implementations. Organizations must build privacy-by-design principles into their technology strategies to ensure long-term viability and regulatory compliance.
The most significant risk facing sales technology investments is the potential for technology sprawl to overwhelm rather than enhance sales performance. As new tools and capabilities emerge, organizations must maintain discipline in their technology selection and integration processes to avoid creating fragmented systems that increase complexity without delivering proportional value.
Key Takeaways
- Implementation Quality Trumps Technology Sophistication: 45% of B2B enablement tech deployments remain underutilized due to poor implementation rather than inadequate technology capabilities, emphasizing the critical importance of change management and user adoption strategies.
- Market Growth Demands Strategic Focus: The sales technology market’s projected growth from $47.3 billion to $229.3 billion by 2034 reflects both opportunity and risk, requiring organizations to balance innovation adoption with implementation discipline to avoid technology sprawl.
- ROI Realization Requires Patience and Resources: Organizations achieving 35% productivity improvements and 50% administrative time reductions typically invest 12-18 months in comprehensive implementation processes that include extensive training, data quality improvements, and ongoing optimization efforts.
- AI Integration Demands Data Foundation: While generative AI adoption doubled in 2024, successful AI-powered sales enablement requires high-quality, well-integrated data systems that many organizations have yet to establish, making data infrastructure a prerequisite for AI success.
References
[1] Ostrow, Peter. “The Taxonomy Automation Gap Constrains Revenue Enablement Technology Effectiveness.” Forrester Research, July 16, 2025. https://www.forrester.com/blogs/the-taxonomy-automation-gap-constrains-revenue-enablement-technology-effectiveness/
[2] “Sales Tech Market Size, Share | CAGR of 17.1%.” Market.us, 2024. https://market.us/report/sales-tech-market/
[3] “Sales Technology Stack Optimization: Maximizing Tool ROI.” Expandia, 2024. https://expandia.ch/blog/sales-technology-stack-optimization.html
[4] “2025 technology industry outlook.” Deloitte Insights, February 11, 2025. https://www.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/technology/technology-media-telecom-outlooks/technology-industry-outlook.html
[5] “20 CRM statistics for 2025.” Folk CRM, July 28, 2025. https://www.folk.app/articles/20-crm-statistics-for-2024
[6] “22 Sales Enablement Statistics You Need to Know.” Fit Small Business, July 16, 2024. https://fitsmallbusiness.com/sales-enablement-statistics/
[7] “How CRM Technology Drives Revenue: 20 Key Stats for 2025.” CRO Club, May 26, 2025. https://croclub.com/data-reporting/crm-statistics/
[8] “51 Sales Statistics and Performance Benchmarks for 2025.” Vena Solutions, April 2, 2025. https://www.venasolutions.com/blog/sales-statistics

