Executive Summary
The fractional sales management model has emerged as a transformative solution for businesses seeking high-level sales expertise without the full-time commitment and costs of traditional hiring. With 120,000 fractional leaders operating in 2024—representing a 100% increase from 60,000 in 2022—this approach is reshaping how organizations access strategic sales leadership [1].
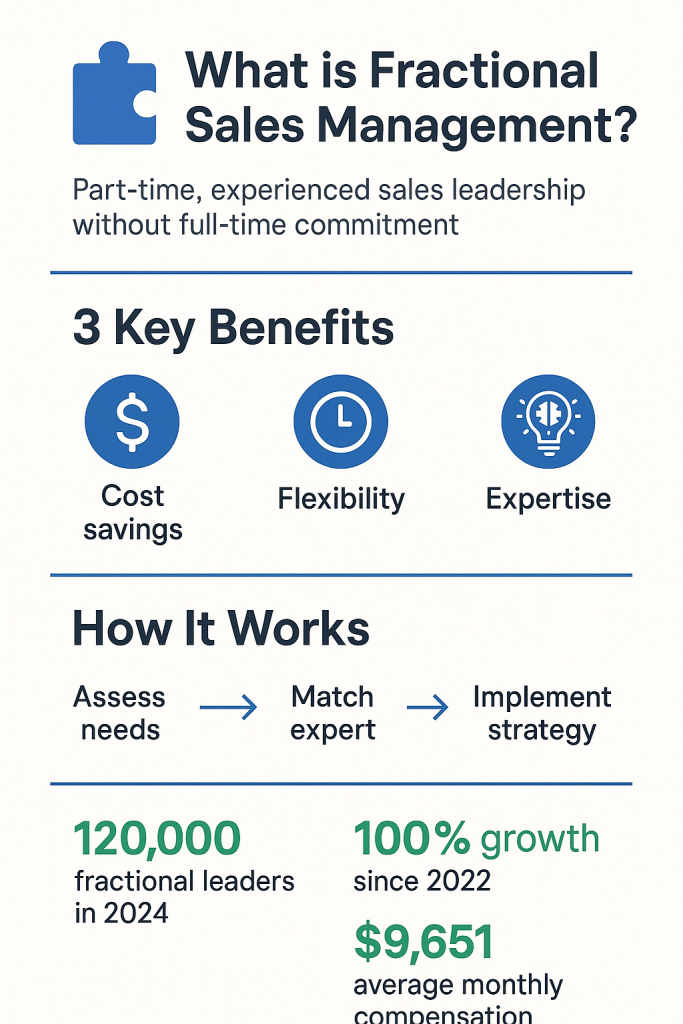
Fractional sales management involves engaging experienced sales professionals on a part-time basis, typically 5-20 hours per week, to provide strategic direction, team development, and operational oversight. The model offers compelling economics, with average monthly compensation of $9,651 compared to full-time sales management salaries ranging from $120,000-$200,000 annually plus benefits [1].
However, this model isn’t universally applicable. Research indicates optimal effectiveness for companies with revenues under $100 million and sales teams of 2-15 people, where the fractional executive can maintain sufficient authority and focus to drive meaningful impact [2]. Organizations requiring more than three days per week of executive support or those with highly complex operations may find full-time leadership more appropriate.
Market Context and Evolution
The post-pandemic business landscape has fundamentally altered how organizations approach leadership and talent acquisition. The traditional model of full-time executive hiring faces increasing challenges, including extended recruitment timelines, escalating compensation demands, and the growing preference for flexible work arrangements among senior professionals [2].
According to Forbes Finance Council analysis, the broader workforce is experiencing an unprecedented shift toward independent work, with projections indicating that the majority of the workforce will be freelance by 2027. This trend encompasses a rise of more than 19 million independent workers from 2017 to 2024, with expectations to reach 86.5 million by 2027—representing over 50% of the total workforce [2].
This transformation extends beyond individual contributors to executive-level positions. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reports a 57% increase in fractional leadership roles since 2020, reflecting both supply-side preferences for flexibility and demand-side needs for cost-effective expertise [3]. Small and medium-sized businesses, traditionally unable to afford top-tier operational expertise, now have access to sophisticated leadership support at early growth stages.
The sales function has been particularly receptive to this model due to its results-oriented nature and the critical importance of experienced leadership in driving revenue growth. Gartner peer community research indicates that 57% of business leaders believe fractional executive roles will become more common, with many expressing willingness to work under such arrangements [4].
Understanding Fractional Sales Management
Fractional sales management represents a strategic approach to sales leadership that involves engaging experienced sales professionals on a part-time, contract basis to provide high-level sales management and strategic direction. Unlike traditional consulting engagements or full-time employment, fractional sales managers integrate into the organization as embedded decision-makers with defined authority and accountability [5].
Core Characteristics
The fractional sales management model is distinguished by several key characteristics that differentiate it from other forms of sales support. These professionals typically work 5-20 hours per week depending on organizational needs and complexity, with the flexibility to scale engagement up or down based on business requirements and growth phases [5].
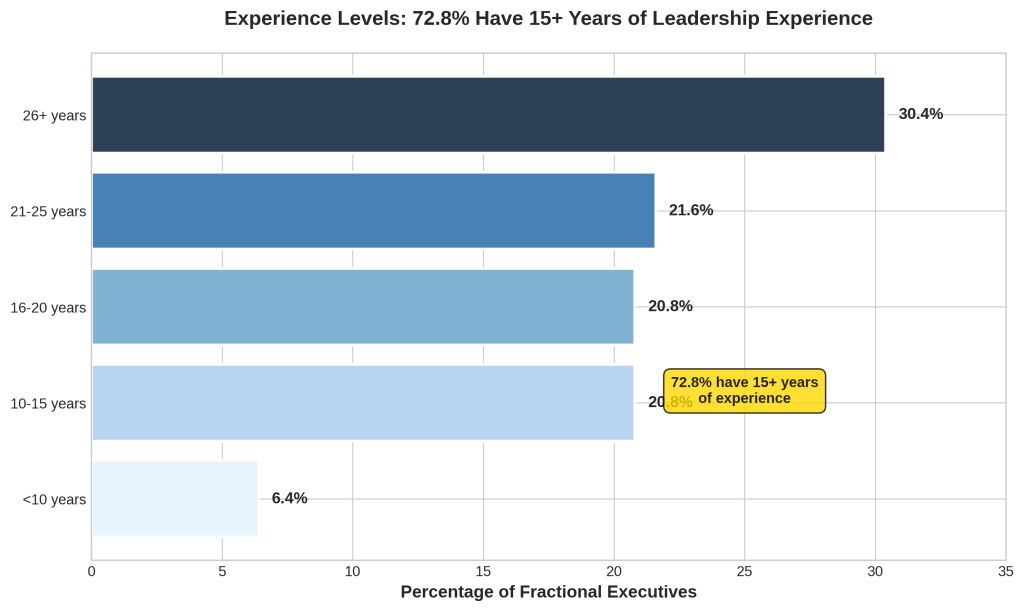
Experience levels among fractional sales executives are notably high, with research indicating that 72.8% possess more than 15 years of leadership experience. The distribution breaks down as follows: 30.4% have 26+ years of experience, 21.6% have 21-25 years, 20.8% have 16-20 years, 20.8% have 10-15 years, and only 6.4% have less than 10 years of experience [1].
Scope of Responsibilities
Fractional sales managers assume comprehensive leadership responsibilities that mirror those of full-time executives, albeit with focused time allocation. Their primary functions include developing and implementing sales strategies, establishing performance metrics and accountability systems, coaching and developing sales team members, and optimizing sales processes and technologies [5].
These professionals also handle critical hiring and onboarding functions, working to build and scale sales teams as organizations grow. They establish sales playbooks, implement customer relationship management systems, and provide analytical insights to drive continuous improvement in sales performance and efficiency.
Integration Model
Successful fractional sales management requires treating these executives as integral team members rather than external consultants. Research from Forbes Finance Council emphasizes that real-time accessibility via Slack, email, and phone is essential for fractional executives to make meaningful contributions and address urgent challenges as they arise [2].
The integration challenge is significant, as fractional executives must quickly understand organizational culture, existing processes, and team dynamics while establishing credibility and authority. This requires clear communication of roles, responsibilities, and decision-making authority from the outset of the engagement.
Market Analysis and Growth Trends
The fractional sales management market has experienced remarkable growth, driven by converging factors including talent scarcity, cost pressures, and evolving work preferences among senior professionals. Comprehensive market research reveals a sector in rapid expansion with strong fundamentals supporting continued growth.
Market Size and Growth Trajectory
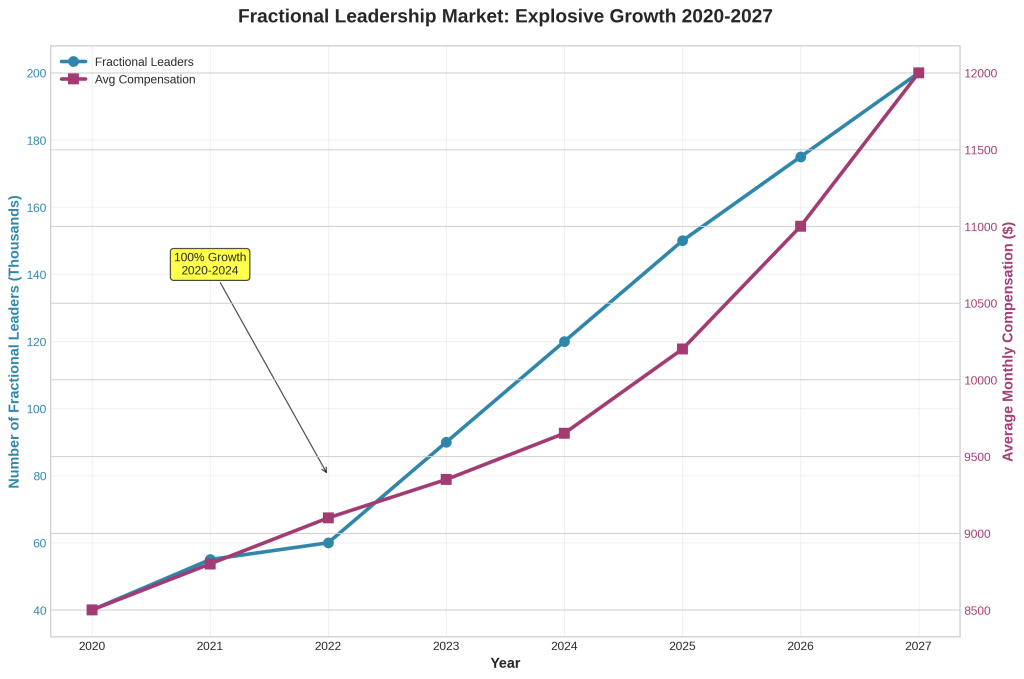
The overall fractional leadership market has demonstrated explosive growth over the past four years. According to the Frak Conference State of Fractional Industry Report 2024, which surveyed 250 fractional professionals across 29 US states, the total number of fractional leaders increased from 60,000 in 2022 to 120,000 in 2024—representing a 100% growth rate in just two years [1].
Within this broader market, fractional sales leadership has shown particularly strong expansion. Vendux data indicates that the number of fractional sales leaders in the U.S. and Canada grew from 5,000 in 2020 to 9,000 in 2024, representing an 80% increase over four years [1].
| Year | Total Fractional Leaders | Fractional Sales Leaders | Average Monthly Compensation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | ~40,000 | 5,000 | $8,500 |
| 2021 | ~55,000 | 6,200 | $8,800 |
| 2022 | 60,000 | 7,100 | $9,100 |
| 2023 | ~90,000 | 8,200 | $9,350 |
| 2024 | 120,000 | 9,000 | $9,651 |
Compensation Trends and Economics
The economic attractiveness of fractional sales management has improved significantly for both practitioners and organizations. Vendux data shows that average monthly compensation for fractional sales leaders reached $9,651 in 2024, up from $9,350 in 2023—representing a 3.2% year-over-year increase. More significantly, average hourly rates rose to $213 in 2024, compared to $176 in 2023, marking a 21% increase in hourly compensation [1].
This compensation growth reflects increasing demand for experienced sales leadership and the premium organizations are willing to pay for flexible, high-quality expertise. The hourly rate increase substantially outpaces general wage inflation, indicating strong market dynamics favoring fractional professionals.
Industry Distribution and Adoption Patterns
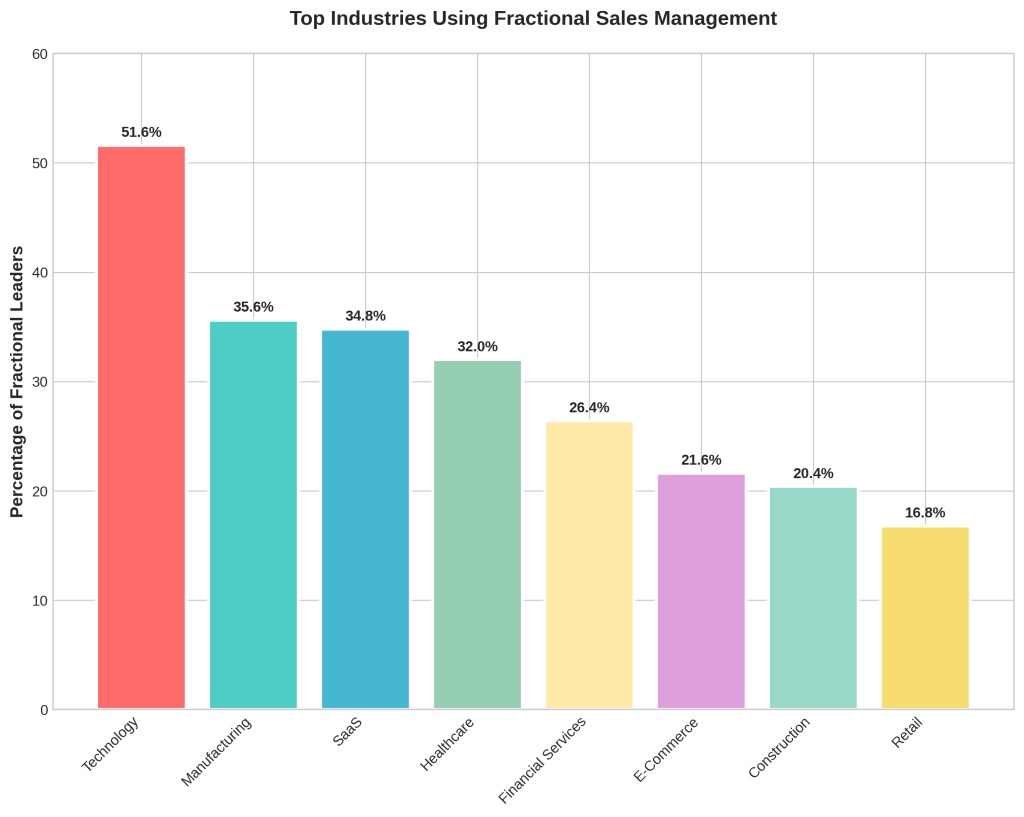
Fractional sales management adoption varies significantly across industries, with technology-focused sectors leading adoption rates. Research indicates that 51.6% of fractional leaders serve technology companies, followed by 35.6% in manufacturing and 34.8% in Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) organizations [1].
| Industry | Adoption Rate | Primary Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | 51.6% | Rapid scaling needs, specialized expertise |
| Manufacturing | 35.6% | Complex sales cycles, industry knowledge |
| SaaS | 34.8% | Growth-stage companies, subscription models |
| Healthcare | 32.0% | Regulatory compliance, relationship building |
| Financial Services | 26.4% | Trust-based selling, compliance requirements |
| E-Commerce | 21.6% | Digital transformation, omnichannel strategies |
The concentration in technology, SaaS, and healthcare sectors reflects industries experiencing rapid growth, complex sales processes, and significant regulatory or technical requirements that benefit from experienced leadership. These sectors also tend to have higher tolerance for flexible work arrangements and innovative organizational structures.
Revenue Diversification Among Practitioners
A notable characteristic of the fractional sales management market is the diversified revenue approach adopted by practitioners. Research indicates that only 2% of fractional professionals focus solely on fractional work, with the vast majority maintaining multiple income streams [1].
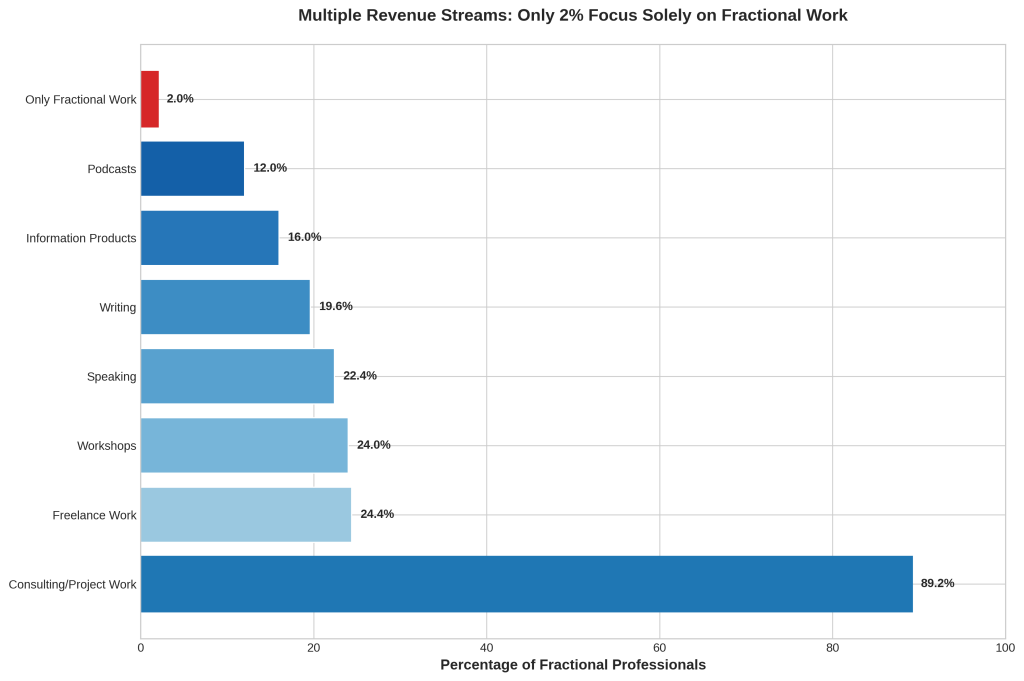
The most common additional activities include consulting and project work (89.2%), freelance work (24.4%), conducting workshops (24%), and speaking engagements (22.4%). This diversification strategy provides income stability while allowing practitioners to leverage their expertise across multiple channels and build personal brands that support their fractional work [1].
Benefits and Limitations Analysis
The fractional sales management model offers compelling advantages while presenting distinct challenges that organizations must carefully evaluate. A balanced assessment reveals both the transformative potential and inherent limitations of this approach to sales leadership.
Economic and Strategic Benefits
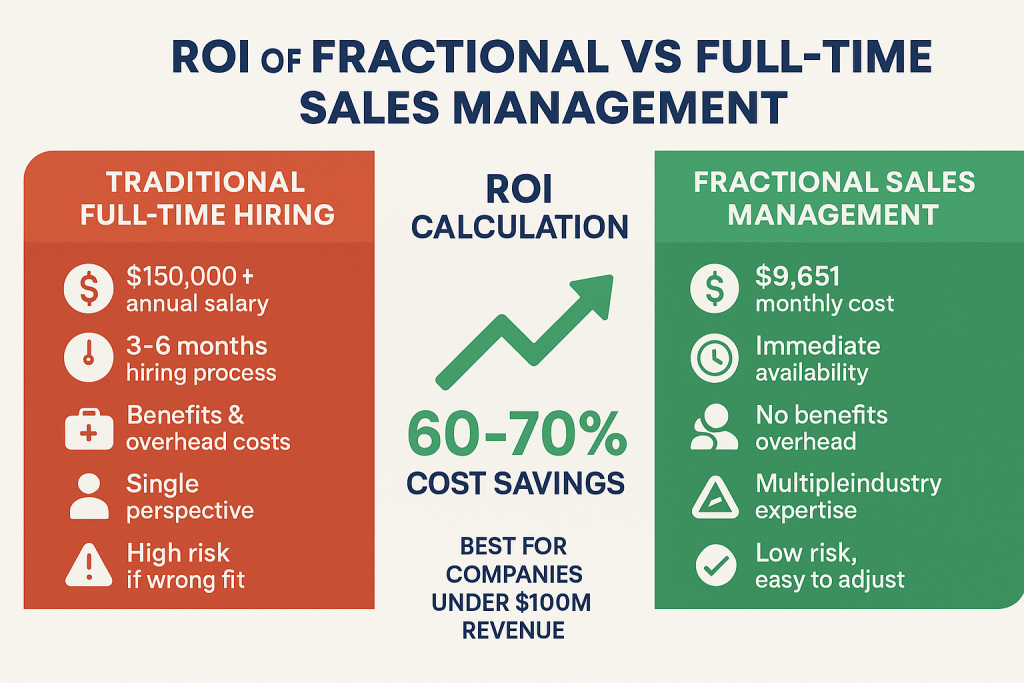
The most immediate advantage of fractional sales management lies in its economic efficiency. Organizations can access senior-level sales expertise at a fraction of the cost of full-time hiring. With average monthly compensation of $9,651 for fractional sales leaders compared to full-time sales management salaries ranging from $120,000-$200,000 annually plus benefits, companies can achieve 60-70% cost savings while maintaining access to high-quality leadership [1].
Beyond direct cost savings, the fractional model eliminates the extended recruitment timelines typical of executive hiring. Traditional sales management recruitment often requires 3-6 months from initiation to onboarding, during which sales performance may suffer from lack of leadership. Fractional sales managers can typically begin engagement within days or weeks, providing immediate strategic direction and operational oversight [2].
| Aspect | Fractional Sales Management | Full-Time Sales Management |
|---|---|---|
| Annual Cost | $115,812 (avg monthly) | $150,000-$250,000 + benefits |
| Time Commitment | 5-20 hours/week | 40+ hours/week |
| Implementation Speed | Immediate availability | 3-6 months hiring process |
| Flexibility | High – adjust as needed | Low – fixed commitment |
| Experience Level | 72.8% have 15+ years | Varies widely |
| Risk Level | Low – easy to change | High – difficult to replace |
Expertise and Perspective Advantages
Fractional sales managers bring unique value through their exposure to multiple organizations and industries. Unlike full-time executives who develop deep but narrow expertise within single companies, fractional professionals accumulate diverse experiences across various business models, market conditions, and organizational challenges [5].
This breadth of experience enables fractional sales managers to identify and implement best practices more rapidly than executives learning through trial and error within single organizations. They can recognize patterns, anticipate challenges, and recommend solutions based on proven approaches from similar situations in other companies.
The collective expertise model also provides continuity advantages. When working with fractional service firms, organizations benefit from team-based support that reduces single-point-of-failure risks associated with individual executives. If a fractional sales manager becomes unavailable, the supporting organization can provide continuity through other team members familiar with the client’s situation [2].
Scalability and Flexibility Benefits
The fractional model offers unparalleled scalability for growing organizations. Companies can adjust the level of sales management support based on current needs, business cycles, and growth phases without the complications of hiring or terminating full-time employees. This flexibility proves particularly valuable for seasonal businesses, project-based organizations, or companies experiencing rapid growth or contraction [5].
During expansion phases, organizations can increase fractional executive engagement hours or add specialized expertise in specific areas such as channel development, key account management, or sales operations. Conversely, during slower periods, they can reduce engagement levels while maintaining access to strategic guidance and oversight.
Critical Limitations and Challenges
Despite compelling benefits, fractional sales management faces significant limitations that organizations must carefully consider. The most fundamental constraint involves time availability and depth of engagement. Forbes Finance Council research indicates that fractional leadership works best for companies requiring less than three days per week of executive support and those with revenues under $100 million [2].
Organizations with complex operations, multiple product lines, or extensive sales teams may find fractional executives unable to provide sufficient depth of engagement to drive meaningful results. The part-time nature of the relationship can limit the executive’s ability to build deep relationships with team members, understand nuanced organizational dynamics, or provide the continuous presence that some situations require.
Authority and Integration Challenges
A critical success factor for fractional sales management involves granting appropriate authority and decision-making power to the fractional executive. Gartner peer community research emphasizes that “unless that fractional executive has all of the authority of a hired employee, it can be a waste of time and money” [4].
Organizations that treat fractional executives as external consultants rather than embedded decision-makers significantly limit their effectiveness. The fractional executive must have authority to make personnel decisions, implement process changes, and allocate resources within defined parameters. Without this authority, they cannot drive the organizational changes necessary for improved sales performance.
Integration challenges extend beyond formal authority to include cultural acceptance and team dynamics. Sales teams may initially resist direction from part-time leadership, particularly if they perceive the fractional executive as temporary or lacking commitment to the organization’s long-term success.
Performance Measurement and Accountability
The part-time nature of fractional sales management can complicate performance measurement and accountability structures. Traditional sales management metrics assume full-time engagement and continuous oversight, which may not align with fractional arrangements. Organizations must develop modified performance frameworks that account for limited time availability while maintaining appropriate accountability standards.
Additionally, the success of fractional sales management depends heavily on clear goal setting and priority alignment. Forbes Finance Council research notes that fractional executives “may struggle in environments with unclear goals and shifting priorities” due to their limited time requiring laser focus on highest-impact initiatives [2].
Industry and Situational Constraints
Certain industries and business situations may be poorly suited for fractional sales management. Companies where sales leadership represents a core competency—such as marketing agencies relying on chief marketing officers—may require full-time executive presence to maintain competitive advantage [2].
Similarly, organizations in highly regulated industries with complex compliance requirements may need continuous executive oversight that exceeds the capacity of part-time arrangements. The relationship-intensive nature of some sales environments may also require full-time presence to build and maintain critical customer relationships.
Implementation Framework
Successful implementation of fractional sales management requires systematic planning, clear expectations, and structured integration processes. Organizations must carefully assess their readiness, define success criteria, and establish governance frameworks that maximize the value of fractional executive engagement.
Readiness Assessment and Prerequisites
Before engaging fractional sales management, organizations should conduct comprehensive readiness assessments to determine model suitability. The assessment should evaluate current sales team size and complexity, with optimal candidates typically having 2-15 salespeople and relatively straightforward sales processes [5].
Revenue considerations are equally important, with research indicating optimal effectiveness for companies with annual revenues under $100 million. Organizations exceeding this threshold often require more intensive executive support than fractional arrangements can provide [2].
Cultural readiness represents another critical factor. Organizations must demonstrate willingness to grant fractional executives appropriate authority and integrate them as embedded decision-makers rather than external consultants. This requires leadership commitment to supporting the fractional executive’s initiatives and ensuring team acceptance of part-time leadership.
Selection and Matching Process
The selection process for fractional sales managers should emphasize industry experience, cultural fit, and demonstrated results in similar organizational contexts. Given that 72.8% of fractional executives possess more than 15 years of experience, organizations should prioritize candidates with relevant industry knowledge and proven track records in comparable situations [1].
Reference checking becomes particularly important in fractional arrangements, as organizations have limited time to assess executive effectiveness before making longer-term commitments. Candidates should provide detailed case studies and measurable results from previous fractional engagements, including specific metrics improvements and organizational outcomes.
The matching process should also consider communication styles, availability patterns, and technology preferences to ensure seamless integration with existing teams and processes. Fractional executives must be comfortable with remote collaboration tools and capable of maintaining effective communication despite limited physical presence.
Engagement Structure and Governance
Successful fractional sales management requires clearly defined engagement structures that specify time commitments, communication protocols, and decision-making authority. Most effective arrangements involve 5-20 hours per week depending on organizational complexity and current challenges [5].
Governance frameworks should establish regular check-in schedules, performance review processes, and escalation procedures for critical decisions. Forbes Finance Council research emphasizes the importance of real-time accessibility via Slack, email, and phone to enable fractional executives to address urgent challenges and maintain team connectivity [2].
Organizations should also define clear success metrics and review periods, typically quarterly, to assess progress and adjust priorities as needed. The limited time availability of fractional executives requires laser focus on initiatives that drive maximum impact, necessitating regular priority reassessment and alignment [2].
Integration and Onboarding Best Practices
Effective onboarding processes for fractional sales managers should compress traditional executive integration timelines while ensuring comprehensive understanding of organizational context. This includes detailed briefings on company history, competitive positioning, sales processes, team dynamics, and current challenges.
Technology integration represents a critical component, with fractional executives requiring immediate access to customer relationship management systems, sales analytics platforms, and communication tools. Organizations should prepare comprehensive system access and training materials to minimize onboarding time and maximize early productivity.
Team introduction processes should emphasize the fractional executive’s authority and decision-making role while addressing potential concerns about part-time leadership. Clear communication about the fractional executive’s background, expertise, and expected contributions helps establish credibility and acceptance among team members.
Future Outlook and Trends
The fractional sales management market is positioned for continued expansion, driven by fundamental shifts in work preferences, organizational structures, and economic pressures. Multiple converging trends suggest this model will become increasingly mainstream across various industries and company sizes.
Workforce Evolution and Demographic Shifts
The broader transformation toward independent work arrangements provides a strong foundation for fractional executive growth. Forbes Finance Council projections indicate that independent workers will comprise more than 50% of the workforce by 2027, representing a fundamental shift in employment relationships [2].
This trend extends beyond individual contributors to senior executives seeking greater autonomy and work-life integration. The post-pandemic emphasis on flexibility has permanently altered executive expectations, with many experienced professionals preferring fractional arrangements that provide variety, reduced stress, and better work-life balance.
Demographic factors also support continued growth, as experienced executives approach traditional retirement ages but remain interested in meaningful work engagement. The fractional model provides an attractive transition option that leverages accumulated expertise while offering reduced time commitments and increased flexibility.
Technology Enablement and Remote Work Normalization
Advances in collaboration technology and the normalization of remote work have eliminated many traditional barriers to fractional executive effectiveness. Cloud-based customer relationship management systems, video conferencing platforms, and project management tools enable fractional sales managers to maintain effective oversight and team connectivity despite limited physical presence.
Artificial intelligence and sales automation technologies are also reducing the administrative burden on sales managers, allowing fractional executives to focus on higher-value strategic activities that better justify their engagement. These technological improvements increase the feasibility and effectiveness of part-time sales leadership arrangements.
Economic Pressures and Cost Optimization
Ongoing economic uncertainties and cost pressures continue to drive organizational interest in flexible, cost-effective leadership solutions. The 60-70% cost savings achievable through fractional sales management provide compelling value propositions for organizations seeking to optimize expenses while maintaining access to senior expertise [1].
Small and medium-sized businesses, in particular, face increasing competitive pressures that require sophisticated sales strategies previously available only to larger organizations. Fractional sales management democratizes access to senior-level expertise, enabling smaller companies to compete more effectively against larger competitors.
Market Maturation and Professionalization
The fractional executive market is experiencing increasing professionalization, with specialized firms, standardized processes, and industry best practices emerging. This maturation reduces implementation risks and increases organizational confidence in fractional arrangements.
Professional associations, certification programs, and industry standards are developing to support fractional executive quality and effectiveness. These developments will likely accelerate adoption by providing organizations with better frameworks for evaluating and managing fractional relationships.
Potential Challenges and Limitations
Despite positive growth trends, several factors could limit fractional sales management expansion. Economic recovery and improved labor market conditions might reduce cost pressures that currently drive fractional adoption. Additionally, as the market matures, compensation levels may increase to the point where cost advantages diminish.
Regulatory changes affecting independent contractor classifications could also impact the fractional market structure. Organizations may face increased compliance requirements or reclassification risks that complicate fractional arrangements.
The success of fractional sales management ultimately depends on continued demonstration of measurable results and organizational satisfaction. Any systematic performance issues or negative outcomes could slow adoption rates and limit market growth.
Industry-Specific Evolution
Different industries will likely experience varying rates of fractional sales management adoption based on their specific characteristics and requirements. Technology and SaaS companies, which currently represent 51.6% and 34.8% of fractional leadership engagements respectively, will likely continue leading adoption due to their comfort with flexible work arrangements and results-oriented cultures [1].
Traditional industries such as manufacturing and financial services may experience slower but steady adoption as they recognize the value of flexible expertise and cost optimization. Healthcare organizations may increase fractional adoption as regulatory complexity and relationship requirements become better understood and addressed through specialized fractional providers.
Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The fractional sales management market has experienced explosive growth, with 120,000 fractional leaders operating in 2024—a 100% increase from 60,000 in 2022. Fractional sales leaders specifically grew from 5,000 in 2020 to 9,000 in 2024, representing 80% growth over four years.
- Economic Value: Organizations can achieve 60-70% cost savings through fractional sales management, with average monthly compensation of $9,651 compared to full-time sales management salaries of $120,000-$200,000 annually plus benefits. Hourly rates have increased 21% year-over-year to $213 in 2024.
- Experience Premium: Fractional sales executives bring exceptional experience levels, with 72.8% possessing more than 15 years of leadership experience and 30.4% having 26+ years of experience. This experience premium provides organizations with senior-level expertise typically unavailable at comparable cost levels.
- Optimal Application: Fractional sales management works best for companies with revenues under $100 million, sales teams of 2-15 people, and requirements for less than three days per week of executive support. Success requires granting appropriate authority and treating fractional executives as embedded decision-makers rather than external consultants.
References
[1] Column Content. (2025, March 21). Fractional Work Statistics: 100+ Trends You Need to Know (2025). Based on Frak Conference State of Fractional Industry Report 2024 and Vendux data. https://columncontent.com/fractional-work-statistics/
[2] Kunkel, R. (2025, February 20). The Rise of Fractional Leadership: A Lasting Business Shift. Forbes Finance Council. https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbesfinancecouncil/2025/02/20/the-rise-of-fractional-leadership-a-lasting-shift-in-the-business-landscape/
[3] Horne. (2025). What is a Fractional Executive? | Expertise On Demand. U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics data cited. https://horne.com/fractional-executives/
[4] Gartner Peer Community. (2024, April 23). Fractional CFOs (part time/contract, usually work for multiple orgs) are growing in popularity. Do you think fractional CSOs are on the horizon? Poll results and community discussion. https://www.gartner.com/peer-community/poll/fractional-cfos-part-time-contract-usually-work-multiple-orgs-growing-popularity-think-fractional-csos-horizon-want-to-work
[5] Mindracer Consulting. (2023, August 3). The Ultimate Guide to Fractional Sales Management. https://www.mindracerconsulting.com/blog/fractional-sales-management

